-
你什么仪式九二卡加
查看全部 -
赴日嗯哒航空
查看全部 -
operator
查看全部 -
operate
查看全部 -
int main
查看全部 -
Bijidsad
查看全部 -
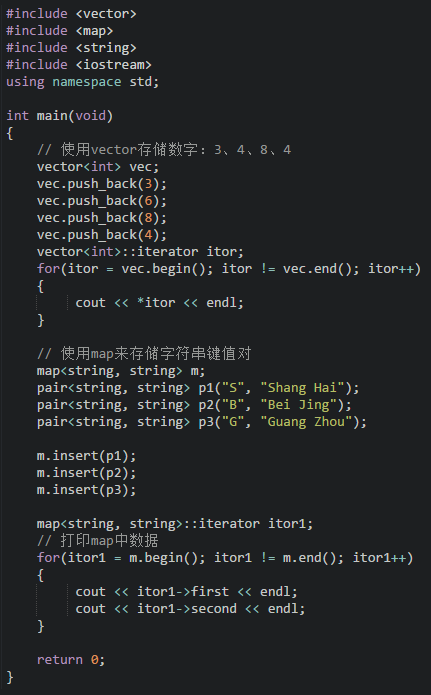
#include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> #include <vector> #include <list> #include <map> #include <string> using namespace std; /******** 通过使用标准模板库,学习其用法 *********/ int main(void){ map<string,string> m; pair<string,string> p1("H","hello"); pair<string,string> p2("W","world"); pair<string,string> p3("B","bejign"); // m.push_back(p1); // m.push_back(p2); //map中没有push_back,和list,vector不同 m.insert(p1); m.insert(p2); m.insert(p3); cout<<m["H"]<<endl; cout<<m[”B“]<<endl; //map的遍历也必须使用迭代器,也可以使用索引的符号来进行遍历 //用迭代器进行遍历,迭代器适用于所有的STL map<string,string>::iterator itor = m.begin(); for(;itor != m.end();itor++){ // cout << *itor <<endl; //map输出需要输出两个 cout<<itor->first<<endl; cout<<itor->second<<endl; cout<<endl; } return 0; }查看全部 -
map使用方法: #include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> #include <vector> #include <list> #include <map> #include <string> using namespace std; /******** 通过使用标准模板库,学习其用法 *********/ int main(void){ map<int,string> m; pair<int,string> p1(3,"hello"); pair<int,string> p2(6,"world"); pair<int,string> p3(8,"bejign"); // m.push_back(p1); // m.push_back(p2); //map中没有push_back,和list,vector不同 m.insert(p1); m.insert(p2); m.insert(p3); //map的遍历也必须使用迭代器,也可以使用索引的符号来进行遍历 cout<<m[3]<<endl; cout<<m[6]<<endl; //用迭代器进行遍历,迭代器适用于所有的STL map<int,string>::iterator itor = m.begin(); for(;itor != m.end();itor++){ // cout << *itor <<endl; //map输出需要输出两个 cout<<itor->first<<endl; cout<<itor->second<<endl; cout<<endl; } return 0; }输出:
hello
world
3
hello
6
world
8
bejign
Process finished with exit code 0
查看全部 -
list定义及使用方法: #include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> #include <vector> #include <list> #include <map> using namespace std; /******** 通过使用标准模板库,学习其用法 *********/ int main(void){ list<int> list1; list1.push_back(4); list1.push_back(7); list1.push_back(10); // for(int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++){ // cout<<list1[i]<<endl; // } //错误不能用list1[i]来访问list的元素,必须使用迭代器 list<int>::iterator itor = list1.begin(); for(;itor != list1.end();itor++){ cout << *itor << endl; } return 0; }查看全部 -
#include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> #include <vector> #include <list> #include <map> using namespace std; /******** 通过使用标准模板库,学习其用法 *********/ int main(void){ vector<int> vec; vec.push_back(3); vec.push_back(4); vec.push_back(6); vec.pop_back(); cout<<vec.size()<<endl; for(int i = 0; i < vec.size();i++){ cout<<vec[i]<<endl; } //使用迭代器 vector<int>::iterator itor = vec.begin(); //cout<<*itor<<endl; for(;itor != vec.end();itor++){ cout<<*itor<<endl; } cout<<vec.front()<<endl;//打印第一个元素 cout<<vec.back()<<endl;//打印最后一个元素 return 0; }错误:error: unknown type name 'vector'; did you mean 'hecto'?
查看全部 -
map:映射
存储的数据都是成对出现,

具体使用方法:(访问方式和数组类似,map对象名[key])

注意m[“S”]
 查看全部
查看全部 -
list:链表模板
特点:数据插入速度快
每个节点:数据域&指针部分
双链表:既可以从头找到尾,也可尾到头。
插入操作,向量比链表较复杂,两者使用方法类型
 查看全部
查看全部 -
empty() //返回值是一个布尔类型,当当前向量是一个空向量时,返回的是ture,否则返回为false begin() end() clear()//不管向量有多少个元素,最后0个元素 fronnt()//返回第一个元素 back()//返回最后一个元素 size()//返回向量中数据的个数 push_back(elem)//将数据插入向量尾 pop_back()//删除向量尾部数据 int main(void){ vector<int> vec; vec.push_back(10);//在向量尾部加一个10 vec.push_pop();//将尾部的10抹掉 cout<<vec.size()<<endl;//总数为0 } 遍历数组法1: for(int k = 0;k < vec.size();k++){ cout<<vet[k]<<endl; } 遍历数组法2:用迭代器iterator进行遍历,可以访问标准模板库对象重的每个元素了 int main(void){ vector vec; vec.push_back("hello"); /* * 如何定一个向量的迭代器: * vector<类型>::iterator 迭代器的变量名 */ vetor<string>::iterator citer = vec.begin();//只有在向量需要将第一个元素迭代器传给一个迭代器变量时才会用到begin() for(;citer != vec.end(); citer++){//end()向量最后一个元素的下一个位置,citer作为迭代器(类似指针) cout << *citer << endl; } return 0; }; return 0; }; 查看全部
查看全部 -
c++标准模板库:
STL:标准模板库
STL:Standard Template Lib
1.vector 向量 (本质:对数组的封装)
特点:读取能在常数时间完成
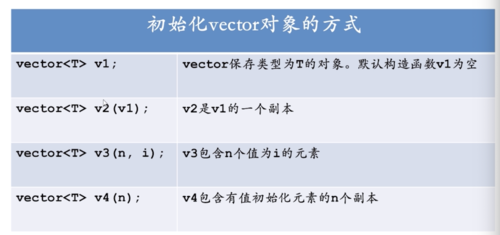
具体在使用时:
vector<int> ivec1;//初始化一个空的向量 vector<int> ivec2(ivet1); vector<string> svac1; vector<string> svec2(ivec); vetor<int> ivet4(10,-1);//用10个-1这样的元素初始化了ivet4这个向量 vetor<string> svec(10,"hi!"); //用10个这样的字符串元素初始化了ivet4这个向量
查看全部 -
5.8练习:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; /** * 定义一个矩形类模板Rect * 成员函数:calcArea()、calePerimeter() * 数据成员:m_length、m_height */ template <typename T> class Rect { public: Rect(T length,T height); T calArea(); T calePerimeter(); public: T m_length; T m_height; }; /** * 类属性赋值 */ template <typename T> Rect<T>::Rect(T length,T height) { m_length = length; m_height = height; } /** * 面积方法实现 */ template <typename T> T Rect<T>::calArea() { return m_length * m_height; } /** * 周长方法实现 */ template <typename T> T Rect<T>::calePerimeter() { return ( m_length + m_height) * 2; } int main(void) { Rect<int> rect(3, 6); cout << rect.calArea() << endl; cout << rect.calePerimeter() << endl; return 0; }查看全部
举报
0/150
提交
取消



