C#数据应用安全性
确保应用程序安全的用户方面是一个两阶段过程:用户首先需要进行身份验证,再进行授权,以验证该用户是否可以使用需要的资源。
验证用户信息(Windows客户端程序)
安全性的两个基本支柱是身份验证和授权。身份验证是标识用户的过程。授权在验证了所标识用户是否可以访问特定资源之后进行。
使用windows Identity
使用windows标识可以验证运行应用程序的用户。一般应用于windows客户端程序。
WindowsIndentity类表示一个Windows用户,如果没有用Windows账户标识用户,也可以使用实现了IIdentity接口的其他类。通过IIdentity接口可以访问用户名、该用户是否通过身份验证,以及验证类型等信息。
不仅仅是WindowsIdentity,所有的标识类都实现了IIdentity接口。
public class WindowsIdentity : ClaimsIdentity, ISerializable, IDeserializationCallback, IDisposable{}
public class ClaimsIdentity : IIdentity{}
示例:
/// <summary>
/// 输出WindowsIdentity的信息
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
private static WindowsIdentity ShowIdentityInformation()
{
// 返回表示当前 Windows 用户的WindowsIdentity 对象。
WindowsIdentity identity = WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent();
if (identity == null)
{
Console.WriteLine("not a windows identity");
return null;
}
//省份类型
Console.WriteLine("IdentityType:"+identity);
//windows登录名
Console.WriteLine("Name:"+identity.Name);
//是否对用户进行了身份验证
Console.WriteLine("Authenticated:"+identity.IsAuthenticated);
//省份验证类型
Console.WriteLine("Authentication Type:"+identity.AuthenticationType);
//该用户是否为匿名账户
Console.WriteLine("Anonymous?"+identity.IsAnonymous);
Console.WriteLine("Access Token:"+identity.AccessToken.DangerousGetHandle());
Console.WriteLine();
return identity;
}
Windows Principal
WindowsPrincipal是一个包含用户的标识和用户的所属角色的类。它实现了IPrincipal接口,IPrincipal接口定义了identity属性和IsInRole()方法,Identity属性返回IIdentity对象,在IsInRole()方法中,可以验证用户是否是指定角色的一个成员。角色是有相同安全权限的用户集合,同时它是用户的管理单元。角色可以是Windows组或自己定义的一个字符串集合。
public class WindowsPrincipal : ClaimsPrincipal{}
public class ClaimsPrincipal : IPrincipal{}
.NET中的Principal类有WindowsPrincipal、GenericPrincipal和RolePrincipal。从.NET 4.5开始,这些Principal类型派生自ClaimsPrincipal类,而ClaimsPrincipal实现了接口IPrincipal接口。你也可以创建实现了IPrincipal接口或派生自ClaimsPrincipal类的自定义Principal类。
在Windows中,用户所属的所有Windows组映射到角色。重载IsInRole()方法,以接受安全标识符、角色字符串或WindowsBuiltInRole枚举的值。
示例:
/// <summary>
/// 输出Principal的额外信息
/// </summary>
/// <param name="identity"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private static WindowsPrincipal ShowPrincipal(WindowsIdentity identity)
{
Console.WriteLine("Show principal information");
WindowsPrincipal principal = new WindowsPrincipal(identity);
if(principal==null)
{
Console.WriteLine("not a windows Principal");
return null;
}
//当前用户是否属于内置的角色User
Console.WriteLine("Users?"+principal.IsInRole(WindowsBuiltInRole.User));
//当前用户是否属于内置的角色Administrator
Console.WriteLine("Administrators?"
+principal.IsInRole(WindowsBuiltInRole.Administrator));
Console.WriteLine();
return principal;
}
//调用代码
WindowsIdentity identity = ShowIdentityInformation();
WindowsPrincipal principal = ShowPrincipal(identity);
使用WindowsPrincipal可以很容易的访问当前用户及其角色的详细信息,可以利用这些信息决定允许或者拒绝用户执行某些操作。一般在用于Windows客户端程序时,非常有用,例如可以限定只有管理员或指定的Windows用户组才能运行该程序。
使用声明
声明(Claim)提供了比角色更大的灵活性。AD(Active Directory)或其他账户身份验证服务,建立了关于用户的声明。例如:用户名的声明、用户所属的组的声明、或关于年龄的声明等。
示例:
/// <summary>
/// 写入声明信息
/// </summary>
/// <param name="claims"></param>
private static void ShowClaims(IEnumerable<Claim> claims)
{
Console.WriteLine("Claims");
foreach(var claim in claims)
{
//获取声明的主题
Console.WriteLine("Subject:"+claim.Subject);
//获取声明的颁发者
Console.WriteLine("Issuer:"+claim.Issuer);
//获取声明的声明类型
Console.WriteLine("Type:"+claim.Type);
//获取声明的值类型
Console.WriteLine("Value type:"+claim.ValueType);
//获取声明的值
Console.WriteLine("Value:"+claim.Value);
//获取跟此声明关联的其他属性值
foreach (var prop in claim.Properties)
{
Console.WriteLine( $"\tProperty:{prop.Key} {prop.Value}");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
调用:
WindowsIdentity identity = ShowIdentityInformation();
WindowsPrincipal principal = ShowPrincipal(identity);
//添加声称
identity.AddClaim(new Claim("Age", "24"));
ShowClaims(principal.Claims);
//使用HasClaim测试声明是否可用
identity.HasClaim(c => c.Type == ClaimTypes.Name);
//检索特定的声明
var gropuClaims = identity.FindAll(c => c.Type == ClaimTypes.GroupSid);
注意:声明类型可以是一个简单的字符串,例如前面使用的“Age”类型。
加密数据
对称加密:可以使用同一个密钥进行加密和解密。
不对称加密:使用不同的密钥(公钥/私钥)进行加密和解密。
公钥/私钥总是成对创建。公钥可以由任何人使用,它甚至可以放在Web站点上,但私钥必须安全的加锁。
使用对称密钥的加密和解密算法比使用非对称密钥的算法快得多。对称密钥的问题是密钥必须以安全的方式互换。在网络通信中,一种方式是先使用非对称的密钥进行密钥互换,再使用对称密钥加密通过网络发送的数据。
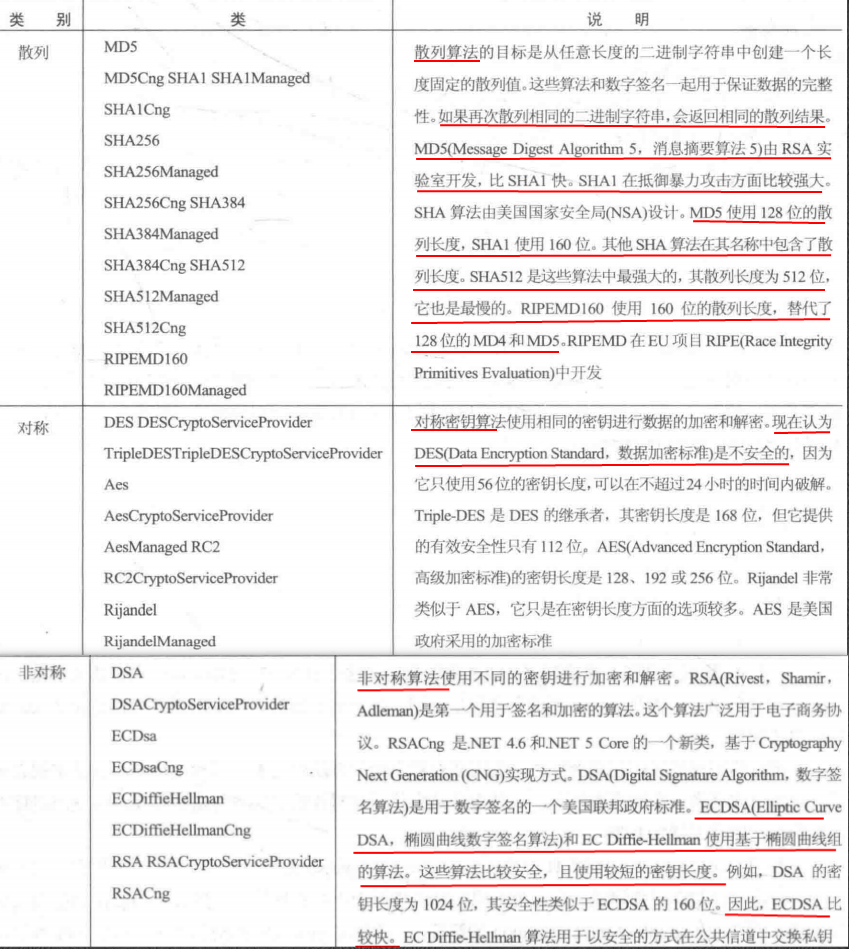
在.NET Framework中,可以使用System.Security.Cryptography命名空间中的类来加密。它实现了几个对称算法和非对称算法。
图片中的表格列出了System.Security.Cryptography命名空间中的加密类及其功能:
表格中不同的算法类用于不同的目的,例如有些类以Cng(Cryptography Next Generation的简称)作为前缀或后缀,CNG是本机Crypto API的更新版本,这个API可以使用基于提供程序的模型,编写独立于算法的程序。
没有Cng、Managed或CryptoServiceProvider后缀的类是抽象基类,如MD5。
Managed后缀表示这个算法用托管代码实现,其他类可能封装了本地Windows API调用。
CryptoServiceProvider后缀用于实现了抽象基类的类。
Cng后缀用于利用新Cryptography CNG API的类。
使用ESDSA算法创建和验证签名
ECDSA比较安全,且使用较短的密钥长度,与DSA相比,ECDSA更快更安全。
下面的示例中,首先创建一个签名,并使用私钥加密,然后使用公钥访问。
using System;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Text;
namespace Safety_Sample
{
/*
* 使用ECDSA算法进行签名。Alice创建一个签名,它用Alice的私钥加密,可以使用Alice的公钥访问
*/
internal class SigningDemo
{
private CngKey _aliceKeySignature;
private byte[] _alicePubKeyBlob;
public void Run()
{
//创建Alice的密钥
InitAliceKeys();
byte[] aliceData = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("Alice");
//给字符串签名
byte[] aliceSignature = CreateSignature(aliceData, _aliceKeySignature);
//将加密的签名写入控制台
Console.WriteLine("Alice created signature:" + Convert.ToBase64String(aliceSignature));
//使用公钥验证该签名是否真的来自于Alice
if (VerifySignature(aliceData, aliceSignature, _alicePubKeyBlob))
{
Console.WriteLine("Alice signature verified successfully");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 验证签名是否正确,使用公钥检查签名
/// </summary>
/// <param name="data"></param>
/// <param name="signature">签名后的数据</param>
/// <param name="pubKey">公钥字节数组</param>
/// <returns></returns>
private bool VerifySignature(byte[] data, byte[] signature, byte[] pubKey)
{
bool retValue = false;
//导入CngKey对象
using(CngKey key = CngKey.Import(pubKey, CngKeyBlobFormat.GenericPublicBlob))
using (var signingAlg=new ECDsaCng(key))
{
#if NET46
retValue = signingAlg.VerifyData(data, signature);
signingAlg.Clear();
#else
//验证签名
retValue = signingAlg.VerifyData(data, signature, HashAlgorithmName.SHA512);
#endif
}
return retValue;
}
/// <summary>
/// 创建签名
/// </summary>
/// <param name="data"></param>
/// <param name="key"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private byte[] CreateSignature(byte[] data, CngKey key)
{
byte[] signature;
//使用ECDsaCng创建签名,ECDsaCng的构造函数接收包含公钥和私钥的CngKey类对象
using (ECDsaCng signingAlg = new ECDsaCng(key))
{
#if NET46
signature = signingAlg.SignData(data);
signingAlg.Clear();
#else
//对数据进行签名(加密)
signature = signingAlg.SignData(data, HashAlgorithmName.SHA512);
#endif
}
return signature;
}
/// <summary>
/// 创建新的密钥对
/// </summary>
private void InitAliceKeys()
{
//创建密钥对,CngKey包含公钥和私钥数据
_aliceKeySignature = CngKey.Create(CngAlgorithm.ECDsaP521);
//导出密钥对中的公钥,后面将要使用它来验证签名
_alicePubKeyBlob = _aliceKeySignature.Export(CngKeyBlobFormat.GenericPublicBlob);
}
}
}
在上述代码中,千万不要使用Encoding类把加密的数据转换为字符串,因为Encoding类验证和转换Unicode不允许使用的无效值,因此把字符串转换回字节数组会得到另一个结果。
在创建密钥对时,除了使用CngKey.Create()方法外,还可以使用CngKey.Open()方法打开存储在密钥存储器中的已有密钥。
使用EC Diffie-Hellman算法实现安全的数据交换
下面的示例相对复杂,使用EC Diffie-Hellman算法交换一个对称密钥,以进行安全的传输。
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Safety_Sample
{
/*
* 使用EC Diffie-Hellman算法交换一个对称密钥,以进行安全的传输
*/
internal class SecureTransferDemo
{
private CngKey _aliceKey;
private CngKey _bobKey;
private byte[] _alicePubKeyBlob;
private byte[] _bobPubKeyBlob;
public static void Run()
{
SecureTransferDemo std = new SecureTransferDemo();
std.RunAsync().Wait();
}
public async Task RunAsync()
{
try
{
CreateKeys();
byte[] encrytpedData = await AliceSendsDataAsync("This is a secret message for Bob");
await BobReceivesDataAsync(encrytpedData);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 使用EC Diffie-Hellman512 算法创建密钥对
/// </summary>
private void CreateKeys()
{
_aliceKey = CngKey.Create(CngAlgorithm.ECDiffieHellmanP521);
_bobKey = CngKey.Create(CngAlgorithm.ECDiffieHellmanP521);
_alicePubKeyBlob = _aliceKey.Export(CngKeyBlobFormat.EccPublicBlob);
_bobPubKeyBlob = _bobKey.Export(CngKeyBlobFormat.EccPublicBlob);
}
/// <summary>
/// 加密
/// </summary>
/// <param name="message"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private async Task<byte[]> AliceSendsDataAsync(string message)
{
Console.WriteLine("Alice sends message:" + message);
byte[] rawData = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(message);
byte[] encryptedData = null;
//创建ECDiffieHellmanCng对象,并使用Alice的密钥对初始化它
using (ECDiffieHellmanCng aliceAlgorithm = new ECDiffieHellmanCng(_aliceKey))
using (CngKey bobPubKey = CngKey.Import(_bobPubKeyBlob, CngKeyBlobFormat.EccPublicBlob))
{
//使用Alice的密钥对和Bob的公钥创建一个对称密钥,返回的对称密钥使用对称算法AES加密数据
byte[] symmKey = aliceAlgorithm.DeriveKeyMaterial(bobPubKey);
Console.WriteLine("Alice creates thsi symmetric key with Bobs public key Information:" + Convert.ToBase64String(symmKey));
//
using (AesCryptoServiceProvider aes = new AesCryptoServiceProvider())
{
aes.Key = symmKey;
aes.GenerateIV();
using (ICryptoTransform encryptor = aes.CreateEncryptor())
using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream())
{
using (CryptoStream cs = new CryptoStream(ms, encryptor, CryptoStreamMode.Write))
{
await ms.WriteAsync(aes.IV, 0, aes.IV.Length);
cs.Write(rawData, 0, rawData.Length);
}
encryptedData = ms.ToArray();
}
//在访问内存流中的加密数据之前,必须关闭加密流,否则加密数据就会丢失最后的位
aes.Clear();
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Alice:message is encrypted:" + Convert.ToBase64String(encryptedData));
Console.WriteLine();
return encryptedData;
}
/// <summary>
/// 解密
/// </summary>
/// <param name="encrytpedData"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private async Task BobReceivesDataAsync(byte[] encrytpedData)
{
Console.WriteLine("Bob receives encrypted data");
byte[] rawData = null;
//读取未加密的初始化矢量
AesCryptoServiceProvider aes = new AesCryptoServiceProvider();
//BlockSize属性返回块的位数,除以8就可以计算出字节数。
int nBytes = aes.BlockSize / 8;
byte[] iv = new byte[nBytes];
for (int i = 0; i < iv.Length; i++)
{
iv[i] = encrytpedData[i];
}
//实例化一个ECDiffieHellmanCng对象,使用Alice的公钥,从DeriveKeyMaterial()方法中返回对称密钥
using (ECDiffieHellmanCng bobAlgorithm = new ECDiffieHellmanCng(_bobKey))
using (CngKey alicePubKey = CngKey.Import(_alicePubKeyBlob, CngKeyBlobFormat.EccPublicBlob))
{
byte[] symmKey = bobAlgorithm.DeriveKeyMaterial(alicePubKey);
Console.WriteLine("Bob creates this symmetric key with Alices public key information:" + Convert.ToBase64String(symmKey));
aes.Key = symmKey;
aes.IV = iv;
using (ICryptoTransform decryptor = aes.CreateDecryptor())
using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream())
{
using (CryptoStream cs = new CryptoStream(ms, decryptor, CryptoStreamMode.Write))
{
await cs.WriteAsync(encrytpedData, nBytes, encrytpedData.Length - nBytes);
}
rawData = ms.ToArray();
Console.WriteLine("Bob decrypts mesage to:" + Encoding.UTF8.GetString(rawData));
}
aes.Clear();
}
}
}
}
关于该示例的详细说明,请参阅原书24.3.2章节。
使用RSA散列签名
RSA是一个广泛使用的非对称算法,在.NET中使用RSACng类。RSACng类基于CNG API,其用法类似于之前使用的ECDSACng类。
示例代码如下,在该示例中,Alice创建一个文档,散列它,以确保它不会改变,给它加上签名,保证是Alice生成了文档。Bob接收文件,并检查Alice的担保,以确保文件没有被篡改。
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Text;
namespace Safety_Sample
{
/*
* 该示例中,Alice创建一个文档,散列它,以确保它不会改变,给它加上签名,保证是Alice生成了文档。Bob接收文件,并检查Alice的担保,以确保文件没有被篡改
*/
internal class RSADemo
{
private CngKey _aliceKey;
private byte[] _alicePubKeyBlob;
public void Run()
{
//创建一个文档、散列码、签名
AliceTasks(out byte[] document, out byte[] hash, out byte[] signature);
BobTasks(document, hash, signature);
}
private void AliceTasks(out byte[] data, out byte[] hash, out byte[] signature)
{
//创建Alice所需的密钥
InitAliceKeys();
//将消息转换为一个字节数组
data = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("Best greetings from Alice");
//散列字节数组
hash = HashDocument(data);
//添加一个签名
signature = AddSignatureToHash(hash, _aliceKey);
}
/// <summary>
/// 使用RSA算法创建密钥
/// </summary>
private void InitAliceKeys()
{
//创建公钥和私钥
_aliceKey = CngKey.Create(CngAlgorithm.Rsa);
//公钥只提供给Bob,所以公钥使用Export方法提取
_alicePubKeyBlob = _aliceKey.Export(CngKeyBlobFormat.GenericPublicBlob);
}
/// <summary>
/// 创建散列码
/// </summary>
/// <param name="data"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private byte[] HashDocument(byte[] data)
{
/*
* 散列码使用一个散列算法SHA384类创建
* 不管文档存在多久,散列码的长度总是相同
* 再次为相同的文档创建散列码,会得到相同的散列码
* Bob需要在文档上使用相同的算法,如果返回相同的散列码,就说明文档没有改变
*/
using (SHA384 hashAlg = SHA384.Create())
{
return hashAlg.ComputeHash(data);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 添加签名
/// </summary>
/// <param name="hash"></param>
/// <param name="key"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private byte[] AddSignatureToHash(byte[] hash, CngKey key)
{
/*
* 添加签名,可以保证文档来自Alice
*
*/
//使用RSACng给散列签名
using (RSACng signingAlg = new RSACng(key))
{
//给散列签名时,SignHash方法需要了解散列算法,此处基于HashAlgorithmName.SHA384算法传入
byte[] signed = signingAlg.SignHash(hash, HashAlgorithmName.SHA384, RSASignaturePadding.Pss);
return signed;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 接收文档数据、散列码和签名
/// </summary>
/// <param name="data"></param>
/// <param name="hash"></param>
/// <param name="signature"></param>
private void BobTasks(byte[] data, byte[] hash, byte[] signature)
{
//导入Alice的公钥
CngKey aliceKey = CngKey.Import(_alicePubKeyBlob, CngKeyBlobFormat.GenericPublicBlob);
//验证签名是否有效
if (!IsSignatureValid(hash, signature, aliceKey))
{
Console.WriteLine("signature not valid");
return;
}
//验证文档是否不变
if (!IsDocumentUnchanged(hash, data))
{
Console.WriteLine("doucment was changed");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("signature valid,doucment unchanged");
Console.WriteLine("document from Alice:" + Encoding.UTF8.GetString(data));
}
/// <summary>
/// 验证签名是否有效
/// </summary>
/// <param name="hash"></param>
/// <param name="signature"></param>
/// <param name="key"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private bool IsSignatureValid(byte[] hash, byte[] signature, CngKey key)
{
using (RSACng signingAlg = new RSACng(key))
{
return signingAlg.VerifyHash(hash, signature, HashAlgorithmName.SHA384, RSASignaturePadding.Pss);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 验证文档数据是否发生了改变
/// </summary>
/// <param name="hash"></param>
/// <param name="data"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private bool IsDocumentUnchanged(byte[] hash, byte[] data)
{
byte[] newHash = HashDocument(data);
//验证散列码是否相同
return newHash.SequenceEqual(hash);
}
}
}
实现数据的保护(略)
最新的基于Microsoft.AspNetCore.DataProtection命名空间下的类实现,可以用于Web 数据的保护。由于版本更新问题,原书中的示例已不能使用。具体见原书24.3.4章节。
文件资源的访问控制
在操作系统中,资源(如文件和注册表键,以及命名管道的句柄)都使用访问控制列表(ACL)来保护。
资源有一个关联的安全描述符,安全描述符包含了资源拥有者的信息,并引用了两个访问控制列表:自由访问控制列表(
Discretionary Access Control List,DACL)和系统访问控制列表(System Access Control List,SACL)。DACL用来确定谁有访问权;SACL用来确定安全事件日志的审核规则。ACL包含一个访问控制项(
Access Control Entries,ACE)列表。ACE包含类型、安全标识符和权限。在DACL中,ACE的类型可以运行访问或拒绝访问。
读取和修改访问控制的类在System.Security.AccessControl命名空间下。
下面的示例演示了如何读取和设置文件的控制权限:
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Security.AccessControl;
using System.Security.Principal;
namespace Safety_Sample
{
internal class SecurityDemo
{
/*
* 如何从文件中读取访问控制列表(访问权限)
*/
public static void Run(string[] args)
{
string filename = null;
if (args.Length == 0)
{
return;
}
filename = args[0];
using (FileStream stream = File.Open(filename, FileMode.Open))
{
//获取文件的访问控制列表(ACL)
FileSecurity securityDescriptor = stream.GetAccessControl();
//返回DACL
/*
* GetAccessRules方法可以确定是否应使用继承的访问规则,
* 最后一个参数定义了应返回的安全标识符的类型,可能的类型有NTAccount和SecurityIdentifier,
* 这两个类都表示用户或组
* NTAccount类按名称查找安全对象
* SecurityIdentifier类按唯一的安全标识符查找安全对象
*/
AuthorizationRuleCollection rules = securityDescriptor.GetAccessRules(true, true, typeof(NTAccount));
//返回SACL
//securityDescriptor.GetAuditRules();
//AuthorizationRule对象是ACE的.NET表示
foreach (AuthorizationRule rule in rules)
{
FileSystemAccessRule fileRule = rule as FileSystemAccessRule;
Console.WriteLine("Access type:" + fileRule.AccessControlType);
Console.WriteLine("Rights:" + fileRule.FileSystemRights);
Console.WriteLine("Identity:" + fileRule.IdentityReference.Value);
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 设置访问权限
/// </summary>
/// <param name="filename"></param>
private void WriteAcl(string filename)
{
NTAccount salesIdentity = new NTAccount("Sales");
NTAccount developersIdentity = new NTAccount("Developers");
NTAccount everyOneIdentity = new NTAccount("Everyone");
//拒绝Sales组写入访问权限
FileSystemAccessRule salesAce = new FileSystemAccessRule(salesIdentity, FileSystemRights.Write, AccessControlType.Deny);
//给Everyone组提供了读取访问权限
FileSystemAccessRule everyoneAce = new FileSystemAccessRule(everyOneIdentity, FileSystemRights.Read, AccessControlType.Allow);
//给Developers组提供了全部控制权限
FileSystemAccessRule developersAce = new FileSystemAccessRule(developersIdentity, FileSystemRights.FullControl, AccessControlType.Allow);
FileSecurity securityDescriptor = new FileSecurity();
securityDescriptor.SetAccessRule(everyoneAce);
securityDescriptor.SetAccessRule(developersAce);
securityDescriptor.SetAccessRule(salesAce);
File.SetAccessControl(filename, securityDescriptor);
}
}
}
注:可以打开文件的属性窗口,选择“安全”选项卡进行验证。
使用数字证书对程序集进行签名(略)
一般用于C/S客户端程序。具体参见原书24.5章节。
参考资源
- 《C#高级编程(第10版)》
本文后续会随着知识的积累不断补充和更新,内容如有错误,欢迎指正。
最后一次更新时间 :2018-09-04
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章