2 回答
TA贡献1936条经验 获得超6个赞
TLDR
我确实读过“……大约 5 分钟来评估……”
没办法太长,这是一个针对许多线和点的实时解决方案。
抱歉,这不是一个完整的答案(我没有合理化和简化方程式),它将找到我留给你的截距点。
我还可以看到解决方案的几种方法,因为它围绕一个三角形(见图)旋转,当平面是解决方案时。下面的方法找到三角形的长边等于短边之和的时间点。
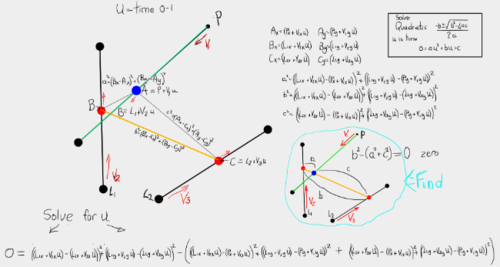
求解你(时间)
这可以作为一个简单的二次方程来完成,其系数从 3 个起点导出,每个点的单位时间向量。为你解决
下图提供了更多详细信息。
点P是点的起始pos
点L1、L2是线端的起点。
矢量V1是单位时间内(沿绿线)的点。
矢量V2、V3用于单位时间内的线路末端。
u是单位时间
A是点(蓝色),B和C是线端点(红色)
存在(可能)一个时间点u,其中A在B和C线上。此时,线AB(作为a)和AC(作为c)的长度总和等于线BC(作为b)(橙色线)的长度。
这意味着当b - (a + c) == 0时,该点在线上。在图像中,点被平方,因为这稍微简化了它。b 2 - (a 2 + c 2 ) == 0
图像底部是根据u, P, L1, L2, V1, V2, V3 的方程(二次) 。
该等式需要重新排列,以便得到(???)u 2 + (???)u + (???) = 0
抱歉,手动执行此操作非常乏味且很容易出错。我手头没有工具,也不使用 python,所以我不知道你使用的数学库。但是它应该能够帮助您找到如何计算(???)u 2 + (???)u + (???) = 0 的系数
更新
忽略上面的大部分内容,因为我犯了一个错误。b - (a + c) == 0与b 2 - (a 2 + c 2 ) == 0不同。第一个是需要的,这是处理部首时的一个问题(请注意,仍然可以使用 虚数a + bi == sqrt(a^2 + b^2)在哪里的解决方案)。i
另一种解决方案
所以我探索了其他选择。
最简单的有一个小缺陷。它将返回拦截时间。但是,必须对其进行验证,因为它还会在拦截线时返回拦截时间,而不是线段BC
因此,当找到结果时,您可以通过将找到的点和线段的点积除以线段长度的平方来测试它。isPointOnLine请参阅测试片段中的功能。
为了解决这个问题,我使用了这样一个事实,即当点在线上时,线BC与从B到A的向量的叉积将为 0。
一些重命名
使用上图,我重命名了变量,这样我就可以更轻松地完成所有繁琐的工作。
/*
point P is {a,b}
point L1 is {c,d}
point L2 is {e,f}
vector V1 is {g,h}
vector V2 is {i,j}
vector V3 is {k,l}
Thus for points A,B,C over time u */
Ax = (a+g*u)
Ay = (b+h*u)
Bx = (c+i*u)
By = (d+j*u)
Cx = (e+k*u)
Cy = (f+l*u)
/* Vectors BA and BC at u */
Vbax = ((a+g*u)-(c+i*u))
Vbay = ((b+h*u)-(d+j*u))
Vbcx = ((e+k*u)-(c+i*u))
Vbcy = ((f+l*u)-(d+j*u))
/*
thus Vbax * Vbcy - Vbay * Vbcx == 0 at intercept
*/
这给出了二次
0 = ((a+g*u)-(c+i*u)) * ((f+l*u)-(d+j*u)) - ((b+h*u)-(d+j*u)) * ((e+k*u)-(c+i*u))
重新排列我们得到
0 = -((i*l)-(h*k)+g*l+i*h+(i+k)*j-(g+i)*j)*u* u -(d*g-c*l-k*b-h*e+l*a+g*f+i*b+c*h+(i+k)*d+(c+e)*j-((f+d)*i)-((a+c)*j))*u +(c+e)*d-((a+c)*d)+a*f-(c*f)-(b*e)+c*b
因此系数是
A = -((i*l)-(h*k)+g*l+i*h+(i+k)*j-(g+i)*j)
B = -(d*g-c*l-k*b-h*e+l*a+g*f+i*b+c*h+(i+k)*d+(c+e)*j-((f+d)*i)-((a+c)*j))
C = (c+e)*d-((a+c)*d)+a*f-(c*f)-(b*e)+c*b
我们可以使用二次公式求解(见右上图)。
请注意,可能有两种解决方案。在示例中,我忽略了第二个解决方案。但是,由于第一个可能不在线段上,如果在0 <= u <= 1范围内,您需要保留第二个解决方案,以防第一个失败。您还需要验证该结果。
测试
为了避免错误,我不得不测试解决方案
下面是一个片段,它生成随机的随机线对,然后生成随机线,直到找到截距。
感兴趣的功能是
movingLineVPoint如果有的话,它返回第一次拦截的单位时间。isPointOnLine来验证结果。
const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
canvas.addEventListener("click",test);
const W = 256, H = W, D = (W ** 2 * 2) ** 0.5;
canvas.width = W; canvas.height = H;
const rand = (m, M) => Math.random() * (M - m) + m;
const Tests = 300;
var line1, line2, path, count = 0;
setTimeout(test, 0);
// creating P point L line
const P = (x,y) => ({x,y,get arr() {return [this.x, this.y]}});
const L = (l1, l2) => ({l1,l2,vec: P(l2.x - l1.x, l2.y - l1.y), get arr() {return [this.l1, this.l2]}});
const randLine = () => L(P(rand(0, W), rand(0, H)), P(rand(0, W), rand(0, H)));
const isPointOnLine = (p, l) => {
const x = p.x - l.l1.x;
const y = p.y - l.l1.y;
const u = (l.vec.x * x + l.vec.y * y) / (l.vec.x * l.vec.x + l.vec.y * l.vec.y);
return u >= 0 && u <= 1;
}
// See answer illustration for names
// arguments in order Px,Py,L1x,l1y,l2x,l2y,V1x,V1y,V2x,V2y,V3x,V3y
function movingLineVPoint(a,b, c,d, e,f, g,h, i,j, k,l) {
var A = -(i*l)-(h*k)+g*l+i*h+(i+k)*j-(g+i)*j;
var B = -d*g-c*l-k*b-h*e+l*a+g*f+i*b+c*h+(i+k)*d+(c+e)*j-((f+d)*i)-((a+c)*j)
var C = +(c+e)*d-((a+c)*d)+a*f-(c*f)-(b*e)+c*b
// Find roots if any. Could be up to 2
// Using the smallest root >= 0 and <= 1
var u, D, u1, u2;
// if A is tiny we can ignore
if (Math.abs(A) < 1e-6) {
if (B !== 0) {
u = -C / B;
if (u < 0 || u > 1) { return } // !!!! no solution !!!!
} else { return } // !!!! no solution !!!!
} else {
B /= A;
D = B * B - 4 * (C / A);
if (D > 0) {
D **= 0.5;
u1 = 0.5 * (-B + D);
u2 = 0.5 * (-B - D);
if ((u1 < 0 || u1 > 1) && (u2 < 0 || u2 > 1)) { return } // !!!! no solution !!!!
if (u1 < 0 || u1 > 1) { u = u2 } // is first out of range
else if (u2 < 0 || u2 > 1) { u = u1 } // is second out of range
else if (u1 < u2) { u = u1 } // first is smallest
else { u = u2 }
} else if (D === 0) {
u = 0.5 * -B;
if (u < 0 || u > 1) { return } // !!!! no solution !!!!
} else { return } // !!!! no solution !!!!
}
return u;
}
function test() {
if (count> 0) { return }
line1 = randLine();
line2 = randLine();
count = Tests
subTest();
}
function subTest() {
path = randLine()
ctx.clearRect(0,0,W,H);
drawLines();
const u = movingLineVPoint(
path.l1.x, path.l1.y,
line1.l1.x, line1.l1.y,
line2.l1.x, line2.l1.y,
path.vec.x, path.vec.y,
line1.vec.x, line1.vec.y,
line2.vec.x, line2.vec.y
);
if (u !== undefined) { // intercept found maybe
pointAt = P(path.l1.x + path.vec.x * u, path.l1.y + path.vec.y * u);
lineAt = L(
P(line1.l1.x + line1.vec.x * u, line1.l1.y + line1.vec.y * u),
P(line2.l1.x + line2.vec.x * u, line2.l1.y + line2.vec.y * u)
);
const isOn = isPointOnLine(pointAt, lineAt);
if (isOn) {
drawResult(pointAt, lineAt);
count = 0;
info.textContent = "Found at: u= " + u.toFixed(4) + ". Click for another";
return;
}
}
setTimeout((--count < 0 ? test : subTest), 18);
}
function drawLine(line, col = "#000", lw = 1) {
ctx.lineWidth = lw;
ctx.strokeStyle = col;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.lineTo(...line.l1.arr);
ctx.lineTo(...line.l2.arr);
ctx.stroke();
}
function markPoint(p, size = 3, col = "#000", lw = 1) {
ctx.lineWidth = lw;
ctx.strokeStyle = col;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(...p.arr, size, 0, Math.PI * 2);
ctx.stroke();
}
function drawLines() {
drawLine(line1);
drawLine(line2);
markPoint(line1.l1);
markPoint(line2.l1);
drawLine(path, "#0B0", 1);
markPoint(path.l1, 2, "#0B0", 2);
}
function drawResult(pointAt, lineAt) {
ctx.clearRect(0,0,W,H);
drawLines();
markPoint(lineAt.l1, 2, "red", 1.5);
markPoint(lineAt.l2, 2, "red", 1.5);
markPoint(pointAt, 2, "blue", 3);
drawLine(lineAt, "#BA0", 2);
}
div {position: absolute; top: 10px; left: 12px}
canvas {border: 2px solid black}
<canvas id="canvas" width="1024" height="1024"></canvas>
<div><span id="info">Click to start</span></div>
TA贡献1824条经验 获得超8个赞
解决方案有两部分我不明白:
解决
b^2 - (a^2 + c^2) = 0而不是sqrt(b^2)-(sqrt(a^2)+sqrt(b^2)) = 0返回的时间戳被限制在范围内
[0,1]
也许我遗漏了一些明显的东西,但无论如何,我设计了一个解决这些问题的解决方案:
求解所有二次项,而不仅仅是一个
返回的时间戳没有限制
sqrt(b^2)-(sqrt(a^2)+sqrt(b^2)) = 0解决了,而不是b^2 - (a^2 + c^2) = 0
随意推荐可以优化的方法:
# pnt, crt_1, and crt_2 are points, each with x,y and dx,dy attributes
# returns a list of timestamps for which pnt is on the segment
# whose endpoints are crt_1 and crt_2
def colinear_points_collision(pnt, crt_1, crt_2):
a, b, c, d = pnt.x, pnt.y, pnt.dx, pnt.dy
e, f, g, h = crt_1.x, crt_1.y, crt_1.dx, crt_1.dy
i, j, k, l = crt_2.x, crt_2.y, crt_2.dx, crt_2.dy
m = a - e
n = c - g
o = b - f
p = d - h
q = a - i
r = c - k
s = b - j
u = d - l
v = e - i
w = g - k
x = f - j
y = h - l
# Left-hand expansion
r1 = n * n + p * p
r2 = 2 * o * p + 2 * m * n
r3 = m * m + o * o
r4 = r * r + u * u
r5 = 2 * q * r + 2 * s * u
r6 = q * q + s * s
coef_a = 4 * r1 * r4 # t^4 coefficient
coef_b = 4 * (r1 * r5 + r2 * r4) # t^3 coefficient
coef_c = 4 * (r1 * r6 + r2 * r5 + r3 * r4) # t^2 coefficient
coef_d = 4 * (r2 * r6 + r3 * r5) # t coefficient
coef_e = 4 * r3 * r6 # constant
# Right-hand expansion
q1 = (w * w + y * y - n * n - p * p - r * r - u * u)
q2 = 2 * (v * w + x * y - m * n - o * p - q * r - s * u)
q3 = v * v + x * x - m * m - o * o - q * q - s * s
coef1 = q1 * q1 # t^4 coefficient
coef2 = 2 * q1 * q2 # t^3 coefficient
coef3 = 2 * q1 * q3 + q2 * q2 # t^2 coefficient
coef4 = 2 * q2 * q3 # t coefficient
coef5 = q3 * q3 # constant
# Moves all the coefficients onto one side of the equation to get
# at^4 + bt^3 + ct^2 + dt + e
# solve for possible values of t
p = np.array([coef1 - coef_a, coef2 - coef_b, coef3 - coef_c, coef4 - coef_d, coef5 - coef_e])
def fun(x):
return p[0] * x**4 + p[1] * x**3 + p[2] * x**2 + p[3] * x + p[4]
# could use np.root, but I found this to be more numerically stable
sol = optimize.root(fun, [0, 0], tol=0.002)
r = sol.x
uniques = np.unique(np.round(np.real(r[np.isreal(r)]), 4))
final = []
for r in uniques[uniques > 0]:
if point_between(e + g * r, f + h * r, i + k * r, j + l * r, a + c * r, b + d * r):
final.append(r)
return np.array(final)
# Returns true if the point (px,py) is between the endpoints
# of the line segment whose endpoints lay at (ax,ay) and (bx,by)
def point_between(ax, ay, bx, by, px, py):
# colinear already checked above, this checks between the other two.
return (min(ax, bx) <= px <= max(ax, bx) or abs(ax - bx) < 0.001) and (min(ay, by) <= py <= max(ay, by) or abs(ay - by) < 0.001)
一个例子(L1 和 L2 是直线的端点):
P = (0,0) with velocity (0, +1)
L1 = (-1,2) with velocity (0, -1)
L2 = (1,2) with velocity (0, -1)
返回的结果是t=1,因为在 1 个时间步后,P 将高出一个单位,而直线的两个端点将分别降低一个单位,因此,该点与线段相交于t=1。
添加回答
举报
