课程名称:Node.js工程师养成计划
课程章节: 第九章
课程讲师:北瑶
课程内容
Egg 的插件机制有很高的可扩展性,一个插件只做一件事
$ mkdir egg-example && cd egg-example $ npm init egg --type=simple $ npm i $ npm run dev $ open http://localhost:7001
以上是eggjs 得安装方法
他的写法根mvc模式有点相似
'use strict';
const { Controller } = require('egg');
class HomeController extends Controller {
async index() {
// const { ctx } = this;
// ctx.body = 'hi, egg';
var serviceData = this.service.user.getUserList()
this.ctx.body = serviceData
}
}
module.exports = HomeController配置路由映射:
// app/router.js
'use strict';
/**
* @param {Egg.Application} app - egg application
*/
module.exports = app => {
app.foo = 'app-foo'
const { router, controller } = app;
router.get('/', controller.home.index);
};// app/service/user.js
const Service = require('egg').Service
class UserService extends Service {
getUserList(){
return [
{id:0,username:'Monica'}
]
}
}
module.exports = UserService通过继承egg得service 返回了一个 getUserList()
在egg中使用插件得方式进行引用 mongoose
为什么要插件
我们在使用 Koa 中间件过程中发现了下面一些问题:
中间件加载其实是有先后顺序的,但是中间件自身却无法管理这种顺序,只能交给使用者。这样其实非常不友好,一旦顺序不对,结果可能有天壤之别。
中间件的定位是拦截用户请求,并在它前后做一些事情,例如:鉴权、安全检查、访问日志等等。但实际情况是,有些功能是和请求无关的,例如:定时任务、消息订阅、后台逻辑等等。
有些功能包含非常复杂的初始化逻辑,需要在应用启动的时候完成。这显然也不适合放到中间件中去实现。
综上所述,我们需要一套更加强大的机制,来管理、编排那些相对独立的业务逻辑。
egg-mongoose
$ npm i egg-mongoose --save
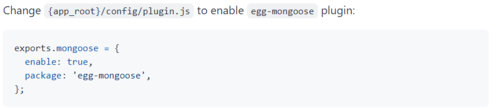
在egg.js中 可以通过声明 确认开启或者关闭
点击查看更多内容
为 TA 点赞
评论
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章
正在加载中
感谢您的支持,我会继续努力的~
扫码打赏,你说多少就多少
赞赏金额会直接到老师账户
支付方式
打开微信扫一扫,即可进行扫码打赏哦