-
流是事件的一个实例,stream是基于事件工作的,所以在流对象上具有异步的特征,可以监听事件,触发事件,流在各个阶段的变化都可以被我们实时监听
查看全部 -
// var http = require('http')
var https = require('https')
var Promise = require('bluebird')
var cheerio = require('cheerio')
var baseUrl = 'https://www.imooc.com/learn/'
var url = 'https://www.imooc.com/learn/348'
var videoIds = [348, 259, 197, 134, 75]
function filterChapters(html) {
var $ = cheerio.load(html)
var chapters = $('.chapter')
var title = $('hd h2').text()
var number = parseInt($('.js-learn-num').text())
// courseData = {
// title:title,
// number:number,
// videos:[{
// chapterTitle: '',
// videos: [
// title: '',
// id: ''
// ]
// }]
// }
var coursesData = {
title: title,
number: number,
videos: []
}
chapters.each(function (item) {
var chapter = $(this)
var chapterTitle = chapter.find('.chapter-description').text()
var videos = chapter.find('.video').children('li')
var chapterData = {
chapterTitle: chapterTitle,
videos: []
}
videos.each(function (item) {
var video = $(this).find('.J-media-item')
var videoTitle = video.text()
var id = video.attr('href').split('video/')[1]
chapterData.videos.push({
title: videoTitle,
id: id
})
})
coursesData.videos.push(chapterData)
})
return coursesData
}
function printCourseInfo(coursesData) {
coursesData.forEach((courseData) => {
console.log(courseData.number) + '人学过' + courseData.title + '\n'
})
coursesData.forEach(courseData => {
console.log('###' + courseData.title + '\n')
courseData.videos.forEach((item) => {
var chapterTitle = item.chapterTitle
console.log(chapterTitle + '\n')
item.videos.forEach(video => {
console.log('【' + video.id + '】' + video.title + '\n')
})
})
});
}
function getPageAsync(url) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
console.log("正在爬取" + url)
https.get(url, function (res) {
var html = ''
res.on('data', function (data) {
html += data
})
res.on('end', function () {
resolve(html)
// var courseData = filterChapters(html)
// printCourseInfo(courseData)
})
}).on('error', function () {
console.log('获取出错')
reject(e)
})
})
}
var fetchCourseArray = []
videoIds.forEach((id) => {
fetchCourseArray.push(getPageAsync(baseUrl + id))
})
Promise.all(fetchCourseArray).then(function (pages) {
//
var courseData = []
pages.forEach(function (html) {
var courses = filterChapters(html)
courseData.push(courses)
})
courseData.sort((a, b) => {
return a.number < b.number
})
printCourseInfo(courseData)
})
查看全部 -
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Promise</title>
<style>
.ball {
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
border-radius: 50%;
}
.ball1 {
background: red;
}
.ball2 {
background: yellow;
}
.ball3 {
background: green;
}
</style>
<script src="./node_modules/bluebird/js/browser/bluebird.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="ball ball1" ></div>
<div class="ball ball2" ></div>
<div class="ball ball3" ></div>
<script>
var ball1 = document.querySelector('.ball1')
var ball2 = document.querySelector('.ball2')
var ball3 = document.querySelector('.ball3')
// 方法一
// function animate(ball, distance, cb) {
// setTimeout(function () {
// var marginLeft = parseInt(ball.style.marginLeft, 10);
// if (marginLeft === distance) {
// cb && cb();
// } else {
// if (marginLeft < distance) {
// marginLeft++;
// } else {
// marginLeft--;
// }
// ball.style.marginLeft = marginLeft + 'px';
// animate(ball, distance, cb)
// }
// }, 13)
// }
// animate(ball1, 100, function () {
// animate(ball2, 200, function () {
// animate(ball3, 300, function () {
// animate(ball3, 150, function () {
// animate(ball2, 150, function () {
// animate(ball1, 150, function () {})
// })
// })
// })
// })
// })
// 方法二
var Promise = window.Promise
function promiseAnimate(ball, distance) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
function _animate() {
setTimeout(function () {
var marginLeft = parseInt(ball.style.marginLeft, 10);
if (marginLeft === distance) {
resolve()
} else {
if (marginLeft < distance) {
marginLeft++;
} else {
marginLeft--;
}
ball.style.marginLeft = marginLeft + 'px';
_animate()
}
}, 13)
}
_animate()
})
}
promiseAnimate(ball1, 100)
.then(function () {
return promiseAnimate(ball2, 200)
})
.then(function () {
return promiseAnimate(ball3, 300)
})
.then(function () {
return promiseAnimate(ball3, 150)
})
.then(function () {
return promiseAnimate(ball2, 150)
})
.then(function () {
return promiseAnimate(ball1, 150)
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
查看全部 -
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Promise</title>
<style>
.ball {
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
border-radius: 50%;
}
.ball1 {
background: red;
}
.ball2 {
background: yellow;
}
.ball3 {
background: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="ball ball1" ></div>
<div class="ball ball2" ></div>
<div class="ball ball3" ></div>
<script>
var ball1 = document.querySelector('.ball1')
var ball2 = document.querySelector('.ball2')
var ball3 = document.querySelector('.ball3')
function animate(ball, distance, cb) {
setTimeout(function () {
var marginLeft = parseInt(ball.style.marginLeft, 10);
console.log(marginLeft);
console.log(distance)
if (marginLeft == distance) {
cb && cb();
} else {
if (marginLeft < distance) {
marginLeft++;
} else {
marginLeft--;
}
ball.style.marginLeft = marginLeft + 'px';
animate(ball, distance, cb)
}
}, 13)
}
animate(ball1, 100, function () {
animate(ball2, 200, function () {
animate(ball3, 300, function () {
animate(ball3, 150, function () {
animate(ball2, 150, function () {
animate(ball1, 150, function () {})
})
})
})
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
查看全部 -
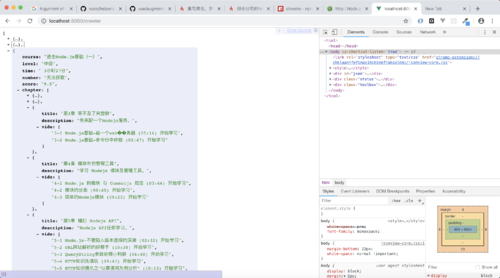
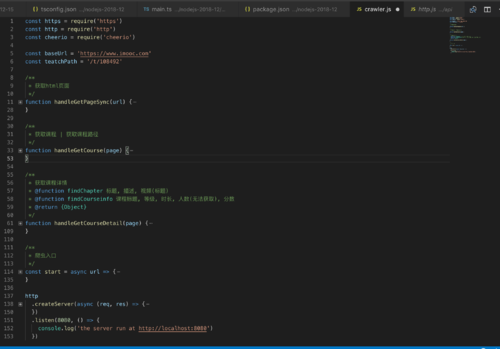
var http = require('http'); var https = require('https'); //var Promise = require('Promise') var Promise = require('bluebird') var cheerio = require('cheerio'); var baseUrl = 'http://www.imooc.com/learn/'; var videoIds = [348, 259, 197, 134, 75]; function filterChapters(html) { var $ = cheerio.load(html); var chapters = $('.chapter.course-wrap'); var title = $('.hd.clearfix h2').text(); //console.log('###课程标题###:' + title); //var number = parseInt($('.meta-value.js-learn-num').text()); //var numberHtml = getHttpsPageAsync('https://www.imooc.com/course/AjaxCourseMembers?ids=348'); //var number = JSON.parse(getHttpsPageAsync('https://www.imooc.com/course/AjaxCourseMembers?ids=348')).data[0].numbers; //console.log('###课程人数###:' + numberHtml); var number = 0; //var courseData = []; var courseData = { title: title, number: number, videos: [] } chapters.each(function(item) { var chapter = $(this) var chapterTitle = chapter.find('h3').text(); //console.log('test:' + chapterTitle); var videos = chapter.find('.video').children('li'); var chapterData = { chapterTitle: chapterTitle, videos: [] } videos.each(function(item) { var video = $(this).find('.J-media-item'); var videoTitle = video.text(); //console.log('test:' + videoTitle); var id = video.attr('href').split('video/')[1]; //console.log('test:' + id); chapterData.videos.push({ title: videoTitle, id: id }) }) courseData.videos.push(chapterData); }) return courseData; } function printCourseInfo(coursesData) { coursesData.forEach(function(courseData) { console.log(courseData.number + ' 人学过' + courseData.title + '\n'); }) coursesData.forEach(function(courseData) { console.log('###' + courseData.title + '\n'); courseData.videos.forEach(function(item) { var chapterTitle = item.chapterTitle; console.log(chapterTitle.trim() + '\n'); item.videos.forEach(function(video) { console.log('【' + video.id + '】' + video.title.trim() + '\n'); }) }) }); } //生成爬取任务,将html作为Promise的resolve方法传递的值 function getPageAsync(url) { return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) { console.log('正在爬取 ' + url) http.get(url, function(res) { var html = ''; res.on('data', function(data) { html += data; }); res.on('end', function() { resolve(html) //var courseData = filterChapters(html); //printCourseInfo(courseData); }); }).on('error', function(e) { reject(e); console.log('获取课程数据出错'); }); }) } function getHttpsPageAsync(url) { //return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) { console.log('正在爬取 ' + url) https.get(url, function(res) { var html = ''; res.on('data', function(data) { html += data; }); console.log('https爬取' + html); res.on('end', function() { return html; //resolve(html) //var courseData = filterChapters(html); //printCourseInfo(courseData); }); }).on('error', function() { //reject(e); console.log('获取课程数据出错'); }); //}) } var fetchCourseArry = [] videoIds.forEach(function(id) { fetchCourseArry.push(getPageAsync(baseUrl + id)) }) //等待所有网页爬取任务完成后再进行filter操作,这时then里传递的是所有任务的resolve中传递值的数组? Promise .all(fetchCourseArry) .then(function(pages) { var coursesData = [] pages.forEach(function(html) { var courses = filterChapters(html) coursesData.push(courses) }) coursesData.sort(function(a, b) { return a.number < b.number; }) printCourseInfo(coursesData); })查看全部 -
Buffer和Stream是node的基础能力查看全部
-
成果 (๑•̀ㅂ•́)و,也算入一点nodejs的门了吧, 感谢老师
 查看全部
查看全部 -
promise是一个对象,通过then方法可以链式编程,并且是在异步请求的基础上,实现了同步操作then.
查看全部 -
promise库
bluebird, Q,
then.js, es6-promise,
ypromise, async,
native-promise-only
查看全部 -
//之前的
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>promise animation</title>
<style>
.ball {
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
border-radius: 50%;
}
.ball1 {
background-color: red;
}
.ball2 {
background-color: green;
}
.ball3 {
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div class="ball ball1" style='margin-left: 0;'></div>
<div class="ball ball2" style='margin-left: 0;'></div>
<div class="ball ball3" style='margin-left: 0;'></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<script>
var ball1 = document.querySelector('.ball1')
var ball2 = document.querySelector('.ball2')
var ball3 = document.querySelector('.ball3')
function animate(ball, distance, cb) {
setTimeout(function () {
// console.log(ball.style.marginLeft);
var marginLeft = parseInt(ball.style.marginLeft, 10)
// console.log(marginLeft);
if (marginLeft === distance) {
// 期望的点
cb && cb();
// animate(ball, distance, cb)
} else {
if (marginLeft > distance) {
// console.log(111);
marginLeft--;
} else {
marginLeft++;
}
// 改变样式
ball.style.marginLeft = marginLeft + 'px';
animate(ball, distance, cb)
}
},10)
}
//
animate(ball1, 100, function () {
animate(ball2, 200, function () {
animate(ball3, 300, function () {
animate(ball3, 150, function () {
animate(ball2, 150, function () {
animate(ball1, 150, function () {
})
})
})
})
})
})
</script>
查看全部 -
一、stream种类
1、readable:
(1)reasume:流动模式
(2)pause:暂停模式
2、writable
3、duplex:双攻流,可读可写
tcp socket、zlip、queptal
4、transform:双攻流,可读可写,转换流
不保存数据
zlip、queptal
二、pipe
1、pipe方法会自动监听data,err事件。
2、pipe方法可以自动控制后端压力。
三、上一节的代码可以简写成
var fs = require('fs'); fs.createReadStream('websocket.gif').pipe(fs.createWriteStream('websoket-pipe.gif'));查看全部 -
一、cat *.js | grep http 过滤包含Http的内容
二、buffer:保存原始数据
流:暂存和移动数据
三、涉及流的模块:http、文件系统、压缩模块、tcpsocket、紫禁城标准式输出。
流是buffer的形式存在。
四、拷贝时防爆仓处理
1、readStream的data中添加if。
2、writeSteam的drain处理。
var fs = require('fs'); var readStream = fs.createReadStream('websocket.gif'); var writeSteam = fs.createWriteStream('websocket-stream.gif'); readStream.on('data', function(chunk) { if(writeSteam.write(chunk) === false) { console.log('still cached'); readStream.pause(); } // writeSteam.write(chunk); }); readStream.on('end', function() { writeSteam.end(); }); writeSteam.on('drain', function() { console.log('data drains'); readStream.resume(); })查看全部
举报








