①课程介绍
课程名称:Python3入门机器学习 经典算法与应用 入行人工智能
课程章节:7-5,7-6
主讲老师:liuyubobobo
内容导读
- 第一部分 高维数据向低维数据映射
- 第二部分 sklearn中的PCA
- 第三部分 代码展示
②课程详细
第一部分 高维数据向低维数据映射
在PCA求解出所有主成分中,就要对高维数据进行降维,也就是向低维映射。
导入函数
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
创建噪点的随机数据
X = np.empty((100, 2))
X[:,0] = np.random.uniform(0., 100., size=100)
X[:,1] = 0.75 * X[:,0] + 3. + np.random.normal(0, 10., size=100)
导入自己封装的函数,并创建模型
from nike.PCA import PCA
pca = PCA(n_components=2)
pca.fit(X)
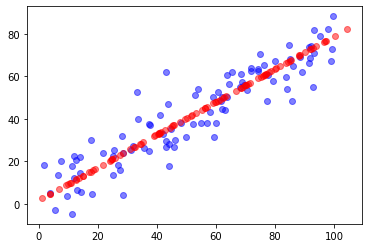
接下来我对数据进行降维并升维,来可视化展示一下数据向低维映射之后的降噪作用
X_reduction = pca.transform(X)
X_restore = pca.inverse_transform(X_reduction)
plt.scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], color='b', alpha=0.5)
plt.scatter(X_restore[:,0], X_restore[:,1], color='r', alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
可以看出数据在降维之后,在升维数据并没有太大噪点波动
第二部分 sklearn中的PCA
导入sklearn中封装的PCA,在机器学习包中的sklearn不是
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
创建对象,降到1维
pca = PCA(n_components=1)
训练模型,根据数据
pca.fit(X)
并展示找出的所有主成分,
pca.components_
#pca.components_
#array([[-0.79066966, -0.612243 ]])
转换数据-降维
X_reduction = pca.transform(X)
X_reduction.shape
#(100, 1)
转换数据-升维
X_restore = pca.inverse_transform(X_reduction)
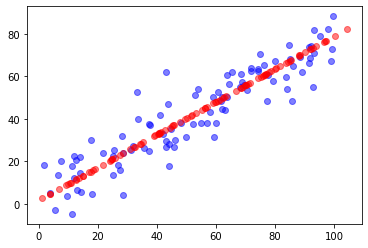
可视化展示sklearn中pca降维升维的过程
plt.scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], color='b', alpha=0.5)
plt.scatter(X_restore[:,0], X_restore[:,1], color='r', alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
第三部分 代码展示
import numpy as np
class PCA:
def __init__(self,n_components):
"""初始化PCA"""
assert n_components >= 1 ,'n_components must big to 1'
#存有多少个主成分,也就是多少维
self.n_components = n_components
#存主成分内容
self.components_ = None
def fit(self, X, eta=0.01, n_iters=1e4):
assert self.n_components <= X.shape[1],\
'n_components must smoil to X'
#运行前对x减去均值,来达到调整坐标系,并优化计算的目的
def demean(X):
return X - np.mean(X, axis=0)
def f(w, X):
return np.sum((X.dot(w) ** 2)) / len(X)
#求梯度
def df(w, X):
return X.T.dot(X.dot(w)) * 2. / len(X)
#对w进行处理使之成为单位向量,方便运算
def direction(w):
return w / np.linalg.norm(w)
#使用梯度上升法,求出X对应的第一主成分
def first_component(X, initial_w, eta, n_iters=1e4, epsilon=1e-8):
w = direction(initial_w)
cur_iter = 0
while cur_iter < n_iters:
gradient = df(w, X)
last_w = w
w = w + eta * gradient
w = direction(w)
if (abs(f(w, X) - f(last_w, X)) < epsilon):
break
cur_iter += 1
return w
X_pca = demean(X)
#主成分列表 ,KxN的空矩阵
self.components_ = np.empty(shape=(self.n_components,X.shape[1]))
# 循环n次,求出前n个主成分
for i in range(self.n_components):
# 下面要用梯度上升法,搜索对于当前XPca的第一主成分
# 初始生成w
initial_w = np.random.random(X_pca.shape[1])
w = first_component(X_pca, initial_w, eta, n_iters)
self.components_[i,:] = w
# 减去w轴方向上的主成分
X_pca = X_pca - X_pca.dot(w).reshape(-1, 1) * w
# 然后循环,基于新的x_pca进行求主成分,减去
return self
def transform(self,X):
"""给定的X,映射到个个主成分分量中"""
assert X.shape[1] == self.components_.shape[1],\
'X must equel to components_'
assert self.components_ is not None,\
'fit must first to transform'
return X.dot(self.components_.T)
def inverse_transform(self, X):
"""给定的X,反向映射回原来的特征空间"""
assert X.shape[1] == self.components_.shape[0], \
'X must equel to components_'
assert self.components_ is not None, \
'fit must first to transform'
return X.dot(self.components_)
def __repr__(self):
return "PCA(n_components=%d)" % self.n_components
③课程思考
- 到这里,再机器学习中使用搜索的方式,进行降维,降维的好处,降维的过程都进行了详细的解释,也讲解了sklearn中pca基本的运行方式
- 下一部分就将使用真实的的数据来看看pca真正的威力
④课程截图
点击查看更多内容
1人点赞
评论
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章
正在加载中
感谢您的支持,我会继续努力的~
扫码打赏,你说多少就多少
赞赏金额会直接到老师账户
支付方式
打开微信扫一扫,即可进行扫码打赏哦