-
^异或:参与运算的两个二进制相同则为0.否则为1.
~取反
<<左移 >>右移
查看全部 -
 。查看全部
。查看全部 -
Staff(const Staff & staff);赋值构造函数
查看全部 -
memcpy函数。用法:(目标地址,源地址,数据长度)
数据长度的单位是字节。(1 byte = 8 bit)
c++中需要调用<cstring>库
查看全部 -
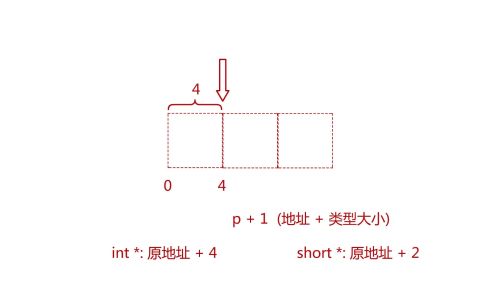 指针的运算。查看全部
指针的运算。查看全部 -
指针加减法实际不是操作指针本身,而是通过指针存储的地址+指针类型大小,得出需要被操作的新内存地址查看全部
-
浮点数类型float。运算过程复杂,且精度不高,不能存放较大的数字。
查看全部 -
std::string 是 C++ 中用来存放字符串的类型
查看全部 -
1
查看全部 -
函数指针的声明方法为:
返回值类型 ( * 指针变量名) ([形参列表]);
注1:“返回值类型”说明函数的返回类型,“(指针变量名 )”中的括号不能省,括号改变了运算符的优先级。若省略整体则成为一个函数说明,说明了一个返回的数据类型是指针的函数,后面的“形参列表”表示指针变量指向的函数所带的参数列表。例如:
int func(int x); /* 声明一个函数 */
int (*f) (int x); /* 声明一个函数指针 */
f=func; /* 将func函数的首地址赋给指针f */
或者使用下面的方法将函数地址赋给函数指针:
f = &func;
查看全部 -
普通变量使用.
指针变量使用->
查看全部 -
笔记测试一下笔记测试一下笔记查看全部
-
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Mat {
friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Mat& m);
public:
int row = 0;
int col = 0;
float * * mat = nullptr;
private:
void init(int row, int col)
{
if (row && col) {
mat = new float*[row];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
mat[i] = new float[col];
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++){
mat[i][j] = 0;
if(i == j){
mat[i][j] = 2;
}
}
}
}
}
public:
Mat(int row = 0, int col = 0)
{
this->row = row;
this->col = col;
init(row, col);
}
Mat(const Mat &m)
{
this->row = m.row;
this->col = m.col;
init(row, col);
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++){
mat[i][j] = m.mat[i][j];
}
}
}
~Mat()
{
if (mat != nullptr) {
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++){
if (mat[i]) {
delete[] mat[i];
mat[i] = nullptr;
}
}
if (mat){
delete[] mat;
}
mat = nullptr;
}
}
Mat & operator = (const Mat &m)
{
if (mat != nullptr) {
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++){
if (mat[i]) {
delete[] mat[i];
mat[i] = nullptr;
}
}
if (mat){
delete[] mat;
}
mat = nullptr;
}
row = m.row;
col = m.col;
init(row, col);
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++){
mat[i][j] = m.mat[i][j];
}
}
return *this;
}
Mat operator * (const Mat &m)
{
Mat res(row, m.col);
for (int i = 0; i < res.row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < res.col; j++) {
res.mat[i][j] = 0.0f;
}
}
if (m.row != col){
}
else {
for (int i = 0; i < res.row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < res.col; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < res.row; k++) {
res.mat[i][j] += mat[i][k] * m.mat[k][j];
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Mat& m)
{
for(int i = 0; i < m.row; i ++) {
for(int j = 0; j < m.col; j ++) {
cout << m.mat[i][j] << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
return out;
}
int main()
{
Mat ma(3, 3);
Mat mb(3, 3);
Mat res = ma * mb;
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
查看全部 -
从函数中取出一个对象
理解:函数的返回值是一个对象啊
通过把返回值写在参数里面,怎么实现返回的是对象呢?
查看全部 -
向函数中传递一个对象:
若是直接在函数的参数列表中传递对象,那么这个传递到函数内部的对象仅仅是副本,造成资源浪费。
所以,一般选择使用指针或者引用作为函数列表中的对象引用
使用指针作为函数列表的参数时,为了增加健壮性还需要对指针进行判空操作。
因此可以选择使用引用传递对象
而且,可以使用const修饰来增加对象的存在周期,且指向不可修改。
查看全部
举报








