3 回答
TA贡献1850条经验 获得超11个赞
我对WYSIWYG项目有完全相同的要求。
这个怎么运作 ?
通过将 HTML 元素映射到它们的纯文本版本,同时保持元素的原始大小。
然后对于每个匹配项,使用先前的映射和setSelectionRange选择回匹配项中包含的每个元素的相应部分
正如我在这个相关问题中所解释的那样,使用execCommand标记每个。然后您可以使用getSelection() .anchorNode.parentElement 来获得一个现成的包装选择,在此处与您的匹配相对应。
然后你可以应用任何你想要的风格!
使用这种方法,您将拥有一些重要的优势:
支持多项选择(我不知道单个浏览器允许使用其本机搜索进行多项选择)
支持在多个元素上进行搜索传播(这里也是,大多数使用的浏览器都没有此功能)
支持正则表达式:)
根据需要操作匹配项,对样式没有限制,您甚至可以修改内容(例如用于自动更正目的)
如果您也在进行 WYSIWYG,则映射到源窗格。(查看如何在内容窗格中选择在下面的 ACE 编辑器中突出显示相应的源)
这是一个快速展示:
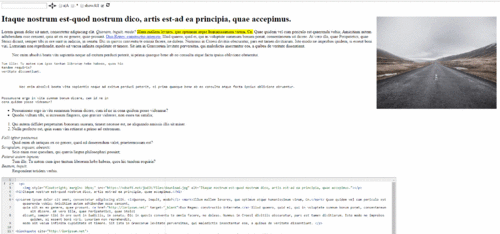
提示 我强烈建议您将所有 execCommand 调用放在requestAnimationFrame() 中,因为每次调用都会触发强制回流,这将使您的应用程序性能下降。通常,浏览器会触发 60 次回流/秒,但在这里,假设您有 300 个匹配项,您将添加 300 次额外的回流。通过在 requestAnimationFrame() 中调用 execCommand,您将告诉浏览器使用计划的回流而不是添加更多。
TA贡献1757条经验 获得超8个赞
您可以使用的一件事是Range对象的getClientRects方法:https : //developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/range/getClientRects
这允许您添加带有搜索坐标的 div,允许您突出显示文本而无需操作 DOM。
查找节点并不是那么简单(尤其是在结构复杂的情况下),但是您可以遍历所有文本节点以匹配要搜索的元素的 textContent 中的搜索索引。
因此,首先将搜索结果与 DOM 进行匹配。在示例中,我使用递归生成器,但任何递归循环都可以。基本上,您需要做的是遍历每个文本节点以匹配搜索索引。因此,您遍历每个后代节点并计算文本长度,以便将搜索与节点匹配。
完成此操作后,您可以根据这些结果创建一个Range,然后添加具有使用getClientRects获得的矩形坐标的元素。通过给出 z-index 负值和绝对位置,它们将出现在文本下方的正确位置。因此,您将获得高亮效果,但不会触及您正在搜索的 HTML。像这样:
document.querySelector('#a').onclick = (e) => {
let topParent = document.querySelector('#b');
let s, range;
let strToSearch = document.querySelector('#search').value
let re = RegExp(strToSearch, 'g')
removeHighlight()
s = window.getSelection();
s.removeAllRanges()
// to handle multiple result you need to go through all matches
while (match = re.exec(topParent.textContent)) {
let it = iterateNode(topParent);
let currentIndex = 0;
// the result is the text node, so you can iterate and compare the index you are searching to all text nodes length
let result = it.next();
while (!result.done) {
if (match.index >= currentIndex && match.index < currentIndex + result.value.length) {
// when we have the correct node and index we add a range
range = new Range();
range.setStart(result.value, match.index - currentIndex)
}
if (match.index + strToSearch.length >= currentIndex && match.index + strToSearch.length < currentIndex + result.value.length) {
// when we find the end node, we can set the range end
range.setEnd(result.value, match.index + strToSearch.length - currentIndex)
s.addRange(range)
// this is where we add the divs based on the client rects of the range
addHighlightDiv(range.getClientRects())
}
currentIndex += result.value.length;
result = it.next();
}
}
s.removeAllRanges()
}
function* iterateNode(topNode) {
// this iterate through all descendants of the topnode
let childNodes = topNode.childNodes;
for (let i = 0; i < childNodes.length; i++) {
let node = childNodes[i]
if (node.nodeType === 3) {
yield node;
} else {
yield* iterateNode(node);
}
}
}
function addHighlightDiv(rects) {
for (let i = 0; i < rects.length; i++) {
let rect = rects[i];
let highlightRect = document.createElement('DIV')
document.body.appendChild(highlightRect)
highlightRect.classList.add('hl')
highlightRect.style.top = rect.y + window.scrollY + 'px'
highlightRect.style.left = rect.x + 'px'
highlightRect.style.height = rect.height + 'px'
highlightRect.style.width = rect.width + 'px'
}
}
function removeHighlight() {
let highlights = document.querySelectorAll('.hl');
for (let i = 0; i < highlights.length; i++) {
highlights[i].remove();
}
}
.hl {
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
z-index: -1;
}
<input type="text" id="search" /><button id="a">search</button>
<div id="b">
<h1>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet</h1>, consectetur
<h2>adipiscing elit, sed do</h2> eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud <strong>exercitation <span>ullamco laboris</span> nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo</strong> consequat. Duis aute irure dolor
in reprehenderit in voluptate velit <em>esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur.</em> Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident, sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum.
</div>
添加回答
举报
