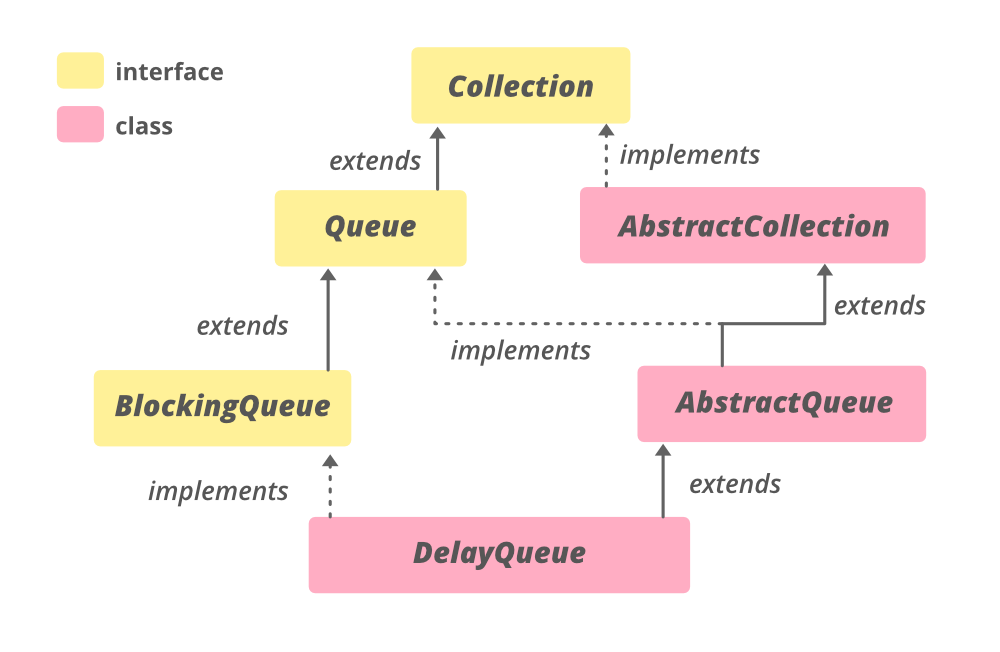
DelayQueue 是BlockingQueue接口的实现类,它根据"延时时间"来确定队列内的元素的处理优先级(即根据队列元素的“延时时间”进行排序)。另一层含义是只有那些超过“延时时间”的元素才能从队列里面被拿出来进行处理。
- DelayQueue 队列将阻止其元素对象从队列中被取出,直到达到为元素对象设置的延迟时间。DelayQueue 在队列的头部存储最近过期的元素,如果队列内没有元素过期,使用poll()方法获取队列内的元素将会返回null。
- DelayQueue 类及其迭代器实现了Collection和Iterator接口的所有可选方法,但迭代器方法
iterator()不能保证以特定的顺序遍历DelayQueue的元素。
- DelayQueue 不接收null元素,DelayQueue 只接受那些实现了java.util.concurrent.Delayed接口的对象,并将其放入队列内。DelayQueue 通过调用元素对象的getDelay(TimeUnit) 方法获取该元素剩余的“延迟时间”。getDelay()的 TimeUnit时间单位是一个枚举类型 : DAYS(天), HOURS(小时), MINUTES(分钟), SECONDS(秒), MILLISECONDS(毫秒), MICROSECONDS(微妙), NANOSECONDS(纳秒)
public interface Delayed extends Comparable{
long getDelay(TimeUnit unit);
}
下面我们就写一个java Class实现Delayed 接口,只有实现了Delayed 接口的类对象才能放入DelayQueue。因为Delayed接口继承自Comparable接口,所以我们必须实现getDelay方法和compareTo方法。
class DelayObject implements Delayed {
private String name;
private long time; //延时时间
public DelayObject(String name, long delayTime) {
this.name = name;
this.time = System.currentTimeMillis() + delayTime;
}
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
long diff = time - System.currentTimeMillis();
return unit.convert(diff, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed obj) {
if (this.time < ((DelayObject)obj).time) {
return -1;
}
if (this.time > ((DelayObject)obj).time) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
Date date = new Date(time);
SimpleDateFormat sd = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
return "\nDelayObject:{"
+ "name=" + name
+ ", time=" + sd.format(date)
+ "}";
}
}
测试延时队列DelayQueue的使用效果
public class DelayQueueTest {
@Test
void testDelayObject() throws InterruptedException {
//实例化一个DelayQueue
BlockingQueue DQ = new DelayQueue<>();
//向DelayQueue添加四个元素对象,注意延时时间不同
DQ.add(new DelayObject("A", 1000 * 10)); //延时10秒
DQ.add(new DelayObject("B", 4000 * 10)); //延时40秒
DQ.add(new DelayObject("C", 3000 * 10)); //延时30秒
DQ.add(new DelayObject("D", 2000 * 10)); //延时20秒
SimpleDateFormat sd = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
//将对象从DelayQueue取出,注意取出的顺序与延时时间有关
System.out.println( DQ.take()); //取出A
System.out.println( DQ.take()); //取出D
System.out.println( DQ.take()); //取出C
System.out.println( DQ.take()); //取出B
}
}
从下面的打印结果及上文的代码可以看出
- 队列中元素放入的顺序是A、B、C、D,取出的顺序是A、D、C、B,这是因为队列中的元素按照延时时间进行了排序。
- 另外我们可以看到,每隔10秒才可以从队列中取出一个元素,这是因为只有超过“延时时间”的元素才能从队列里面被拿出来。而我们设置的延时时间是10s、20s、30s、40s。
DelayObject:{name=A, time=2021-03-23 14:14:20}
DelayObject:{name=D, time=2021-03-23 14:14:30}
DelayObject:{name=C, time=2021-03-23 14:14:40}
DelayObject:{name=B, time=2021-03-23 14:14:50}
欢迎关注我的博客,里面有很多精品合集
- 本文转载注明出处(必须带连接,不能只转文字):[字母哥博客] www.zimug.com 。
点击查看更多内容
为 TA 点赞
评论
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章
正在加载中
感谢您的支持,我会继续努力的~
扫码打赏,你说多少就多少
赞赏金额会直接到老师账户
支付方式
打开微信扫一扫,即可进行扫码打赏哦