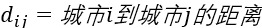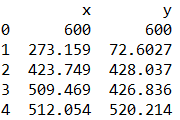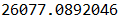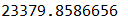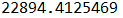上一篇文章介绍了模拟退火算法的基本原理(模拟退火算法与其python实现(一)),这篇文章介绍一下模拟退火算法在数学建模中最常应用的一类问题——Traveling salesman problem,也就是旅行商问题,这类问题的描述如下:
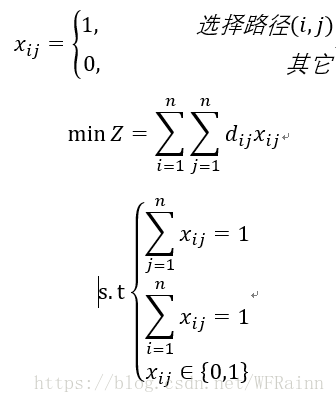
一个旅行商从城市1 出发,需要到其它城市n去推销货物,最后返回城市1 。若任意两个城市间的距离已知,旅行商如何选择最佳行走路线?
这种问题也就是上篇提到的NP-hard问题中很典型的一类,如果使用枚举法,随着城市数目的增多,计算量将几何倍数的递增。那么,如何使用SA算法来求近似最优解呢,首先我们这个问题转化为数学模型:
设
我们所求即为函数Z的最小值,下面我们便使用python来构建TSP问题的SA模型并尝试求得近似最优解
首先导入问题数据并处理:
from __future__ import division
import pandas as pd
import utils
import numpy as np
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
citys=pd.read_table('./data/tsp100.txt',sep='\t',header=None)
citys.columns=['x']
citys['y']=None
for i in range(len(citys)):
coordinate=citys['x'][i].split()
citys['x'][i]=float(coordinate[0])
citys['y'][i]=float(coordinate[1])
print citys.head(5)其中:
1.string.split()可以剪切字符串,其用法如下:
接着看下数据长什么样
数据集存储了各个城市的坐标,我们把第一个城市作为我们的起点,同时也是我们的终点。接着在数据集中除去这个城市以便于计算。
start=list(citys.iloc[0]) end=list(citys.iloc[0]) citys=citys.drop([0]) citys.index=[i for i in range(len(citys))]
接着我们便可以初始化我们的行走路线了,我们直接将数据集中城市存储的顺序做为我们最初的行走路线
paths=[i for i in range(len(citys))]# initiate path
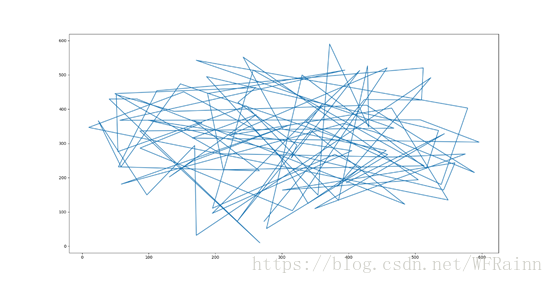
通过matplotlib可以得到初始路径的路线图:
然后我们按照在上文提到的规则设置初始温度,即随机选择几组状态,计算能量差值最大的一组,以此为依据得到初始温度,我们设接受概率为0.5。
''' random path and calculate distance to sreach for optimal initiate temperature ''' distance1=0 distance2=0 dif=0 for i in range(10): #np.random.shuffle(path) newPaths1=list(np.random.permutation(paths)) newPaths2=list(np.random.permutation(paths)) distance1=utils.CalLength(citys,newPaths1,start,end) distance2=utils.CalLength(citys,newPaths2,start,end) difNew=abs(distance1-distance2) if difNew>=dif: dif=difNew Pr=0.5 #initiate accept possibility T0=dif/Pr#initiate terperature
1.其中计算距离的函数定义在utils模块中:
import math def CalDistance(x,y): return math.sqrt(x**2+y**2) def CalLength(citys, paths,start,end): length=0 n=1 for i in range(len(paths)): if i==0: length+=CalDistance(start[0]-citys['x'][paths[i]],start[1]-citys['y'][paths[i]]) n+=1 elif n<len(paths): length+=CalDistance(citys['x'][paths[i]]-citys['x'][paths[i+1]],citys['y'][paths[i]]-citys['y'][paths[i+1]]) n+=1 else: length+=CalDistance(citys['x'][paths[i]]-end[0],citys['y'][paths[i]]-end[1]) return length
2.np.random.permutation(list)可以打乱数据在list中的排序,但不会直接替换原list,而np.random.shuffle(list)会直接替换。
现在我们可以初始化其它参数:
T=T0 Tmin=T/50 k=10*len(paths) #times of internal circulation length=0#initiate distance according to the initiate path length=utils.CalLength(citys,paths,start,end) print length t=0 #time
计算得到初始路径所需要走的距离为:
然后执行降温过程,这里,关于邻域函数的设置,我们首先设置为调换路径中某对节点的位置。
while T>Tmin: for i in range(k): a=0 b=0 newPaths=paths while a==b: a=np.random.randint(0,len(paths)) b=np.random.randint(0,len(paths)) te=newPaths[a] newPaths[a]=newPaths[b] newPaths[b]=te newLength=utils.CalLength(citys,newPaths,start,end) if newLength<length: length=newLength else: #metropolis principle p=math.exp(-(newLength-length)/T) r=np.random.uniform(low=0,high=1) if r<p: length=newLength t+=1 print t T=T0/(1+t) print length
最后执行结果如下
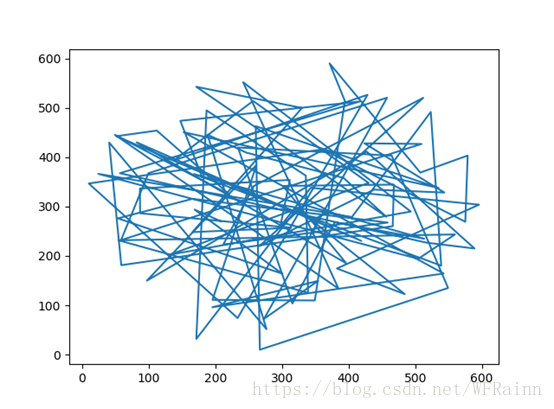
路径图为下:
现在我们尝试一下改进SA算法:
首先,我们更改初始路径,使初始路径也随机生成:
paths=list(np.random.permutation(paths))
接着,我们改进一下邻域函数,将函数设置为根据温度的大小,调换多对节点的位置,这样,能够增加遍历整体的概率。
for j in range(int(T0/500)): a=0 b=0 while a==b: a=np.random.randint(0,len(paths)) b=np.random.randint(0,len(paths)) te=newPaths[a] newPaths[a]=newPaths[b] newPaths[b]=te newLength=utils.CalLength(citys,newPaths,start,end)
接着我们可以设置一个增温过程,即有一定概率重新升温,以避免算法在局部最小值处停滞不前。我们设置重升温的概率为0.15。
back=np.random.uniform(low=0,high=1) if back>=0.85: T=T*2 continue
最终,我们SA模型如下:
paths=list(np.random.permutation(paths)) while T>Tmin: for i in range(k): newPaths=paths for j in range(int(T0/500)): a=0 b=0 while a==b: a=np.random.randint(0,len(paths)) b=np.random.randint(0,len(paths)) te=newPaths[a] newPaths[a]=newPaths[b] newPaths[b]=te newLength=utils.CalLength(citys,newPaths,start,end) if newLength<length: length=newLength else: #metropolis principle p=math.exp(-(newLength-length)/T) r=np.random.uniform(low=0,high=1) if r<p: length=newLength back=np.random.uniform(low=0,high=1) if back>=0.85: T=T*2 continue t+=1 print t T=T0/(1+t) print length
执行算法,得到结果:
代码与数据已上传至github:https://github.com/JiaruiFeng/Simulated-Annealing-solving-TSP-with-python
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章