-
实现继承的方式:
function Person(){}
function Student(){}
1.Student.prototype=Person.prototype;//别用
2.Student.prototype=new Person();//在有参数时不是很好用
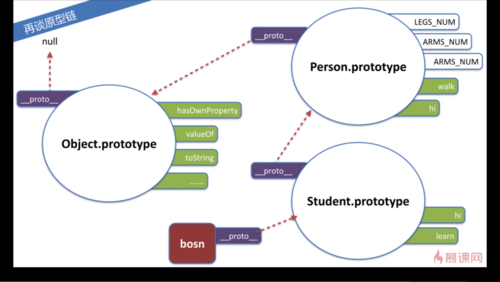
3.Student.prototype=Object.create(Person.prototype);//较为理想,ES5之后才能用,为了兼容,可以用下图方法:

Student.prototype.constructor=Person;
 查看全部
查看全部 -
instanceof:左对象右函数构造器(又必须为函数不然报错),判断左边的对象的原型链上有没有右边的构造器的prototype。
不同而window或iframe间的对象类型检测不能使用instanceof!
查看全部 -
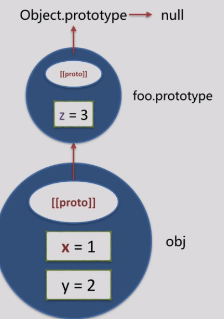
var obj = {x:1};
obj.__proto__;//Object{}
Object.getPrototypeOf(obj);//获取obj的原型,Object{}
Object.getPrototypeOf(obj)===Object.prototype;//true
function foo(){}
foo.prototype.__proto__;//Object{}
foo.prototype.__proto__===Object.prototype;//true
obj.toString();//"[object Object]"
object.valueOf();//Object{x:1}
不是所有的对象的原型链上独有Object.prototype
var obj2 = Object.create(null);//这个就没有,这是创建了一个空对象,并且这个对象的原型指向null
也并不是所有的函数对象都会有prototype这个属性
function abc(){};
var binded = abc.bind(null);
typeof binded;//"function"
binded.prototype;//undefined,binded就没有prototype属性。
查看全部 -
改变prototype:如果是针对某个对象的修改,会改变已经实例化的对象的属性,但是如果是字面量赋值给prototype,却不会印象已经实例化的对象,但会印象后续实例化的对象。如下图:


 查看全部
查看全部 -
构造函数有个内置属性name,是不可改写的.实例化的对象没有内置属性name
对象的prototype属性的constructor属性可判断对象的原型是谁,还可以用实例化的obj的constructor属性来实例化新的对象。
查看全部 -
Object.create = function (o) { var F = function () {}; F.prototype = o; return new F(); };
new 法实际执行的代码:
var o1 = new Object(); o1.[[Prototype]] = Base.prototype; Base.call(o1);
查看全部 -
function Person(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;//不在Person的prototype对象属性上!!!
}
//当var newPerson=new Person();时,this指向newPerson。同时newPerson可以直接访问Person上的属性和方法,但Person得Peson.prototype.method()访问!!
Person.prototype.hi = function(){
document.write("Hi,my name is "+this.name+".I'm "+this.age+"years old now.");
};
Person.prototype.LEGS_NUM = 2;
Person.prototype.ARMS_NUM = 2;
Person.prototype.walk = function(){
document.write(this.name+"is working.");
};
//以上两个方法和两个属性都是加在Person的prototype上的,为了继承!!!
function Student(name,age,className){
Person.call(this,name,age);//this为Student
this.className = className;
}
Student.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);//Object.create创建一个空对象,并且这个对象的原型指向Object.create的参数。
//上面一句不能Student.prototype = Person.prototype;
//不然会导致修改Student.prototype修改时,Person.prototype也改了
//也不能new Person给Student,因为new出来的都是对像,而Student是函数,有自己的参数,可以把Person看为父对象函数,Student为子对象函数
Student.prototype.constructor = Student;//不设置时,consrtuctor会指向Person
Student.prototype.hi = function(){
document.write("Hi,my name is "+this.name+".I'm "+this.age+"years old now,and from "+this.className+".");
};//会覆盖Person.prototype的hi方法(因为之下而上的访问顺序)
Student.prototype.learn = function(subject){
document.write(this.name + " is learning " + subject + " at " +this.className + ".");
};
//test
var bosn =new Student("Bosn",27,"Class 3,Grade 2");
bosn.hi();
bosn.LEGS_NUM;
bosn.walk();
bosn.learn('math');
function Person(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;//不在Person的prototype对象属性上!!!
}
//当var newPerson=new Person();时,this指向newPerson。同时newPerson可以直接访问Person上的属性和方法,但Person得Peson.prototype.method()访问!!
Person.prototype.hi = function(){
document.write("Hi,my name is "+this.name+".I'm "+this.age+"years old now.");
};
Person.prototype.LEGS_NUM = 2;
Person.prototype.ARMS_NUM = 2;
Person.prototype.walk = function(){
document.write(this.name+"is working.");
};
//以上两个方法和两个属性都是加在Person的prototype上的,为了继承!!!
function Student(name,age,className){
Person.call(this,name,age);//this为Student
this.className = className;
}
Student.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);//Object.create创建一个空对象,并且这个对象的原型指向Object.create的参数。
//上面一句不能Student.prototype = Person.prototype;
//不然会导致修改Student.prototype修改时,Person.prototype也改了
Student.prototype.constructor = Student;//不设置时,consrtuctor会指向Person
Student.prototype.hi = function(){
document.write("Hi,my name is "+this.name+".I'm "+this.age+"years old now,and from "+this.className+".");
};//会覆盖Person.prototype的hi方法(因为之下而上的访问顺序)
Student.prototype.learn = function(subject){
document.write(this.name + " is learning " + subject + " at " +this.className + ".");
};
//test
var bosn =new Student("Bosn",27,"Class 3,Grade 2");
bosn.hi();
bosn.LEGS_NUM;
bosn.walk();
bosn.learn('math');
function Person(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;//不在Person的prototype对象属性上!!!
}
//当var newPerson=new Person();时,this指向newPerson。同时newPerson可以直接访问Person上的属性和方法,但Person得Peson.prototype.method()访问!!
Person.prototype.hi = function(){
document.write("Hi,my name is "+this.name+".I'm "+this.age+"years old now.");
};
Person.prototype.LEGS_NUM = 2;
Person.prototype.ARMS_NUM = 2;
Person.prototype.walk = function(){
document.write(this.name+"is working.");
};
//以上两个方法和两个属性都是加在Person的prototype上的,为了继承!!!
function Student(name,age,className){
Person.call(this,name,age);//this为Student
this.className = className;
}
Student.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);//Object.create创建一个空对象,并且这个对象的原型指向Object.create的参数。
//上面一句不能Student.prototype = Person.prototype;
//不然会导致修改Student.prototype修改时,Person.prototype也改了
Student.prototype.constructor = Student;//不设置时,consrtuctor会指向Person
Student.prototype.hi = function(){
document.write("Hi,my name is "+this.name+".I'm "+this.age+"years old now,and from "+this.className+".");
};//会覆盖Person.prototype的hi方法(因为之下而上的访问顺序)
Student.prototype.learn = function(subject){
document.write(this.name + " is learning " + subject + " at " +this.className + ".");
};
//test
var bosn =new Student("Bosn",27,"Class 3,Grade 2");
bosn.hi();
bosn.LEGS_NUM;
bosn.walk();
bosn.learn('math');
查看全部 -
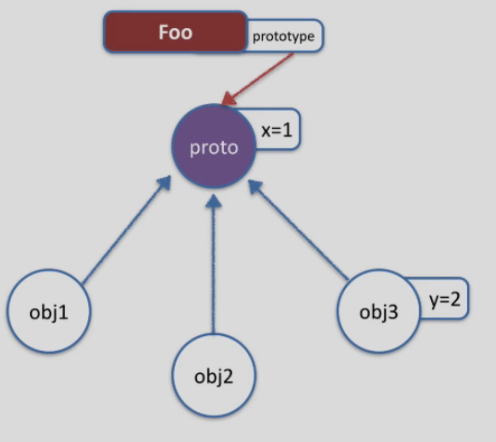
使用对象字面量创建原型方法,会重写原型链,要小心!
基于原型的继承

 查看全部
查看全部 -
面向对象程序设计(Object-oriented programming,OOP)是一种程序设计范型,同时也是一种程序开发的方法。对象指的是类的实例。它将对象作为程序的基本单元,将程序和数据封装其中,以提高软件的重用性、灵活性和扩展性
(继承 封装 多态 抽象)
查看全部 -
Function是特殊的对象,五种原始类型一种对象
查看全部 -
函数数组日期都是对象类型的
查看全部 -
原始类型外是对象类型
查看全部 -
数据常见类型
查看全部 -
常用数据类型
查看全部 -
数字运算 字符串拼接 字符串隐式转化数字
查看全部
举报



