-
Exception:
一、非检查异常(RuntimeException)
1、空指针异常(NullPointerException);
2、数组下表越界异常(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException);
3、类型转换异常(ClassCastException);
4、算数异常(ArithmeticException);
二、检查异常
1、文件异常;
2、SQL异常;
查看全部 -
==: 判断两个字符串在内存中首地址是否相同,即判断是否是同一个字符串对象
equals(): 比较存储在两个字符串对象中的内容是否一致
查看全部 -
这个挺有意思查看全部
-
嘻嘻嘻嘻嘻嘻查看全部
-
哈哈哈哈哈哈哈查看全部
-
collection:list查看全部
-
public class Poker implements Comparable<Poker> { private String color; private String point; public Poker(String color, String point) { this.color = color; this.point = point; } public Poker() { } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public String getPoint() { return point; } public void setPoint(String point) { this.point = point; } @Override public String toString() { return color + point; } public int getColorValue() { int val; if (this.getColor().equals("方块")) { val = 1; } else if (this.getColor().equals("梅花")) { val = 2; } else if (this.getColor().equals("红桃")) { val = 3; } else if (this.getColor().equals("黑桃")) { val = 4; } else { val = 0; } return val; } public int getPointValue() { int val; if (this.getPoint().equals("2")) { val = 2; } else if (this.getPoint().equals("3")) { val = 3; } else if (this.getPoint().equals("4")) { val = 4; } else if (this.getPoint().equals("5")) { val = 5; } else if (this.getPoint().equals("6")) { val = 6; } else if (this.getPoint().equals("7")) { val = 7; } else if (this.getPoint().equals("8")) { val = 8; } else if (this.getPoint().equals("9")) { val = 9; } else if (this.getPoint().equals("10")) { val = 10; } else if (this.getPoint().equals("J")) { val = 11; } else if (this.getPoint().equals("Q")) { val = 12; } else if (this.getPoint().equals("K")) { val = 13; } else if (this.getPoint().equals("A")) { val = 14; } else { val = 0; } return val; } @Override public int compareTo(Poker poker) { if (this.getPointValue() > poker.getPointValue()) { return 1; } else if (this.getPointValue() < poker.getPointValue()) { return -1; } else { if (this.getColorValue() > poker.getColorValue()) { return 1; } } return 0; } }public class Player { private Integer id; private String name; private List<Poker> pokerList; public Player(Integer id, String name) { this.id = id; this.name = name; pokerList = new ArrayList<>(); } public Player() { pokerList = new ArrayList<>(); } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public List<Poker> getPokerList() { return pokerList; } public void setPokerList(List<Poker> pokerList) { this.pokerList = pokerList; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Poker getMaxPoker(List<Poker> pokerList) { Poker maxPoker = pokerList.get(0); for(int i=1; i<pokerList.size(); i++) { Poker comparePoker = pokerList.get(i); if (maxPoker.compareTo(comparePoker) < 0) { maxPoker = comparePoker; } } return maxPoker; } @Override public String toString() { String pokerString = "["; for (int i=0; i<pokerList.size(); i++) { pokerString += pokerList.get(i).toString(); if (i != pokerList.size()-1) { pokerString += ", "; } } pokerString += "]"; return name + ":" + pokerString; } }public class PlayGame { List<Poker> pokerList = new ArrayList<>(); List<Player> playerList = new ArrayList<>(); private void createPoker() { System.out.println("-----创建poker--------"); String[] colors = {"方块", "梅花", "红桃", "黑桃"}; String[] points = {"2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10", "J", "Q", "K", "A"}; for (String color : colors) { for (String point : points) { Poker poker = new Poker(color, point); pokerList.add(poker); } } System.out.println("-----扑克牌创建成功--------"); System.out.print("为:【"); for (int i=0; i < pokerList.size(); i++) { System.out.print(pokerList.get(i).toString()); if (i == pokerList.size() - 1) { System.out.println("】"); } else { System.out.print(", "); } } } private void shuffle() { System.out.println("-----开始洗牌--------"); Collections.shuffle(pokerList); System.out.println("-----洗牌结束--------"); } private void createPlayer() { System.out.println("-----创建玩家--------"); Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int i = 1; while (i < 3) { Player newPlayer = new Player(); System.out.println("-----请输入第" + i + "个玩家的ID和姓名--------"); while(true) { try { System.out.println("输入ID:"); int id = input.nextInt(); for (Player player : playerList) { if (player.getId() == id) { System.out.println("该ID已被占用,重新输入"); } } newPlayer.setId(id); break; } catch (InputMismatchException e) { input.next(); System.out.println("输入错误,重新输入!"); } catch (Exception e) { continue; } } System.out.println("输入姓名:"); String name = input.next(); newPlayer.setName(name); playerList.add(newPlayer); i++; } for (Player player : playerList) { System.out.println("-----欢迎玩家:" + player.getName()); } } private void catchPoker() { System.out.println("-----开始发牌--------"); List<Integer> catchList = new ArrayList<>(); Integer catchInt; Random random = new Random(); for (int i=0; i<5; i++) { for (Player player : playerList) { do { catchInt = random.nextInt(52); } while(catchList.contains(catchInt)); catchList.add(catchInt); System.out.println("-----玩家:" + player.getName() + "拿牌"); Poker catchPoker = pokerList.get(catchInt); player.getPokerList().add(catchPoker); } } System.out.println("-----发牌结束!--------"); } private void playForWin() { System.out.println("-----开始游戏--------"); Player winner = null; Poker maxPoker = null; for (Player player : this.playerList) { Poker poker = player.getMaxPoker(player.getPokerList()); System.out.println("玩家:" + player.getName() + "最大的手牌为:" + poker.toString()); if (maxPoker == null) { maxPoker = poker; winner = player; } else if(maxPoker.compareTo(poker) < 0) { maxPoker = poker; winner = player; } } System.out.println("-------------玩家:" + winner.getName() + "获胜!------------"); for (Player player : this.playerList) { System.out.println(player.toString()); } } public static void main(String[] args) { PlayGame playGame = new PlayGame(); playGame.createPoker(); playGame.shuffle(); playGame.createPlayer(); playGame.catchPoker(); playGame.playForWin(); } }查看全部 -
基础三字符串查看全部
-
通过实现Comparable接口,如果类型是字符串比较还是按照第一个字符比较再第二个依次类推

如果是int型或者Integer型则会按照数字大小比较

如何使用Comparator,需要传递新的Comparator对象

总结:
讲解sort()方法的时候还介绍了两个接口

搭配使用!
查看全部 -
将字符串转换成基本类型有两种方法:<p>1. 调用包装类的 parseXxx 静态方法</p><p>2. 调用包装类的 valueOf() 方法转换为基本类型的包装类,会自动拆箱</p><p><a href="http://img1.sycdn.imooc.com//53abeaad000109af04610098.jpg"><img alt="" src="http://img1.sycdn.imooc.com//53abeaad000109af04610098.jpg" /></a></p>查看全部
-
基本类型转换为字符串有三种方法:
1. 使用包装类的 toString() 方法
2. 使用String类的 valueOf() 方法
3. 用一个空字符串加上基本类型,得到的就是基本类型数据对应的字符串
 查看全部
查看全部 -
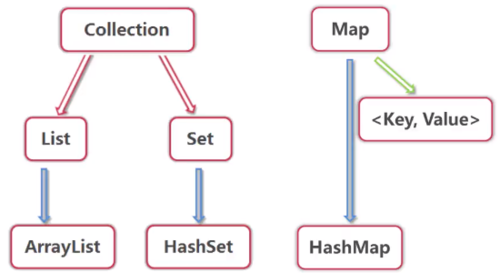
list元素有序且可以重复,称为序列
list可以精确控制每个元素的插入位置,或删除某个位置元素
Arraylist---数组序列,是list一个重要实现类
查看全部 -
在Java中,如果两个对象想要进行排序,那么他们都必须得是可以比较的,Java中使用Comparable这个接口去表示某个对象是可以比较的
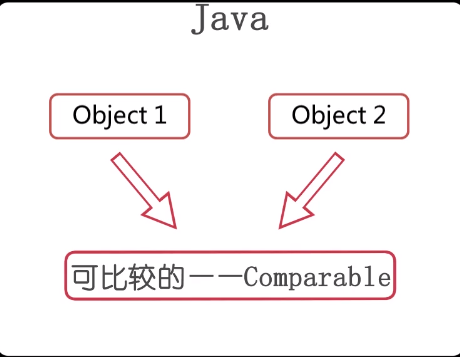
Comparable相当于给对象定义了一个默认的排序规则
Java中还提供另一个接口-Comparator接口,可以理解为是一个定义临时的比较规则的接口


Comparator接口(它的实现类更像是一个比较工具)
 查看全部
查看全部 -
对于像Integer这样基本类型的包装类以及String泛型的ListCollections.sort()都是非常管用非常方便的

对于其他泛型元素必须实现Comparable接口
查看全部 -
“==” 和 equals() 有什么区别呢?
==: 判断两个字符串在内存中首地址是否相同,即判断是否是同一个字符串对象
equals(): 比较存储在两个字符串对象中的内容是否一致
查看全部
举报











