-
使用时间: java.util 包的Day; 或 Java.text 包的 DaySimpleFormat查看全部
-
String类
字符串本身就是String类的实例对象
String类的常用方法
1、int length();返回当前字符串的长度
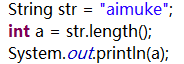
2、
查看全部 -
将基本类型转换为字符串:3种方法 1. String S= String.toString(I) 2. String.valueof(I) 3. I+""查看全部
-
基本类型不能调用方法
查看全部 -
//扑克牌类
public class Pocker implements Comparable<Pocker> {
private String color;
private String point;
public Pocker() {
super();
}
public Pocker(String color, String point) {
super();
this.color = color;
this.point = point;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String getPoint() {
return point;
}
public void setPoint(String point) {
this.point = point;
}
//重写ToString方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return color + point;
}
//设置花色的值
public int getColorVal() {
int value = 0;
switch (this.color) {
case "黑桃":
value = 4;
break;
case "红桃":
value = 3;
break;
case "梅花":
value = 2;
break;
case "方块":
value = 1;
break;
}
return value;
}
//设置点数的值
public int getPointVal() {
int value = 0;
switch (this.getPoint()) {
case "2":
case "3":
case "4":
case "5":
case "6":
case "7":
case "8":
case "9":
case "10":
value = Integer.parseInt(this.getPoint());
break;
case "J":
value = 11;
break;
case "Q":
value = 12;
break;
case "K":
value = 13;
break;
case "A":
value = 14;
break;
}
return value;
}
//重写compareTo方法
@Override
public int compareTo(Pocker p) {
if (this.getPointVal() > p.getPointVal()) {
return 1;
} else if (this.getPointVal() < p.getPointVal()) {
return -1;
} else {
if (this.getColorVal() > p.getColorVal()){
return 1;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
}
}
//玩家类
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Player {
private int id;
private String name;
public List<Pocker> hasPocker;
public Player() {
super();
hasPocker = new ArrayList<Pocker>();
}
public Player(int id, String name) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
hasPocker = new ArrayList<Pocker>();
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//获取手牌中的最大牌
public Pocker getMax(List<Pocker> haspocker){
Pocker max=haspocker.get(0);
for(int i=0;i<haspocker.size()-1;i++){
if(max.compareTo(haspocker.get(i+1))<0){
max=haspocker.get(i+1);
}
}
return max;
}
}
//主程序类
public class Game {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Pocker> pockerList = new ArrayList<Pocker>();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Random random = new Random();
String[] colors = { "黑桃", "红桃", "梅花", "方块" };
String[] points = { "A", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10",
"J", "Q", "K" };
for (int i = 0; i < colors.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < points.length; j++) {
Pocker p = new Pocker(colors[i], points[j]);
pockerList.add(p);
}
}
// 通过取随机作为下标打乱排序
System.out.println("-----------开始洗牌-----------");
List<Pocker> newList = new ArrayList<Pocker>();
for (int i = 0; i < pockerList.size(); i++) {
int index = random.nextInt(pockerList.size());
if (!newList.contains(pockerList.get(index))) {
newList.add(pockerList.get(index));
} else {
i -= 1;
}
}
System.out.println("-----------洗牌结束-----------");
Player player1= new Player();
Player player2 = new Player();
List<Player> playerList = new ArrayList<Player>();
playerList.add(player1);
playerList.add(player2);
for(int i=1;i<=2;i++){
System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"位玩家的信息:");
while (true) {
try {
System.out.println("请输入ID:");
int id = sc.nextInt();
for (Player player : playerList) {
if (player.getId() == id) {
System.out.println("该ID已被占用,重新输入");
throw new Exception();
}
}
playerList.get(i-1).setId(id);
break;
} catch (InputMismatchException e) {
sc.next();
System.out.println("输入错误,重新输入!");
} catch(Exception e){
continue;
}
}
System.out.println("请输入昵称:");
String name = sc.next();
playerList.get(i-1).setName(name);
}
System.out.println("-----------匹配成功-----------");
System.out.println("-----------开始发牌-----------");
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(player1.getName()+"拿牌");
player1.hasPocker.add(newList.get(i));
} else {
System.out.println(player2.getName()+"拿牌");
player2.hasPocker.add(newList.get(i));
}
}
System.out.println("-----------游戏开始-----------");
System.out.println("-----------开始比牌-----------");
for(int i=3;i>=1;i--){
System.out.println(" "+i+" ");
}
Pocker max1=player1.getMax(player1.hasPocker);
Pocker max2=player2.getMax(player2.hasPocker);
if(max1.compareTo(max2)>0){
System.out.println(player1.getName()+"获胜");
}else{
System.out.println(player2.getName()+"获胜");
}
System.out.println("-----------玩家亮牌-----------");
for (Player player : playerList) {
System.out.println(player.getName()+"的手牌:"+player.hasPocker.toString());
}
System.out.println("-----------游戏结束-----------");
}
}
查看全部 -
捕获到的异常,可以在当前方法的 catch 块中处理,也可抛出给调用者去处理
查看全部 -
字符串中字符的索引从0开始,范围为 0 到 length()-1
使用 indexOf 进行字符或字符串查找时,如果匹配返回位置索引;如果没有匹配结果,返回 -1
使用 substring(beginIndex , endIndex) 进行字符串截取时,包括 beginIndex 位置的字符,不包括 endIndex 位置的字符
查看全部 -
sort()查看全部
-
public class Student{
public String id;
public String name;
public Set courses;
public Student(String id,String name){
this.id=id;
this.name=name;
this.courses=new HashSet();
}
}
查看全部 -
public class Course{
public String id;
public String name;
public Course(String id,String name){
this.id=id;
this.name=name;
}
}
查看全部 -
LIst-ArrayList
查看全部 -
我尼玛什么鬼
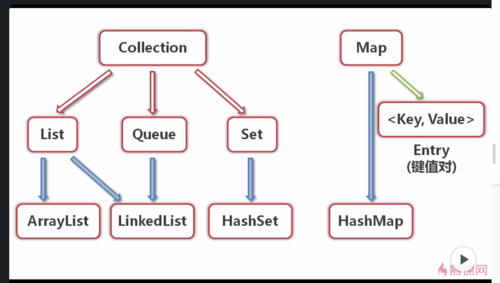 查看全部
查看全部 -
Set中,添加摸个对象,无论添加多少次最终只会保留一个该对象
并且,保留的是第一次添加的那个
查看全部 -
Set接口及其实现类——HashSet
Set是元素无序并且不可以重复的集合,被称为集
HashSet——哈希集,是Set的一个重要实现类
查看全部 -
泛型List集合
泛型不能使用基本类型,必须使用其包装类。
泛型集合可以添加泛型的子类型的对象实例
泛型集合中,不能添加泛型规定的类型及其子类型以外的对象,否则会报错
查看全部
举报







