反射机制概述
反射视为动态语言的关键,反射机制允许程序在执行期借助于Reflection API取得任何类的内部信息,并能直接操作认一对象的内部属性及方法。
加载完类之后在,在堆内存的方法区就产生了一个Class类型的对象(一个类只有一个Class对象),这个对象就包含了完整的类的结构信息。我们可以通过这个对象看到类的结构。这个对象就像一面镜子,透过这个镜子看到类的结构,所以,我们形象的称之为:反射。

调用运行时类的属性
Class clazz1 = Person.class;
System.out.prinln(clazz1);
2. 通过运行时类的对象,调用getClass()
Person p1 = new Person();
Class clazz2 = p1.getClass();
System.out.println(clazz2);
3. 调用Class的静态方法:forName(String classPath)
Class clazz3 = Class.forName("java.lang.String");
System.out.println(clazz3);
4. 使用类的加载器:ClassLoader
ClassLoader classLoader = ReflectionTest.class.getClassLoader();
Class clazz4 = classLoader.loadClass("com.atguigu.java.Person");
System.out.println(clazz4);
理解Class类并获取Class实例
在反射之前,在一个类的外部,不可以通过Person类的对象调用其内部私有结构。(如:name、showNation()以及私有的构造器)。
调用私有构造器
Constructor cons1 = clazzz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
cons1.setAccessible(true); // 私有的都需要执行这一步
Person p1 = (Person) cons1.newInstance("jerry");
System.out.println(p1);
2. 调用私有属性
Field name = clazz.getDeclaredField("name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(p1,"HanMeimei");
System.out.prinln(p1);
3. 调用私有方法
Method showNation = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("showNation",String.class) ;
showNamtion.setAccessible(true);
showNation.invoke(p1,"中国"); // 执行私有方法
String nation = (String) showNation.invoke(p1,”中国"); //
System.out.prinln(nation);
相关疑惑?
通过直接new的方式或反射的方式都可以调用公共的结构,开发中到底用哪个?
建议:使用new的方式 什么时候使用反射: 当我们编译阶段不确定要造哪个类的对象,那我们这时需要用到反射 2. 反射与封装是否相矛盾
类的加载与ClassLoader的理解
类的加载过程:
程序经过java.exec命令以后,会生成一个或多个字节码文件(.class结尾)。
接着我们使用java.exe命令对某个字节码文件进行解释运行。相当于将某个字节码文件加载到内存中。此过程成为类的加载。加载到内存中的类,我们称为运行时类,此运行时的类,就作为Class的一个实例。
2. Class的实例对应着一个运行时类
3. 加载到内存中的运行时类,会缓存一定的时间。在此时间之内,我们可以通过不同的方式来获取此运行时类
什么是类的加载器



通过反射创建运行时类的对象
Class clazz = Person.class;
Person obj = (Person)clazz.newInstance();
获取运行时类的完整结构
获取类的属性:
Class clazz = Person.class;
Field[] fields = clazz.getFields(); // 可以获取当前类以及父类中定义的public属性
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields(); // 可以获取当前类中所有定义的属性
获取类属性的内部结构:
for(Field f: declaredFields){
获取类属性的权限修饰符
int modifier = f.getModifiers();
System.out.print(Modifier.toString(modifier));
获取类属性的数据类型
Class type = f.getType();
System.out.println(type.getName());
获取类属性的变量名
String fName = f.getName();
System.out.print(fName);
}
## 获取类的方法
Class clazz = Person.class;
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods(); // 可以获取当前类以及父类中定义的public方法
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods(); // 可以获取当前类中所有定义的方法
获取类方法的内部结构:
获取方法的注解:
Annotation[] annos = m.getAnnotations();
for(){sout(a));
获取权限修饰符:
System.out.print(Modifier.toString(m.getModifiers()));
获取返回值类型:
System.out.print(m.getReturnType().getName());
获取形参列表:
Class[] parameterTypes = m.getParameterTypes();
if(!(parameterTypes == null || parameterTyupes.length ==0)){
for(Class p:parameterTypes){
System.out.print(p.getName)
}
}
获取抛出的异常:
Class[] exceptionTypes = m.getExceptionTypes();
if(!(exceptionTypes == null || exceptionTypes.length ==0)){
for(Class p:exception Types){
System.out.print(p.getName)
}
}
获取运行时类构造器结构
Class clazz = Person.class;
Constructor[] construcotrs = clazz.getConstructors(); // 获取当前运行时类中声明为public的构造器
for(Constructor c : constructors){
System.out.println(c);
}
Constructor[] construcotrs = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors(); // 获取当前运行时类中所有构造器
for(Constructor c : constructors){
System.out.println(c);
}
获取运行时类父类和父类的类型(功能性代码vs逻辑性代码)
// 获取运行时类的父类
Class clazz = Person.class;
Class superclass = clazz.getSuperclass();
System.out.println(superclass);
// 获取运行时类带泛型的父类
Class clazz = Person.class;
Type genericSuperclass = clazz.getGenericSuperclass();
System.out.println(superclass);
// 获取运行时类带泛型父类的泛型
Class clazz = Person.class;
Type genericSuperclass = clazz.getGenericSuperclass();
ParameterizedType paramType = (ParameterizedType) genericSuperclass;
Type[] actualTypeArguments = paramType.getActualTypeArguments(); // 为什么是数组呢,因为像Map类型的泛型会有两个参数:Map<k,v>
System.out.println(genericSuperclassj[0]o.getTypeName());
获取运行时类实现的接口
Class clazz = Person.class;
Class[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces();
Class[] interfaces1 = clazz.getSuperclass.getInterfaces(); // 获取父类的接口
for(Class c: interfaces){
System.out.println(c);
}
获取运行时类所在的包
Class clazz = Person.class;
Package pack = clazz.getPackage();
System.out.prinln(pack);
获取运行时类声明的注解
Class clazz = Person.class;
Annotation[] annotaions = clazz.getAnnotations();
for(Annotation annos: annotations){
System.out.println(annos);
}
调用运行时类的指定结构(重要)
获取和操作运行时类指定的属性
Class clazz = Person.class; // 首先创建运行时类的对象 Person p = clazz.newInstance(); Field id = clazz.getField("id"); // 要求运行时类属性声明为public,通常不用此方法 Field id = clazz.getDeclaredField("id"); id.setAccessible(true); // public以下的权限需要设置为true // 设置当前属性的值 id.set(p,1001); // 获取当前属性的值 int pid = (int)id.get(p);
获取和操作运行时类中指定的方法(掌握)
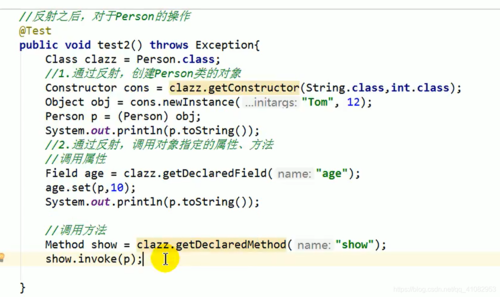
Class clazz = Person.class; Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance(); Method show = clazz.getDecalaredMethod("show",String.class); //参数1: 获取指定方法的名称,参数2:指明获取方法的形参列表 show.setAccessible(true); show.invoke(p,"CHN") // 参数1:方法的调用者 参数2:给方法形参赋值的实参 String nation = (String) show.invoke(p,"CHN") // 有返回值的方法的调用 // 调用静态方法 调用静态方法不需要实例化 Method showStatic = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("showStatic"); showStatic.setAccessible(true); Object returnVal = showStatic.invoke(Person.class); // 括号里面为null也可以,因为每个对象的static方法都是一样的 System.out.prinln(returnVal); //null 如果是void方法的话返回值为null
获取和操作运行时类中指定的构造器(不常用,常用newInstance)
Class clazz = Peson.class; Constructor cons = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class); cons.setAccessible(true); Person per = (Person) cons.newInstance("Tom"); System.out.println(per);
反射的应用:动态代理AOP(aspect orient proxy)(Sprint里面会再讲)
静态代理
// 工厂接口:代理类需要代理做的事情
interface ClothFactory{
void produceCloth();
}
// 代理类
class ProxyClothFactory implements ClothFactory{
private ClothFactory factory;
public ProxyClothFactory(ClothFactory factory){
this.factory = factory; // 创建被代理类的对象
}
@Override
public void produceCloth() {
System.out.println("代理工厂的准备工作");
// 被代理类做的事情
factory.produceCloth();
System.out.println("代理工厂做的后续工作");
}
}
// 被代理类
class NikeClothFactory implements ClothFactory{
public void produceCloth(){
System.out.println("Nike生产一批运动服");
}
}
public class StaticProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] argv){
// 创建被代理类的对象
ClothFactory nike = new NikeClothFactory();
// 创建代理类对象
ClothFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyClothFactory(nike);
proxyFactory.produceCloth();
}
}
动态代理:
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
// 被代理类需要让代理类需要做的事情
interface Human{
String getBelief();
void eat(String food);
}
// 被代理类
class SuperMan implements Human{
@Override
public String getBelief(){
return "I believe I can fly";
}
@Override
public void eat(String food){
System.out.println("我喜欢吃" + food);
}
}
// 问题:
// 1. 如何根据发加载到内存中的被代理类,动态的创建一个代理类及其对象?
// 2. 当通过代理类的对象调用方法时,如何动态的去调用被代理类中的同名方法?
//创建代理类对象
class ProxyFactory{
// obj为被代理类
public static Object getProxyInstance(Object obj){
MyInvocationHandler handler = new MyInvocationHandler();
handler.bind(obj);
// 创建一个代理类对象:参数1:获取obj类的类加载器,参数2:获取obj实现的接口,参数3:获取obj中调用的方法
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(obj.getClass().getClassLoader(),obj.getClass().getInterfaces(),handler);
}
}
class MyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler{
private Object obj;
// 绑定被代理类
public void bind(Object obj){
this.obj = obj;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 调用被代理类中的方法:method是反射的
HumanUti1 util1 = new HumanUti1();
HumanUtil2 util2 = new HumanUtil2();
util1.method1();
Object returnValue = method.invoke(obj,args);
util2.method2();
return returnValue;
}
}
// 调用通用方法:
class HumanUti1{
public void method1(){
System.out.println("-------通用方法1-------");
}
}
class HumanUtil2{
public void method2(){
System.out.println("-----通用方法2---------");
}
}
public class ProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SuperMan superMan = new SuperMan();
// 实例化动态代理类
Human proxyInstance = (Human)ProxyFactory.getProxyInstance(superMan);
// 通过代理类对象调用方法时调用的都是被代理类中的方法
String belief = proxyInstance.getBelief();
System.out.println(belief);
proxyInstance.eat("鸡腿");
// 代理类动态性的体现:
NikeClothFactory nikeClothFactory = new NikeClothFactory();
ClothFactory proxyClothFactory = (ClothFactory)ProxyFactory.getProxyInstance(nikeClothFactory);
proxyClothFactory.produceCloth();
}
}
动态代理复习:



如何根据加载到内存中的被代理类,动态创建一个代理类及其对象:通过Proxy.newProxyInstance()实现
当通过代理类的对象调用方法a时,如何动态的去调用被代理类中的同名方法a:通过InvocationHandler接口的实现类及其方法invoke()
作者:dandeseed
链接:https://juejin.cn/post/6986106756954849288
来源:掘金
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章









