前言
之前因为很喜欢 ReLIFE 那部动画,所以从百度云上下载了 500MB 左右的漫画全集(此时应该喊 “完结撒花” 吗(笑)),打算在手机上看。可是直接用图库之类的软件看起来会很累,所以花了点时间做了个应用(程序员的唯一好处): ViewPager 嵌套 ListView,横向为每一话的漫画,纵向是该话的内容。
初步跑起来是可以看,但纵向滑动的时候很卡。经查发现是解码 jpg 为 bitmap 这个地方很慢,所以看来只能异步加载。试了一下,虽然流畅一点,可是列表在 “飘” 的时候,会看到很多默认图片,之后才显示出来漫画的图片。如果一次性全部解码到内存呢?我曾这么想过,但立刻被证实是愚蠢的想法,漫画的一话内容,可能会有几十张图片,张张大图,全部解码,内存必然会爆掉。幸亏做 rec 的时候,发现 bitmap 可以从 biyebuffer 中复制像素数据,也可以将像素数据复制到 bytebuffer 中, 所以试过 “愚蠢方案” 之后,我打算利用这个特性来做一个“基于虚拟内存的图片缓存方案”。
ByteBuffer
顾名思义,这是一个 “缓存” 之类的东西,但是我更愿意将它理解为 java 语言的“高级指针”。
平时我们也会经常使用缓存,比如一个 byte 数组。而 ByteBuffer 除了包含一块元素为 byte 类型的存储区域以外,还包含了一个指向这块区域某处的 position、这块区域结束位置的 limit,并且一个 bytebuffer 还能“生出(duplicate)”另一个与其共享存储区域,但 position 和 limit 完全独立的 bytebuffer 出来。
除此之外,bytebuffer 具备一些好玩的功能,比如虽然我们以一个 byte 数组来创建一个 bytebuffer,但却可以将其转为一个 intbuffer、charbuffer 之类,元素类型非 byte 的缓存对象,之前我对 musical.ly 的安卓半年崩溃日志做去重的时候就大量使用了 bytebuffer 和 charbuffer 互转的功能。
不过最厉害的应该是 java 在 FileChannel 类中提供了将磁盘文件的一个区域 map 到内存中作为一个 bytebuffer 的功能,而本文要介绍的“方案”就是基于这个功能来做。
方案一:单文件缓存方案
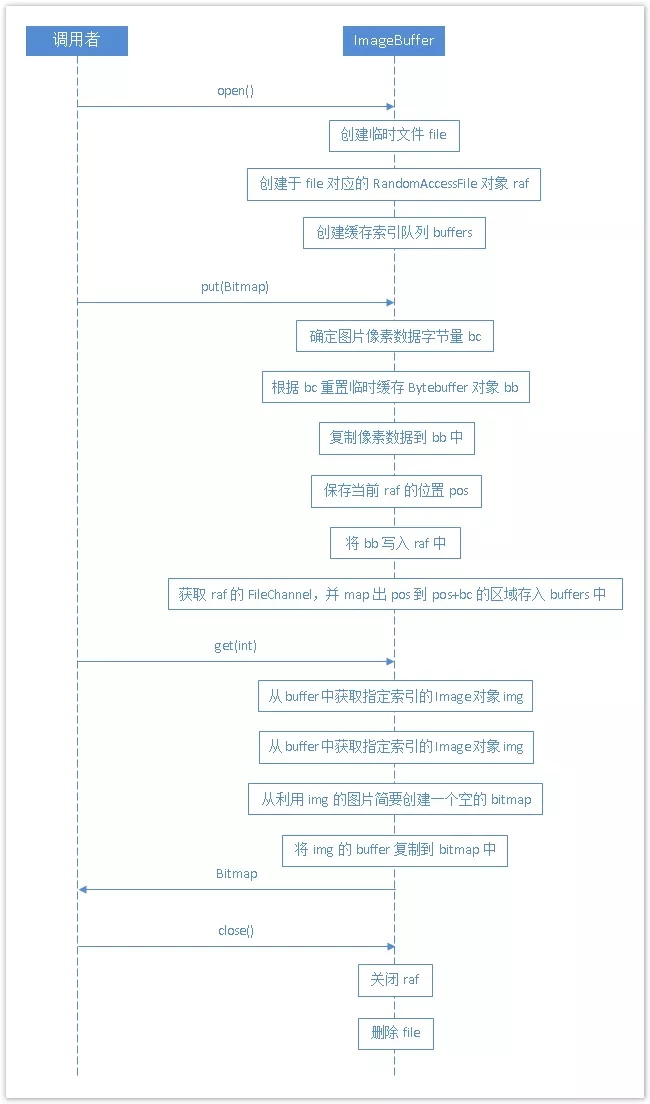
流程图
我将这个工具叫做 “ImageBuffer” 。它主要包含 open、put、get 和 close 几个主要方法,下面这几个方法的实现流程图:
imagebuffer 只是提供了 reset 的功能,但没有提供 remove,而且 reset 也只是将索引队列清空、将 raf 的位置归零而已。之所以不做 remove,是因为从流程图可以看出,像素数据都缓存在文件里面,remove 掉一个缓存元素,除了从索引中这个对象外,实际上对缓存文件没有任何影响,所以名不副实。
另一方面,imagebuffer 可以说是没有容量限制的,而且由于少了解码的操作,还原图片的速度甚至比所谓“多级缓存”的文件缓存要还要快——我就是为了比它快才做 imagebuffer。
从更长远来说,imangebuffer 可以不仅缓存在一个文件里面,而是每一个图片都缓存在一个单独的文件,并在其关闭前一直保留隐射,这样子只是在 put 时稍慢(因为要打开文件),但 get 不受影响,而且删除功能还可以实际实现。进一步,如果缓存文件可以不删除——或者采用 LRU 的方式删除长久不使用的,则只要保存索引,可以作为替代现在 mobtools 中多级缓存中的文件缓存方案。
当然,imagebuffer 有明显的缺点,因为缓存在文件中的是 rgb 的像素数据,所以缓存时文件会比 jpg 的大很多,很浪费磁盘空间。
源码
import android.graphics.Bitmap;import android.graphics.Bitmap.Config;
import java.io.File;import java.io.RandomAccessFile;import java.nio.ByteBuffer;import java.nio.channels.FileChannel.MapMode;import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ImageBuffer { private File file; private RandomAccessFile raf; private int position; private ArrayList<Image> buffers; private byte[] buffer;
public void open() throws Throwable {
open(null);
}
public synchronized void open(File file) throws Throwable { if (this.file == null) { if (file == null) {
file = File.createTempFile("ib_", "");
} if (!file.getParentFile().exists()) {
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
} this.file = file;
raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw");
position = 0;
buffers = new ArrayList<Image>();
}
}
public synchronized void reset() throws Throwable {
raf.seek(0);
position = 0;
buffers = new ArrayList<Image>();
}
public synchronized void close() throws Throwable { if (file != null) {
raf.close();
file.delete();
file = null;
raf = null;
buffer = null;
position = 0;
buffers = null;
}
}
public synchronized boolean put(Bitmap bm) throws Throwable { if (file != null) { int bc = bm.getByteCount(); if (buffer == null || buffer.length < bc) {
buffer = new byte[bc];
}
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.wrap(buffer);
bm.copyPixelsToBuffer(bb); return put(buffer, 0, bc, bm.getWidth(), bm.getHeight(), bm.getConfig());
} return false;
}
public synchronized boolean put(byte[] pixels, int offset, int len, int width, int height, Config config)
throws Throwable { if (file != null) {
raf.write(pixels, offset, len);
ByteBuffer bb = raf.getChannel().map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, position, len);
position += len;
Image image = new Image();
image.config = config;
image.width = width;
image.height = height;
image.buffer = bb; return buffers.add(image);
} return false;
}
public synchronized Bitmap get(int index) throws Throwable { if (buffers == null || index < 0 || buffers.size() < index) { return null;
}
Image image = buffers.get(index);
image.buffer.position(0);
Bitmap bm = Bitmap.createBitmap(image.width, image.height, image.config);
bm.copyPixelsFromBuffer(image.buffer); return bm;
}
public synchronized int size() { return buffers == null ? 0 : buffers.size();
}
private class Image { private int width; private int height; private ByteBuffer buffer; private Config config;
}
}方案二:多文件缓存方案
前段时间做了方案一,但是对于它不能删除失效缓存的特性很是不舒服,所以做了下面基于文件夹(多文件)的方案:
源码
import android.graphics.Bitmap;import android.graphics.Bitmap.Config;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;import java.io.File;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.RandomAccessFile;import java.nio.ByteBuffer;import java.nio.channels.FileChannel.MapMode;import java.util.HashMap;
public class ImageBuffer { private File folder; private byte[] buffer; private HashMap<String, Image> buffers;
public ImageBuffer(String folder) { this(new File(folder));
}
public ImageBuffer(File folder) { this.folder = folder;
buffers = new HashMap<String, Image>();
}
public void put(String key, Bitmap bm) throws Throwable { int bc = bm.getByteCount();
ByteBuffer bb; synchronized (this) { if (buffer == null || buffer.length < bc) {
buffer = new byte[bc];
}
bb = ByteBuffer.wrap(buffer);
}
bm.copyPixelsToBuffer(bb);
put(key, buffer, 0, bc, bm.getWidth(), bm.getHeight(), bm.getConfig());
}
public void put(String key, byte[] pixels, int offset, int len, int width, int height,
Config config) throws Throwable {
saveImage(key, pixels, offset, len, width, height, config);
openImage(key);
}
private void openImage(String name) throws Throwable {
File file = new File(folder, name); synchronized (this) { if (!file.exists()) { return;
}
}
int width = 0; int height = 0;
Config config = null;
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r");
ByteBuffer bb = raf.getChannel().map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, file.length()); int id = bb.getInt(); while (id != -1) { switch (id) { case 0: {
width = bb.getInt();
} break; case 1: {
height = bb.getInt();
} break; case 2: { switch(bb.getInt()) { case 1: config = Config.ALPHA_8; break; case 3: config = Config.RGB_565; break; case 4: config = Config.ARGB_4444; break; case 5: config = Config.ARGB_8888; break;
}
} break;
}
id = bb.getInt();
}
raf.seek(0);
Image image = new Image();
image.file = file;
image.raf = raf;
image.buffer = raf.getChannel().map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, bb.position(), bb.remaining());
image.width = width;
image.height = height;
image.config = config;
synchronized (this) {
buffers.put(name, image);
}
}
private void saveImage(String key, byte[] pixels, int offset, int len, int width, int height, Config config)
throws Throwable {
Image image; synchronized (this) {
image = buffers.remove(key);
} if (image != null) {
closeImage(image, true);
}
File file = new File(folder, key); synchronized (this) { if (!folder.exists()) {
folder.mkdirs();
}
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(fos);
dos.writeInt(0);
dos.writeInt(width);
dos.writeInt(1);
dos.writeInt(height);
dos.writeInt(2); switch(config) { case ALPHA_8: dos.writeInt(1); break; case RGB_565: dos.writeInt(3); break; case ARGB_4444: dos.writeInt(4); break; case ARGB_8888: dos.writeInt(5); break;
}
dos.writeInt(-1);
dos.write(pixels, offset, len);
dos.flush();
dos.close();
}
private void closeImage(Image image, boolean delete) throws Throwable { if (image != null) {
image.raf.close(); if (delete) {
image.file.delete();
}
}
}
public Bitmap get(String key) throws Throwable {
Image image; synchronized(this) {
image = buffers.get(key);
} if (image == null) {
openImage(key); synchronized(this) {
image = buffers.get(key);
} if (image == null) { return null;
}
}
image.buffer.position(0);
Bitmap bm = Bitmap.createBitmap(image.width, image.height, image.config);
bm.copyPixelsFromBuffer(image.buffer); return bm;
}
public void remove(String key) throws Throwable {
remove(key, false);
}
public void remove(String key, boolean delete) throws Throwable {
Image image; synchronized (this) {
image = buffers.remove(key);
}
closeImage(image, delete);
}
public void clear() throws Throwable {
clear(false);
}
public void clear(boolean delete) throws Throwable { synchronized(this) { for (Image image : buffers.values()) {
closeImage(image, delete);
}
buffers.clear();
}
}
public int size() { synchronized(this) { return buffers.size();
}
}
private class Image { private File file; private RandomAccessFile raf; private ByteBuffer buffer; // id = -1
private int width; // id = 0
private int height; // id = 1
private Config config; // id = 2
}
}补充说明
1、分文件存储图片,每一个图片一个文件,故删除和清理有了实际意义,而打开、关闭和重置都没有意义了;
2、图片描述跟随缓存,因此每一个缓存文件都分头部和数据体;
3、删除和清理可以选择逻辑删除和物理删除,逻辑删除只会在内存中删除索引 Image 对象,物理删除就是删除文件了;
4、由于图片独立存储,故同步锁的粒度可以降低,某种程度上提高效率(吧……)。
文/勋勋
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章