spring 的 IOC 容器是基于 BeanFactory 的。在 BeanFactory 中有一个子类 HierarchicalBeanFactory,这个接口定义了两个方法:
- getParentBeanFactory
- containsLocalBean(String name)
从字面上也可以理解,一个是获取父工厂(父容器)的方法,一个是查看当前 Bean 在本地工厂中是否存在。
这里我们主要是看下为什么要有 getParentBeanFactory 这个方法存在以及它的用途。
这里需要提出一个概念:spring 的双亲容器。其实也就是父子容器,子容器可以访问父容器中的 bean,父容器不能访问子容器中的 bean,同时子容器之间相互不能访问。为什么要存在父子容器呢?
我们设想一下,我们自己写的程序一般都需要依赖各种各样的第三方的类库或者是插件,这些类库或者插件中的类在加载的时候,如果跟我们自己写的程序都使用同一个容器进行管理的话,可能会存在一些问题:
- 容器中的 bean 太多了
- 如果我们依赖的类库或者插件与我们自己写的程序中如果存在重名的类的话,会只加载其中一个,这样就会存在冲突问题,毕竟只是重名,不是同一个类
- 同时我们依赖的类库之间如果存在重名,也会导致某些类库加载失败的问题。
如果我们自己的程序与依赖的类库或者插件以及依赖的类库或者插件之间都是使用不同的容器进行加载的话,这样大家就互不干扰呢。
那为什么要定义成父子容器,而不是定义成平辈的容器呢?
我们设想下,一般我们自己的程序都是父容器,第三方的类库是子容器。子容器是可以访问父容器的,这样子容器就可以给父容器提供了扩展自己的可能。如果大家都是平级的,互相不能访问,这样就无从扩展。第三方类库或者插件之间应该要相互独立,不能相互访问。
那为什么我们自己的程序都是父容器,第三方的类库是子容器?
设想下,如果我们自己的程序是子容器的话,那么我们就能获取到父容器中的 bean,这样我们就能改变其中的一些规则,这对第三方的类库来说是不可取的,会严重影响其允许的稳定性。
上面讲了这么多,下面我们自己来写一个小程序让大家能更好的理解这个问题。
我会从 BeanFactory 的角度跟 ApplicationContext 的角度分别来举例。
首先说明下 BeanFactory 跟 ApplicationContext 的区别。 BeanFactory 是 spring 容器的基础,ApplicationContext 在其基础上做了一些扩展,更加的适用于 web 项目。
1、BeanFactory
测试类
package com.test.springtest;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class App implements Serializable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
XmlBeanFactory parentBeanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("application.xml"));
parentBeanFactory.getBean("message");
PluginLoaderFactory pluginLoaderFactory = parentBeanFactory.getBean("pluginLoader",PluginLoaderFactory.class);
XmlBeanFactory childBeanFactory = pluginLoaderFactory.getChildBeanFactory();
Object testA = childBeanFactory.getBean("testA");
Object message = childBeanFactory.getBean("message");
}
}
这里用到了 XmlBeanFactory,其是 BeanFactory 的子类,从 xml 文件中加载 bean 的定义信息。这里是从 application.xml 中读取信息。
PluginLoaderFactory 这个是用来启用子容器的
package com.test.springtest;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
public class PluginLoaderFactory implements BeanFactoryAware {
private BeanFactory parentBeanFactory;
private XmlBeanFactory childBeanFactory;
public void load() {
childBeanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("plugin.xml"));
childBeanFactory.setParentBeanFactory(parentBeanFactory);
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
this.parentBeanFactory = beanFactory;
}
public XmlBeanFactory getChildBeanFactory() {
return childBeanFactory;
}
public void setChildBeanFactory(XmlBeanFactory childBeanFactory) {
this.childBeanFactory = childBeanFactory;
}
}
子容器是从 plugin.xml 中读取信息,与父容器不一样。子容器指定了父容器,这样就可以获取到父容器中的 bean 了。TestA 类信息:
package com.test.springtest;
public class TestA {
private String name;
}
MessageServiceImpl 类信息
package com.test.springtest;
import com.test.circuleDepend.TestA;
public class MessageServiceImpl {
private String text;
}
application.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
default-autowire="byName">
<bean id="message" class="com.test.springtest.MessageServiceImpl">
<property name="text" value="asdfsf"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="pluginLoader" class="com.test.springtest.PluginLoaderFactory" init-method="load"></bean>
</beans>
plugin.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
default-autowire="byName">
<bean id="testA" class="com.test.springtest.TestA">
</bean>
</beans>
通过 App 这个测试类,大家可以看到,子容器是能获取到父容器中定义的 message 这个 bean 的信息的,同时也能获取到自己定义的 testA 的信息。而父容器,也就是 parentBeanFactory 是获取不到子容器定义的 testA 的信息的。这个大家可以自行测试。
这里定义的 TestA 和 MessageServiceImpl 都比较简单,大家可以自行增加一些信息进行测试。
那子容器是如何获取到父容器中定义的 bean 呢?我们通过 childBeanFactory.getBean("message"); 进入 spring 中看看。
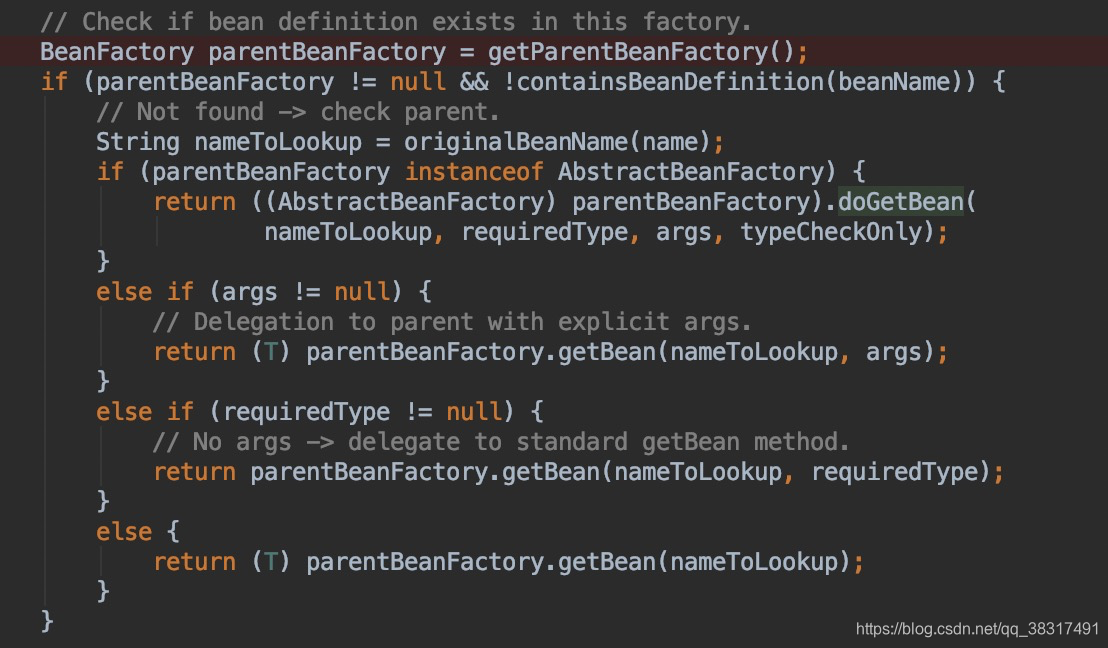
在 AbstractBeanFactory 中的 doGetBean 中我们会看到:
这里就是获取父容器,然后通过父容器去获取 bean 信息。其还是调用 doGetBean 方法获取类的信息。
2、ApplicationContext
测试类:
package com.test.springtest;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class App implements Serializable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext parentcontext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:application.xml");
MessageService messageService = parentcontext.getBean(MessageService.class);
PluginLoader pluginLoader = parentcontext.getBean("pluginLoader",PluginLoader.class);
ConfigurableApplicationContext child = pluginLoader.getChild();
Object testA = child.getBean("testA");
Object message = child.getBean("message");
}
}
PluginLoader :
package com.test.springtest;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class PluginLoader implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext parentApplicationContext;
private ConfigurableApplicationContext childApplicationContext;
public void load() {
childApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:plugin.xml");
childApplicationContext.setParent(parentApplicationContext);
childApplicationContext.refresh();
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.parentApplicationContext = applicationContext;
}
public ConfigurableApplicationContext getChild() {
return childApplicationContext;
}
}
application.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
default-autowire="byName">
<bean id="message" class="com.test.springtest.MessageServiceImpl">
<property name="text" value="asdfsf"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="pluginLoader" class="com.test.springtest.PluginLoader" init-method="load"></bean>
plugin.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
default-autowire="byName">
<bean id="testA" class="com.test.springtest.TestA">
</bean>
</beans>
大家可以通过 App 这个测试类自行测试下。
以上是个人的一些感悟,希望对您有帮助。
共同学习,写下你的评论
暂无评论
作者其他优质文章