访问控制表达式
1. 前言
在实际的开发过程中,权限的分配规则往往非常复杂,如果才能实现快速实现细粒度的权限策略呢?Spring Security 已为我们找到了解决办法。
自从 Spring Security 3.0 支持了使用 Spring 语法表达式来配置安全规则,便大大降低了安全规则实现的复杂度。
本节,我们主要讨论如何通过 Spring Security 访问控制表达式实现安全规则的配置。
2.Spring 内置表达式
Spring Security 使用 Spring EL (Spring 表达式语法)用来支持表达式配置。表达式是作为运算上下文中的根级对象被执行的。
SecurityExpressionRoot 是支持表达式的基础实现类,它提供了一些支持 Web 或者方法层面的安全表达式。
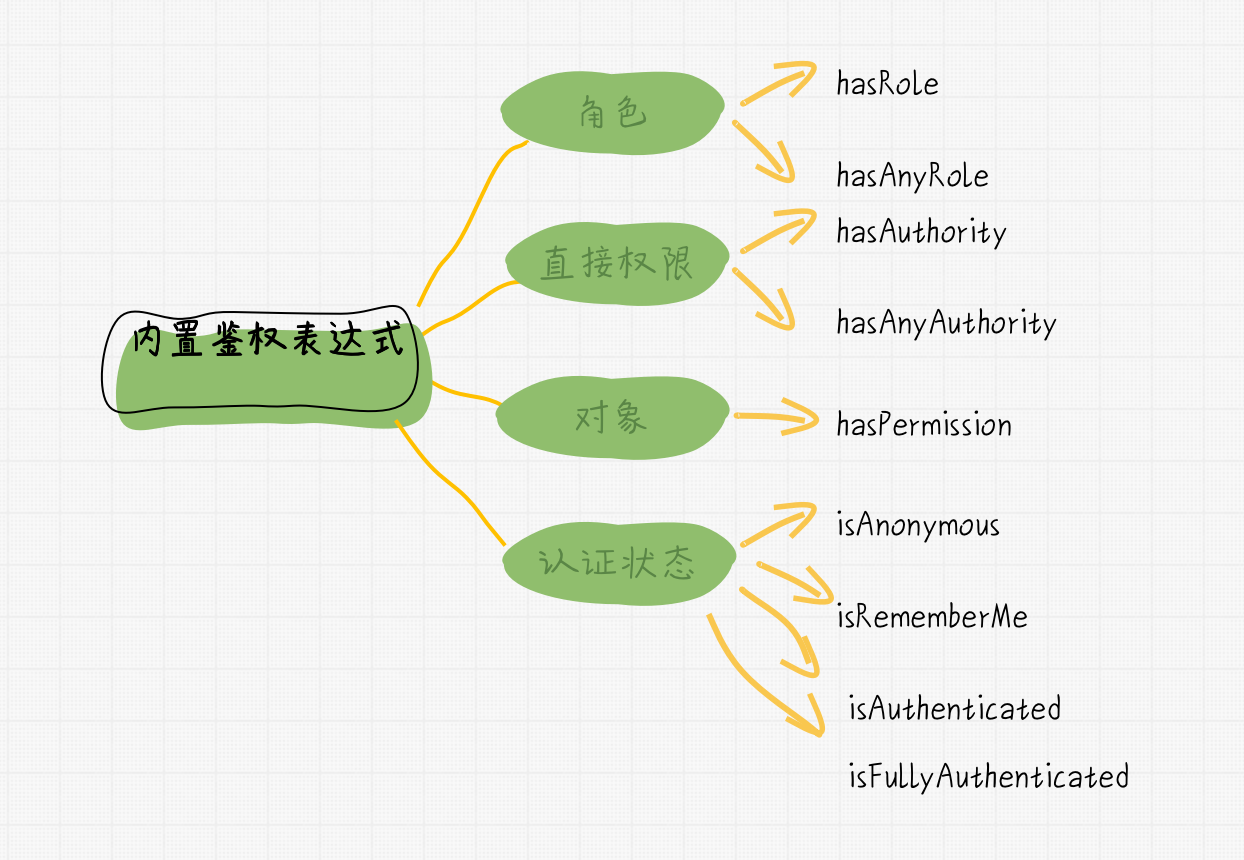
以下为其支持的表达式:
hasRole(String role)
如果当前的用户身份信息中,包含 role 值的角色时,该表达式返回 true。
例如判断是否具有 admin 角色:hasRole('admin')。
需要注意的是,角色名称在 Spring Security 内会自动增加 ROLE_ 前缀,如果需要修改该前缀,可通过 DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler 对象中的 defaultRolePrefix 属性实现。
hasAnyRole(String… roles)
和 hasRole 类似,可以同时判断多个角色,只要包含其中一种即可,多个角色用逗号隔开。
hasAuthority(String authority)
如果当前的身份信息中包含参数中指定权限,则返回 true。
例如:hasAuthority('read')
hasAnyAuthority(String… authorities)
如果当前的身份信息中包含参数中指定权限之一,则返回 true。多个权限之间用逗号 , 分隔。
例如:hasAnyAuthority('read', 'write')
principal
允许当前登录用户直接访问其身份信息 principal 对象。
authentication
允许直接访问当前安全上下文中的认证信息 Authentication 对象。
permitAll
永远返回 true。
denyAll
永远返回 false。
isAnonymous()
如果当前用户的身份信息为匿名用户,则返回 true。
isRememberMe()
如果当前用户的身份信息是来自于「记住我」认证用户,则返回 true。
isAuthenticated()
如果当前用户的身份信息不是匿名用户,则返回 true。
isFullyAuthenticated()
如果当前用户的身份信息既不是匿名用户又不是记住我自动登录用户,则返回 true。
hasPermission(Object target, Object permission)
如果当前用户包含对指定对象的访问权限,则返回 true。
例如:hasPermission(domainObject, 'read')。
hasPermission(Object targetId, String targetType, Object permission)
如果当前用户包含对指定对象的访问权限,则返回 true。
例如:hasPermission(1, 'com.example.domain.Message', 'read')。
3. 内置表达式在 Web 系统中的使用
3.1 表达式的应用配置
要针对 URL 应用表达式规则,我们需要在 <http> 对象上将 use-expressions 属性值置为 true。Spring Security 则会将 <intercept-url> 元素中 access 属性值解释为表达式,并根据表达式规则返回 true 或者 false 的判定结果。
例如:
<http>
<intercept-url pattern="/admin*"
access="hasRole('admin') and hasIpAddress('192.168.1.0/24')"/>
...
</http>
本例中,我们将 /admin 开头的资源定义为只有包含 admin 角色,并且来源 IP 为 192.168.1.x 网段的用户才可以访问。这里出现的 hasIpAddress 方法在前面内容中没有提到,因为它是只有 Web 系统才包含的,被定义在 WebSecurityExpressionRoot 类中。
3.2 使用自定义方法作为表达式
如果我们需要扩展现有的表达式,我们可以使用 Spring Bean 里的方法。
例如,使用自定义 Bean WebSecurity 中的 check 方法:
public class WebSecurity {
public boolean check(Authentication authentication, HttpServletRequest request) {
...
}
}
我们可以在配置文件中这样写:
<http>
<intercept-url pattern="/user/**"
access="@webSecurity.check(authentication,request)"/>
...
</http>
或者在 Java 中直接加入配置:
http
.authorizeRequests(authorize -> authorize
.antMatchers("/user/**").access("@webSecurity.check(authentication,request)")
...
)
3.3 路径参数的使用
很多时候我们的路径是包含参数信息的,而规则的应用往往也和参数信息想匹配。例如针对用户信息的 RESTful 资源地址 /user/{userId}。我们可以在表达式中使用这些参数。
例如,假设我们的扩展表达式方法如下:
public class WebSecurity {
public boolean checkUserId(Authentication authentication, int id) {
...
}
}
此方法的 id 参数需要传入路径中的 userId 的值,那我们在配置表达式时可用如下方式:
<http>
<intercept-url pattern="/user/{userId}/**"
access="@webSecurity.checkUserId(authentication,#userId)"/>
...
</http>
或者用 Java 的方式配置
http
.authorizeRequests(authorize -> authorize
.antMatchers("/user/{userId}/**").access("@webSecurity.checkUserId(authentication,#userId)")
...
);
上述写法的结果都是将 userId 作为参数传入了方法之中,加入用户访问的 URL 地址为 /user/123/resource,则传入的 id 参数为 123。
4. 方法安全表达式
方法安全表达式通常通过注解方式控制方法的访问。这里主要使用了 @Pre 和 @Post 注解。
@Pre 代表执行前,@Post 代表执行后。在方法的安全表达式中,有四个相关的表达式注解,分别是:@PreAuthorize,@PreFilter,@PostAuthorize 和 @PostFilter。要启用这四个标签要,首先要增加全局配置:
<global-method-security pre-post-annotations="enabled"/>
4.1 使用 @PreAuthorize 和 @PostAuthorize 进行访问控制
@PreAuthorize 最主要的作用是决定一个方法能否被执行。例如:
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('USER')")
public void create(Contact contact);
这段代码的含义是,只有包含了 USER 角色的用户,才被允许调用 create 方法。
对于权限,还有另一种更为具体的写法:
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#contact, 'admin')")
public void deletePermission(Contact contact, Sid recipient, Permission permission);
这里我们指定了调用方法中的参数,用来判断当前用户是否对将被删除的 Contact 对象具有 admin 角色。通过这种写法,我们可以将目标对象中的任意方法作为表达式的变量参数。
Spring Security 要在表达式中访问方法参数有几种方式:
- Spring Security 可以使用
@P注解,为变量设置别名。例如:
import org.springframework.security.access.method.P;
...
@PreAuthorize("#c.name == authentication.name")
public void doSomething(@P("c") Contact contact);
- 使用 Spring 的
@Param注解,为变量设置别名。例如:
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param;
...
@PreAuthorize("#n == authentication.name")
Contact findContactByName(@Param("n") String name);
- 如果使用的是 JDK 8 + Spring 4+ ,不需要额外的注解,程序会自动发现参数名称。
Spring Security 的表达式注解支持对象的属性。例如,当我们指定方法入参中的属性名称和我们身份信息中的名称一致时允许访问:
@PreAuthorize("#contact.name == authentication.name")
public void doSomething(Contact contact);
这里我们用到了内置参数 authentication ,该对象保存在 Spring Security 的安全上下文中。我们也可以直接访问到该对象的身份信息属性。
@PostAuthorize 使用场景相对较少,它针对方法的返回进行权限过滤。
4.2 使用 @PreFilter 和 @PostFilter
@PreFilter 过滤器用于处理参数中的集合或者数组对象;@PostFilter 用于过滤返回值中集合或者数组对象。
例如:
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('USER')")
@PostFilter("hasPermission(filterObject, 'read') or hasPermission(filterObject, 'admin')")
public List<Contact> getAll();
5. 小结
本节讨论了 Spring Security 中如何通过表达式的方式简化权限规则配置,主要内容有:
- 表达式方式简化了鉴权配置难度,增强鉴权规则的可读性;
- Spring 内置了非常多的表达式,可以满足大多数场景;
- 表达式是对实例方法的引用,我们可以扩展自己的表达式鉴权方法;
- @PreAuthorize 和 @PostAuthorize 分别代表在方法调用前或方法返回前执行表达式鉴权;
- @PreFilter 和 @PostFilter 是对入参或者返回值的条件过滤。
下节我们讨论一个新的概念「安全对象」。

































































 童雷 ·
童雷 ·
 2026 imooc.com All Rights Reserved |
2026 imooc.com All Rights Reserved |