起源
在Activity中,所有的View都是DecorView的子View,然后DecorView又是被ViewRootImpl所控制,当Activity显示的时候,ViewRootImpl的performTranversals方法开始运行,这个方法很长,不过核心的三个流程就是依次调用performMeasure、performLayout、performDraw三个方法,从而完成DecorView的绘制。
ViewRootImpl#performMeasure
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
} |
这里直接调用了mView的measure方法,参数是两个经过设置的MeasureSpec,接下来我们分析一下MeasureSpec是如何设置的。
MeasureSpec
这个MeasureSpec不是实际测绘值,而是父View传递给子View的布局要求,MeasureSpec涵盖了对子View大小和模式的要求。其中,三种模式要求分别是:
UNSPECIFIED:对子View无任何要求,想要测绘多少由子View决定。
EXACTLY:父View已确定了自己确切的大小。子View将在这个边界内测绘自己的宽高。
AT_MOST:父View对子View没有要求,子View可以达到它想要的大小。
首先这个MeasureSpec是个32位的int值,其中31,32两位代表的是三种模式的要求,分别是00….、01….、11….,makeMeasureSpec方法中,sUseBrokenMakeMeasureSpec默认是false,所以一般执行(size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK)这个语句,这个意思就是说,MeasureSpec的高两位代表的是模式,低30位代表父View的尺寸。
下面是对应的方法:
private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30;
private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static int makeMeasureSpec(@IntRange(from = 0, to = (1 << MeasureSpec.MODE_SHIFT) - 1) int size,
@MeasureSpecMode int mode) {
if (sUseBrokenMakeMeasureSpec) {
return size + mode;
} else {
return (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK);
}
} |
View#measure
计算完MeasureSpec,DecorView就该执行measure方法了。
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
···
final boolean forceLayout = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
···
final boolean needsLayout = specChanged
&& (sAlwaysRemeasureExactly || !isSpecExactly || !matchesSpecSize);
if (forceLayout || needsLayout) {
···
int cacheIndex = forceLayout ? -1 : mMeasureCache.indexOfKey(key);
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) {
// measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
} else {
···
}
···
}
···
}
···
} |
measure方法是final的,所以不能重写,不过measure方法最主要的作用就是调用了onMeasure方法,由于DecorView是继承的FrameLayout,所以本篇文章我们主要分析FrameLayout的onMeasure方法。
FrameLayout#onMeasure
这个onMeasure方法,可能是View绘制中最难理解的了,所以我们逐步分析。
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//获取子View个数
int count = getChildCount();
//判断是否是确定宽高的
//如果宽高都确定,那么boolean为false
//如果有一个不确定,那么boolean为true
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren =
MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
mMatchParentChildren.clear();
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
//遍历所有不为GONE的子View,并加以计算
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
//计算各个子View宽高,包括Margin参数以及padding参数
//该方法详细分析见下文
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
//用按位或的方法合并所有子View的State
//getMeasuredState方法详细解析在下面
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
//如果宽高有不确定的(即warp_content模式),将子View中宽或高是match_parent的添加到mMatchParentChildren中。
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT ||
lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
mMatchParentChildren.add(child);
}
}
}
}
// 计算padding
maxWidth += getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground();
maxHeight += getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
// 与最小宽高作比较,二者取较大的
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
// 与前景图宽高作比较,二者取较大的
final Drawable drawable = getForeground();
if (drawable != null) {
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, drawable.getMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, drawable.getMinimumWidth());
}
//计算并保存measured宽高
//resolveSizeAndState方法分析在下面
//setMeasuredDimension方法分析在下面
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
//计算macth_parent的子View的个数
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
//只有FrameLayout中宽或者高有warp_content属性,
//并且match_parent的子view个数大于1才会执行下面代码。
//因为如果宽高都是match_parent的,或者设置好dp数值的,则mMatchParentChildren永远是空的。
//在这里会重新计算传递给子View的MeasureSpec值,并重新测绘子View。
//关于MeasureSpec值的计算,可以参考下文ViewGroup#getChildMeasureSpec的表格。
//这里需要注意的是,match_parent行所有的结果均改为:EXACTLY + parentSize
if (count > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = mMatchParentChildren.get(i);
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec;
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int width = Math.max(0, getMeasuredWidth()
- getPaddingLeftWithForeground() - getPaddingRightWithForeground()
- lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground() +
lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,
lp.width);
}
final int childHeightMeasureSpec;
if (lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int height = Math.max(0, getMeasuredHeight()
- getPaddingTopWithForeground() - getPaddingBottomWithForeground()
- lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin);
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
height, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec,
getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground() +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin,
lp.height);
}
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
} |
ViewGroup#measureChildWithMargins
该方法作用是测绘子View,在父View的onMeasure中循环调用,达到遍历的效果。
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
//获取子View的LayoutParams
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//计算子View的MeasureSpec
//getChildMeasureSpec方法分析见下文
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
//调用子View的measure方法,对子View进行测绘
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} |
ViewGroup#getChildMeasureSpec
此方法通过父View的MeasureSpec值以及LayoutParams的宽高,来生成子View的MeasureSpec值,具体代码如下:
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
//计算父View的size和mode
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
//计算刨除padding的size
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
}
else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
//noinspection ResourceType
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
} |
上面代码,其实通过一张表格,就能很清楚的解释转换规律
| 竖列代表LayoutParams的宽或高属性\横行父View传递的Mode | EXACTLY | AT_MOST | UNSPECIFIED |
|---|---|---|---|
| 精确值 | EXACTLY + childSize | EXACTLY + childSize | EXACTLY + childSize |
| match_parent | EXACTLY + parentSize | AT_MOST + parentSize | UNSPECIFIED + parentSize |
| warp_content | AT_MOST + parentSize | AT_MOST + parentSize | UNSPECIFIED + parentSize |
View#getMeasuredState
public final int getMeasuredState() {
return (mMeasuredWidth&MEASURED_STATE_MASK)
| ((mMeasuredHeight>>MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT)
& (MEASURED_STATE_MASK>>MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
} |
该方法返回一个表达View宽高measure_state值的整数,第8位代表height是否是MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL,第24为代表width是否是MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL的。
例如:
宽是MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL的
返回:0000 0001 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
高是MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL的
返回:0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 0000 0000
宽高均是MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL的
返回:0000 0001 0000 0000 0000 0001 0000 0000
View#resolveSizeAndState
public static final int MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL = 0x01000000;
public static int resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState) {
//计算父view传递的size和mode
final int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
final int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
final int result;
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (specSize < size) {
//如果父View给的size小于自身测绘出的size,
//则在第24位上加上measure_state标记。
result = specSize | MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL;
} else {
result = size;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
default:
result = size;
}
//如果child在第24为上有measure_state标记,则在result的第24位上也加上measure_state标记,然后返回result。
return result | (childMeasuredState & MEASURED_STATE_MASK);
} |
View#setMeasuredDimension
该方法将计算好的measuredWidth和measuredHeight设置给成员变量mMeasuredWidth及mMeasuredHeight,并且将flag设置成PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET。
在4.3版本以上,如果设置了optical模式,则还要对width、height进一步修改,然后再设置mMeasuredWidth、mMeasuredHeight。
mMeasuredWidth和mMeasuredHeight的值,不光包括size,同时还包括state,具体请看getMeasuredWidth、getMeasuredWidthAndState、getMeasuredHeight、getMeasuredHeightAndState方法
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int opticalWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int opticalHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
measuredWidth += optical ? opticalWidth : -opticalWidth;
measuredHeight += optical ? opticalHeight : -opticalHeight;
}
setMeasuredDimensionRaw(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
private void setMeasuredDimensionRaw(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
} |
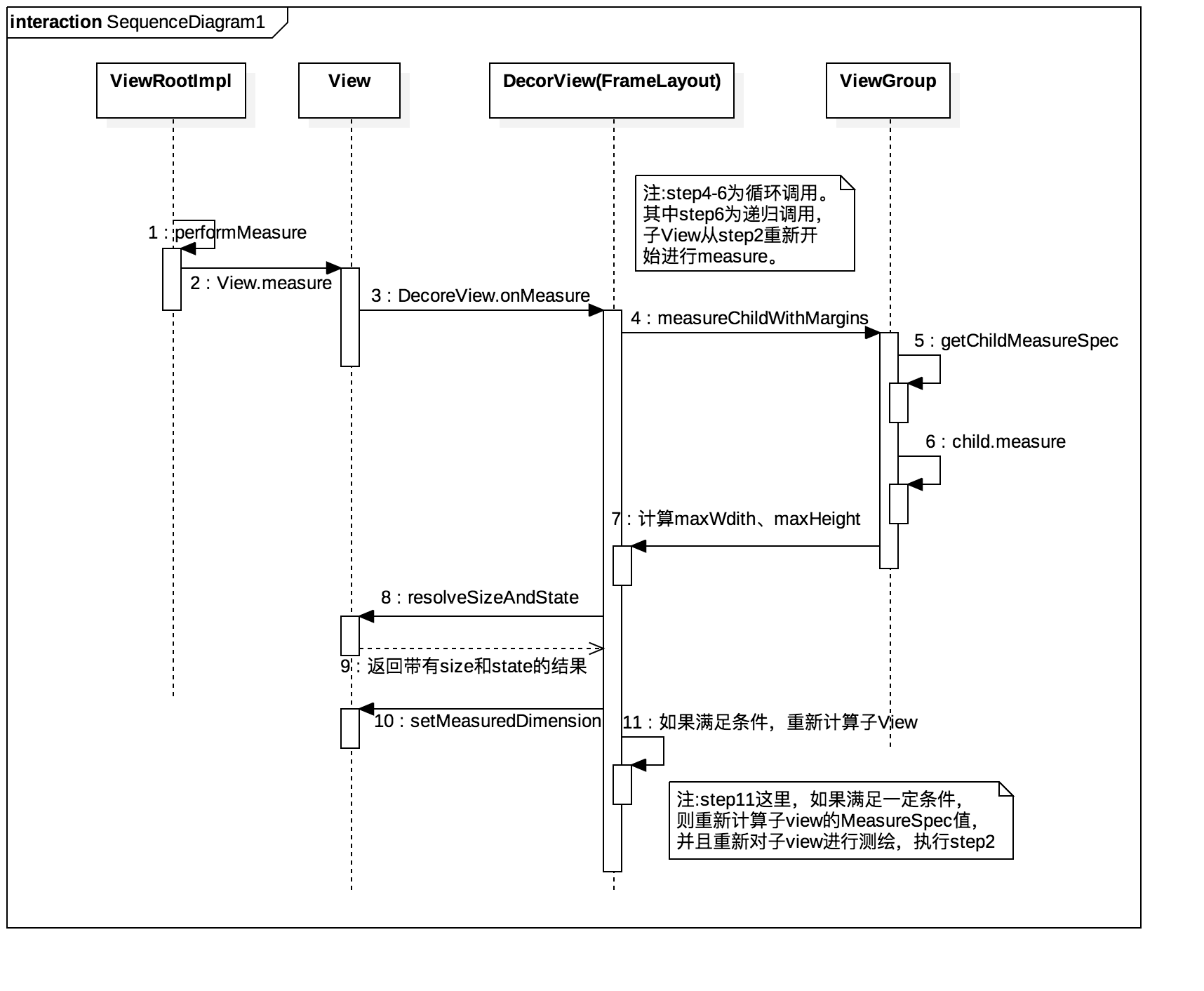
时序图
小结
到这里,关于View的测绘我们大概的走了一遍。Measure的原理就是通过遍历,从上至下,利用传递的MeasureSpec以及子View的LayoutParams,依次进行测绘。不同的layout可能会进行多次的measure,所以熟读源码,合理布局,可以帮我们避免不必要的measure开销,达到提升性能的效果。
最后,感谢阅读,也希望可以和大家多多交流,共同进步。
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章