本系列介绍
本系列《剖析缓存系列》,由浅到深的对缓存进行分析介绍,从缓存形式,更新策略,常见问题,以及JAVA缓存使用(JCache,Spring cache,Ehcache)和缓存服务器redis
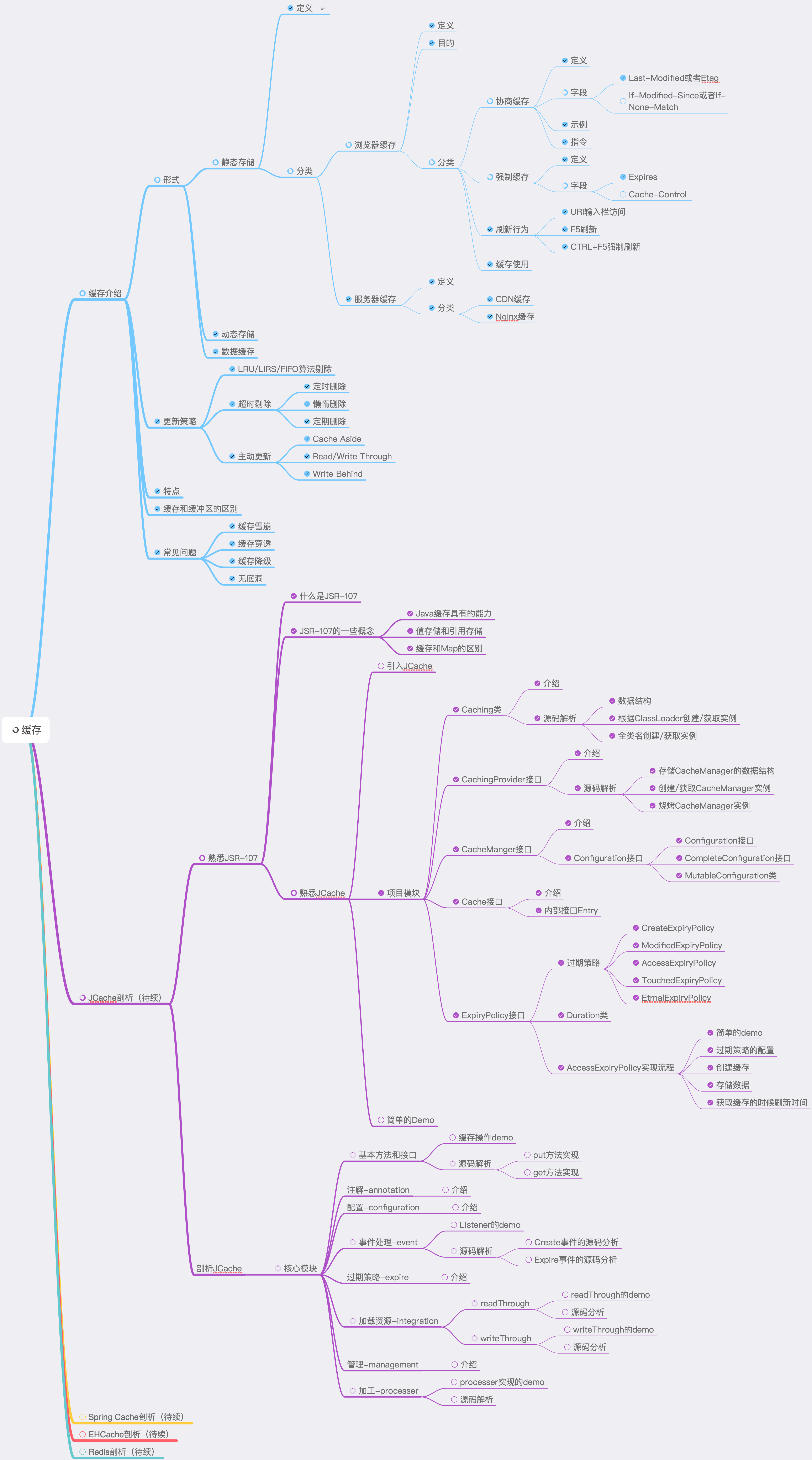
系列目录
本章
本章分为两篇《熟悉JSR-107 JAVA规范》和《剖析JCache》。
《熟悉JSR-107 JAVA缓存规范》偏向熟悉JAVA缓存规范,JAVA缓存使用。
《剖析JCache》 重点讲解高级用法,包括监听器、资源加载、缓存处理以及其cache-ri-impl源码实现等。
基本方法和接口
缓存操作demo
先贴出一个简单的缓存存储-获取操作。看看cache-ri-impl是如何实现这个简单的操作的。
public void simpleCache() {
//创建一个缓存管理器
CacheManager manager = Caching.getCachingProvider().getCacheManager();
//创建一个配置管理器
Configuration<String, String> configuration = new MutableConfiguration<String, String>().setTypes(String.class, String.class);
//生成一个缓存对象
Cache<String, String> simpleCache;
//缓存数据
simpleCache = manager.createCache("simpleCache22", configuration);
simpleCache.put("baron", "china");
//获取数据
String value = simpleCache.get("baron");
System.out.println("Value: " + value);
}
输出结果:
Value: china
put方法实现过程
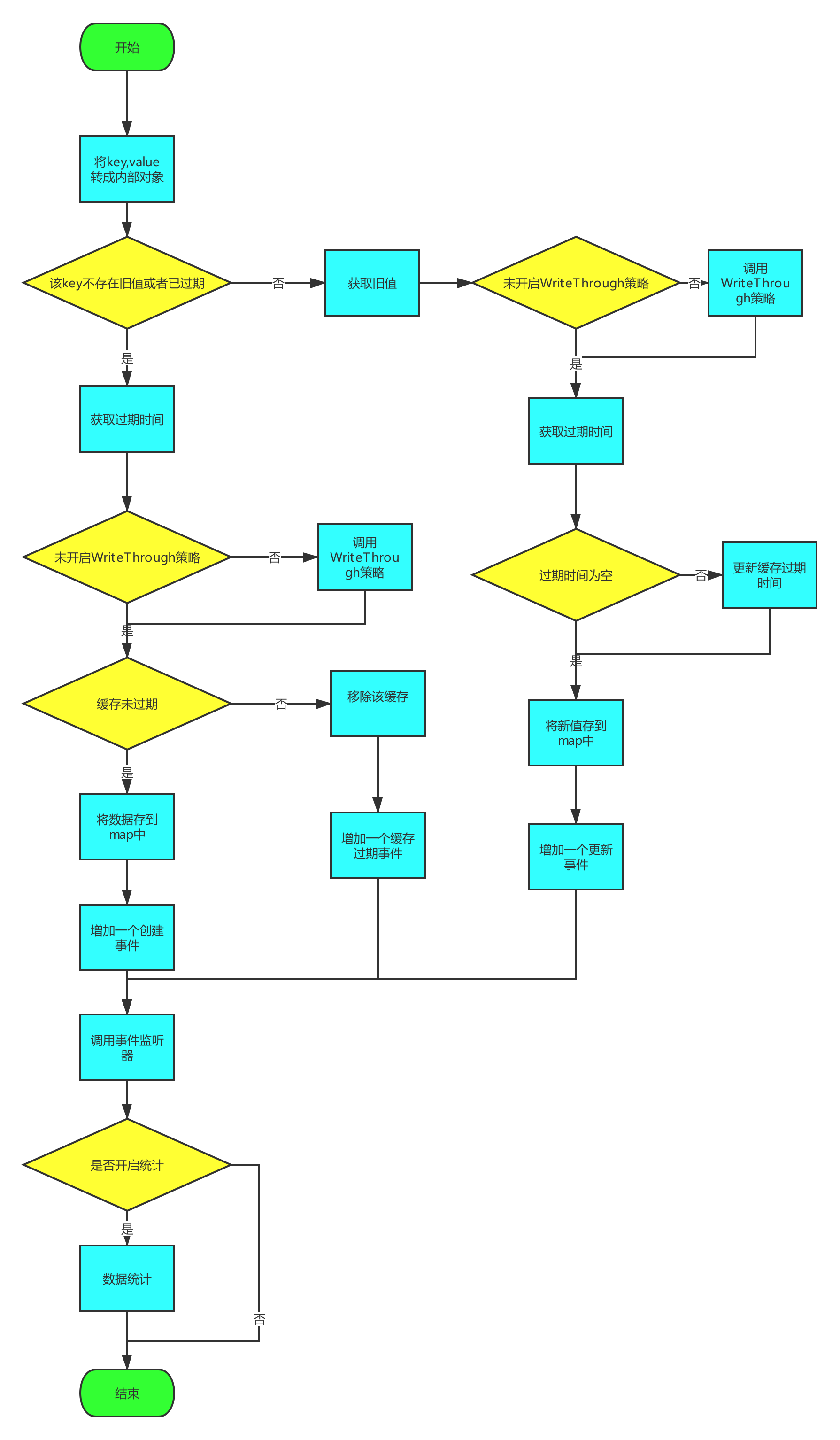
首先先分析simpleCache.put("baron", "china");的实现。
以下是RICache#put(K key, V value)的源码
public void put(K key, V value) {
//已省略非核心代码
//1 创建一个缓存对象事件记录实例
RICacheEventDispatcher<K, V> dispatcher = new RICacheEventDispatcher<K, V>();
//2 实现值存储还是引用存储
Object internalKey = keyConverter.toInternal(key);
Object internalValue = valueConverter.toInternal(value);
//3 判断key是否已存在,若已存在,判断是否过期
RICachedValue cachedValue = entries.get(internalKey);
boolean isOldEntryExpired = cachedValue != null && cachedValue.isExpiredAt(now);
//4 如果旧值已过期,那么移除该值并添加一个过期监听事件
if (isOldEntryExpired) {
V expiredValue = valueConverter.fromInternal(cachedValue.get());
processExpiries(key, dispatcher, expiredValue);
}
//5 key不存在或者key存在但已过期
if (cachedValue == null || isOldEntryExpired) {
//5.1 创建一个 RIEntry,用于下文的writeThrough
RIEntry<K, V> entry = new RIEntry<K, V>(key, value);
Duration duration;
try {
//5.2 执行过期策略
duration = expiryPolicy.getExpiryForCreation();
} catch (Throwable t) {
duration = getDefaultDuration();
}
long expiryTime = duration.getAdjustedTime(now);
//5.3 创建存储对象,这个时候才是真正缓存数据
cachedValue = new RICachedValue(internalValue, now, expiryTime);
//5.4 实现writeThrough
writeCacheEntry(entry);
//5.5 判断是否已过期
if (cachedValue.isExpiredAt(now)) {
processExpiries(key, dispatcher, valueConverter.fromInternal(cachedValue.get()));
} else {
//5.6 将缓存存储到map中
entries.put(internalKey, cachedValue);
putCount++;
// 5.7 增加一个创建监听事件
dispatcher.addEvent(CacheEntryCreatedListener.class, new RICacheEntryEvent<K, V>(this, key, value, EventType.CREATED));
}
} else {
//6 来到这里是,说明该key存在未过期的value,获取到旧的value
V oldValue = valueConverter.fromInternal(cachedValue.get());
RIEntry<K, V> entry = new RIEntry<K, V>(key, value, oldValue);
//6.1 实现writeThrough
writeCacheEntry(entry);
try {
//6.2 执行过期策略
Duration duration = expiryPolicy.getExpiryForUpdate();
if (duration != null) {
long expiryTime = duration.getAdjustedTime(now);
cachedValue.setExpiryTime(expiryTime);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
//leave the expiry time untouched when we can't determine a duration
}
//6.3 更新value
cachedValue.setInternalValue(internalValue, now);
putCount++;
//6.4 增加一个缓存更新监听事件
dispatcher.addEvent(CacheEntryUpdatedListener.class,
new RICacheEntryEvent<K, V>(this, key, value, oldValue,
EventType.UPDATED));
}
//7 执行所有监听事件
dispatcher.dispatch(listenerRegistrations);
}
//8 数据统计
if (statisticsEnabled() && putCount > 0) {
statistics.increaseCachePuts(putCount);
statistics.addPutTimeNano(System.nanoTime() - start);
}
}
源码剖析
以下序号是上文put方法实现过程的代码序号
RICacheEventDispatcher是缓存事件处理类,主要存储缓存操作事件。例如:创建缓存事件,更新缓存事件,缓存过期事件。该对象存储的事件可以通过其内部方法dispatch() 通知各个事件的监听器。- 实现是值存储还是引用存储:
cache-ri-impl是定义了一个RIInternalConverter接口,该接口定义了存储和获取时对value处理的方法。有两个实现类RIReferenceInternalConverter和RISerializingInternalConverter。
RIInternalConverter接口源码:
public interface RIInternalConverter<T> {
/**
* Converts the value to an internal representation.
* 将值转成内部类型,用于内部逻辑处理和存储
*/
Object toInternal(T value);
/**
* Converts an internal representation of a value to a value.
* 将内部类型转成对外类型T,提供给调用方使用
*/
T fromInternal(Object internal);
}
RIReferenceInternalConverter 是引用存储的实现。源码如下
public class RIReferenceInternalConverter<T> implements RIInternalConverter<T> {
//缓存内部和外部都是共享同一个的value
@Override
public T fromInternal(Object internal) {
return (T) internal;
}
@Override
public Object toInternal(T value) {
return value;
}
}
RISerializingInternalConverter 是值存储的实现,内部是用java序列号的方式创建一个新的对象.
@Override
public Object toInternal(T value) {
return new Serialized<T>(value);
}
Serialized(V value) {
if (value == null) {
this.hashCode = 0;
this.bytes = null;
} else {
this.hashCode = value.hashCode();
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(value);
bos.flush();
this.bytes = bos.toByteArray();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Failed to serialize: " + value + " due to " + e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
try {
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// eat this up
} } } }
5.1 RIEntry类并不是真实缓存数据的类,只用于内部逻辑处理时临时存储数据。
5.2 调用过期策略的getExpiryForCreation方法获取Duration(上篇有介绍)。注意的是,这里调用的是创建时触发的过期策略,如果开发者配置的是其他阶段的过期策略,那么返回的Duration对象也会不一样。可以看下面对比
下面是CreatedExpiryPolicy#getExpiryForCreation()获取到的是Duration对象
public Duration getExpiryForCreation() {
return expiryDuration;
}
下面是EternalExpiryPolicy#getExpiryForCreation()获取到的是Duration空对象,代表永不过期。(EternalExpiryPolicy是永不过期的策略)
public static final Duration ETERNAL = new Duration();
public Duration getExpiryForCreation() {
return ETERNAL;
}
5.3 在cache-ri-impl实现中,真实value的类是RICachedValue,其的作用用于存储value和过期时间以及一些初始化参数。详情可看源码。
5.4 WriteThrough是更新数据的一种策略(第一篇更新策略有介绍)。下文会详细讲解实现逻辑,先看看该方法的逻辑:
private void writeCacheEntry(RIEntry<K, V> entry) {
//当开启isWriteThrough的时候,会调用cacheWriter.write方法
if (configuration.isWriteThrough()) {
try {
cacheWriter.write(entry);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
5.6 缓存存储在RIInternalMap<Object, RICachedValue> entries,可以看到value是RICachedValue对象
7 dispatcher.dispatch()就是调用缓存事件处理对象上文的所存储事件(序号4,5.7,6.4)。
调用创建事件监听器代码如下
events = eventMap.get(CacheEntryCreatedListener.class);
if (events != null) {
for (RICacheEntryListenerRegistration<K, V> registration : registrations) {
CacheEntryEventFilter<? super K, ? super V> filter = registration.getCacheEntryFilter();
Iterable<CacheEntryEvent<K, V>> iterable =
filter == null ? events : new RICacheEntryEventFilteringIterable<K, V>(events, filter);
CacheEntryListener<? super K, ? super V> listener = registration.getCacheEntryListener();
if (listener instanceof CacheEntryCreatedListener) {
((CacheEntryCreatedListener) listener).onCreated(iterable);
}
}
}
过程流程图:
get方法实现
get的实现思路其实和put方法差不多。有一点需要注意的是get可实现缓存更新策略是ReadThrough,而put实现的是WriteThrough
缓存事件监听 Cache Entry Listeners
-
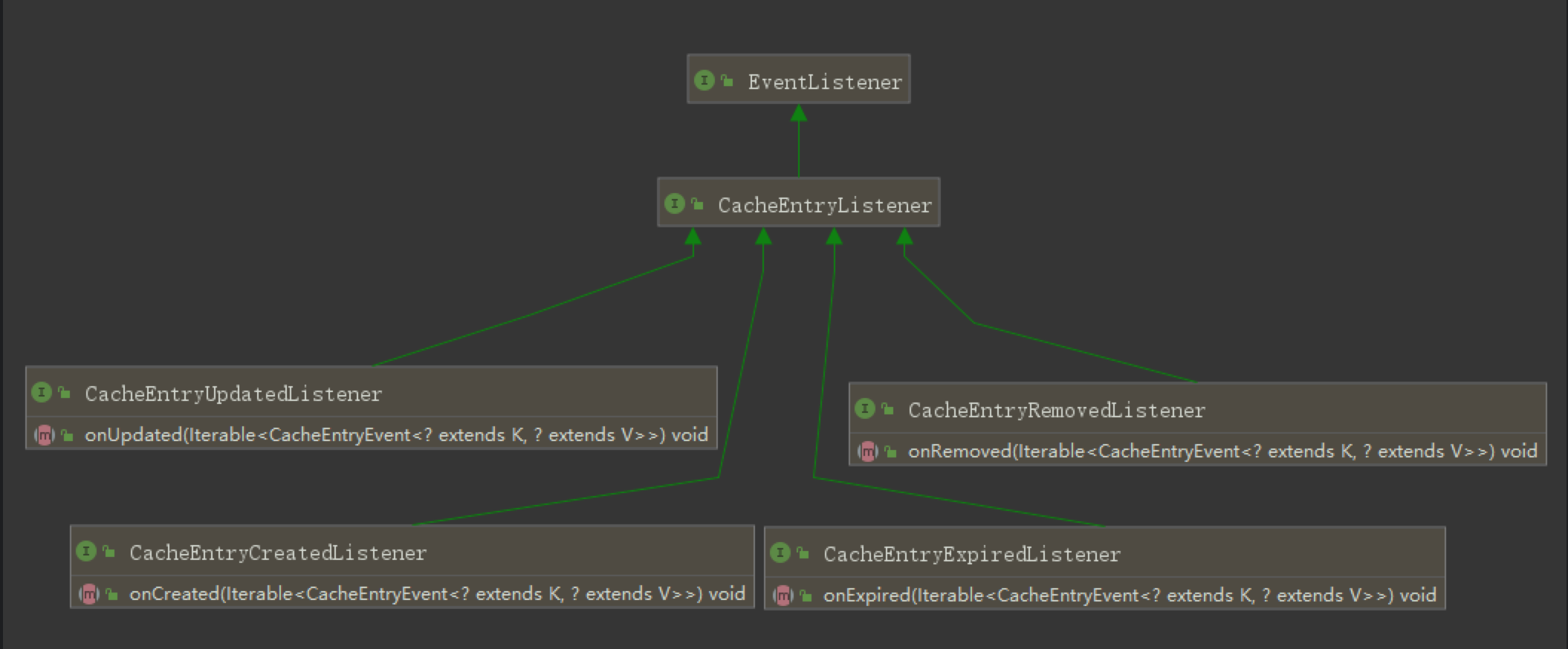
提供四个缓存事件
create,update,remove.expired -
CacheEntryListener接口,由4个事件接接口继承CacheEntryExpiredListener,CacheEntryCreatedListener,CacheEntryUpdatedListener,CacheEntryRemovedListener。4个事件触发都会调用其对应的接口 -
缓存配置监听器:
通过实现CacheEntryListenerConfiguration接口,可以将事件监听器绑定到缓存中。Cache提供了一个方法 registerCacheEntryListener( CacheEntryListenerConfiguration<K, V> cacheEntryListenerConfiguration) -
事件监听器的触发,其实是一个观察者模式,当
Cache某些方法被调用,就会主动去调用监听器方法。例如dispatcher.dispatch(listenerRegistrations); -
配置添加器还涉及到一个
CacheEntryEventFilter类,该类不是必须实现的,它的作用只是在调用监听器之前检验监听器的事件是否正确
简单的demo
这次demo是实现创建事件和过期事件的监听器。
public class SimpleExpireAndCreateListener implements CacheEntryCreatedListener<String,String> , CacheEntryExpiredListener<String,String> {
@Override
public void onCreated(Iterable<CacheEntryEvent<? extends String, ? extends String>> cacheEntryEvents) throws CacheEntryListenerException {
for (CacheEntryEvent<? extends String, ? extends String> entryEvent : cacheEntryEvents) {
System.out.println("Created的Listener方法: " + entryEvent.getKey() + " with value: " + entryEvent.getValue());
}
}
@Override
public void onExpired(Iterable<CacheEntryEvent<? extends String, ? extends String>> cacheEntryEvents) throws CacheEntryListenerException {
for (CacheEntryEvent<? extends String, ? extends String> entryEvent : cacheEntryEvents) {
System.out.println("Expired的Listener方法: " + entryEvent.getKey() + " with value: " + entryEvent.getValue()+" oldValue: "+entryEvent.getOldValue());
}
}
}
SimpleExpireAndCreateListener类实现了CacheEntryCreatedListener和CacheEntryExpiredListener接口。
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CachingProvider cachingProvider = Caching.getCachingProvider();
CacheManager cacheManager = cachingProvider.getCacheManager();
//创建缓存配置类
MutableConfiguration mutableConfiguration = new MutableConfiguration();
mutableConfiguration.setTypes(String.class, String.class);
//设置1分钟过期时间
mutableConfiguration.setExpiryPolicyFactory(AccessedExpiryPolicy.factoryOf(new Duration(SECONDS, 10)));
MutableCacheEntryListenerConfiguration mutableCacheEntryListenerConfiguration = new MutableCacheEntryListenerConfiguration(
FactoryBuilder.factoryOf(SimpleExpireAndCreateListener.class), null, false, false
);
//创建缓存操作类
Cache<String, String> cache = cacheManager.createCache("simpleExpireListenerDemo", mutableConfiguration);
cache.registerCacheEntryListener(mutableCacheEntryListenerConfiguration);
cache.put("过期key", "过期value");
//睡眠1分钟
Thread.sleep(10000);
String value = cache.get("过期key");
System.out.println("获取到value:"+value);
}
运行效果:
Created的Listener方法: 过期key with value: 过期value
Expired的Listener方法: 过期key with value: null oldValue: null
获取到value:null
事件监听器的调用其实在上文put和get源码中就有提及。
annotation
JCache也定义了使用注解缓存的规范,在cache-ri-impl包并没有实现。但是在Spring Cache中,注解缓存却用得很广泛。以后剖析Spring Cache时再说说这注解的实现和使用。
构造模块 configuration
这个模块主要为了方便开发者快速配置缓存,创建缓存,使用和管理缓存。
例如 FactoryBuilder类,就是工厂构建类。他不需要开发者实现Factory接口,主要使用FactoryBuilder就可以创建想要的类实例。
下面是使用例子
//配置readThrough
mutableConfiguration.setReadThrough(true);
mutableConfiguration.setCacheLoaderFactory(FactoryBuilder.factoryOf(ReadThroughLoader.class));
例如MutableConfiguration类,是JCache提供的一个默认配置的CompleteConfiguration实现类,方便开发者可以便捷创建缓存
MutableConfiguration mutableConfiguration = new MutableConfiguration();
mutableConfiguration.setTypes(String.class, String.class);
//创建缓存
Cache<String, String> cache = cacheManager.createCache("simpleCache", mutableConfiguration);
integration
integration 模块只是提供ReadThrough和WriteThrough更新策略的实现规范。
ReadThrough
ReadThrough 是一种更新缓存的策略,读取数据时的策略当缓存没有命中(缓存中没有得到数据),由缓存服务来加载数据。同时,请求可能会阻塞等待或者返回。在cache-ri-impl包中,get()方法中有一步是当缓存数据为空,并且ReadThrough开启时,会去调用ReadThrough实现。
实现ReadThrough需要实现CacheLoader接口,CacheLoader接口定义了两个方法load和loadAll
实现代码如下:
public class ReadThroughLoader implements CacheLoader {
/**
* 模拟数据库
*/
private static final List<String> DATASOURCE ;
private static final Random RANDOMINT;
static {
DATASOURCE = new ArrayList<>();
DATASOURCE.add("datasource1");
DATASOURCE.add("datasource2");
DATASOURCE.add("datasource3");
DATASOURCE.add("datasource4");
RANDOMINT = new Random();
}
@Override
public Object load(Object key) throws CacheLoaderException {
System.out.println("[loader加载] 传入key:"+key);
//模擬查询数据库的数据
String value = DATASOURCE.get(RANDOMINT.nextInt(DATASOURCE.size()));
return value;
}
@Override
public Map loadAll(Iterable keys) throws CacheLoaderException {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
keys.forEach(key->{
//模擬查询数据库的数据
String value = DATASOURCE.get(RANDOMINT.nextInt(DATASOURCE.size()));
map.put(String.valueOf(key), value);
});
return map;
}
}
上文实现是,模拟当缓存没有获取到值时,从数据库中获取数据的过程,然后存储到缓存中。
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CachingProvider cachingProvider = Caching.getCachingProvider();
CacheManager cacheManager = cachingProvider.getCacheManager();
//创建缓存配置类
MutableConfiguration mutableConfiguration = new MutableConfiguration();
mutableConfiguration.setTypes(String.class, String.class);
//开启readThrough模式
mutableConfiguration.setReadThrough(true);
mutableConfiguration.setCacheLoaderFactory(FactoryBuilder.factoryOf( ReadThroughLoader.class));
//创建缓存
cacheManager.createCache("readThroughDemo", mutableConfiguration);
//获取缓存
Cache<String, String> loaderDemo = cacheManager.getCache("readThroughDemo");
String value = loaderDemo.get("key1");
if (null != value) {
System.out.println("命中缓存");
System.out.println("缓存值:"+value);
}
//再获取一次该缓存
String Oncevalue = loaderDemo.get("key1");
System.out.println("再一次获取缓存的值:"+Oncevalue);
}
输出结果:
[loader加载] 传入key:key1
命中缓存
缓存值:datasource3
再一次获取缓存的值:datasource3
从输出结果中可以看到,两次获取同一个key值得数据,第一次触发了ReadThrough,第二次并没有触发。
WriteThrough
WriteThrough的实现思路与ReadThrough类似,WriteThrough
直接看实现
public class WriteThroughWriter implements CacheWriter<String,String> {
public final static String PREFIX = "[writeThrough]";
@Override
public void write(Cache.Entry<? extends String, ? extends String> entry) throws CacheWriterException {
System.out.println("[CacheWrite] write方法 key:"+entry.getKey()+" value:"+entry.getValue());
}
@Override
public void writeAll(Collection<Cache.Entry<? extends String, ? extends String>> entries) throws CacheWriterException {
System.out.println("[CacheWrite] writeAll方法 key:"+entries.toString());
}
@Override
public void delete(Object key) throws CacheWriterException {
System.out.println("[CacheWrite] delete方法 key:"+key);
}
@Override
public void deleteAll(Collection<?> keys) throws CacheWriterException {
System.out.println("[CacheWrite] deleteAll方法 key:"+keys.toString());
}
}
调用代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CachingProvider cachingProvider = Caching.getCachingProvider();
CacheManager cacheManager = cachingProvider.getCacheManager();
MutableConfiguration mutableConfiguration = new MutableConfiguration();
mutableConfiguration.setWriteThrough(true);
mutableConfiguration.setCacheWriterFactory(FactoryBuilder.factoryOf(SimpleExample.class));
cacheManager.createCache("writeThrough", mutableConfiguration);
Cache<Object, Object> writeThrough = cacheManager.getCache("writeThrough");
writeThrough.put("key1", "value1");
}
加工 processor
为了可以让开发者对缓存进行一些操作,改变缓存数据,提供了processor模块,可以调用invoke()/invokeAll()方法时实现
provesor模块主要看MutableEntry和EntryProcessor接口
实现demo
public class ReadThroughEntryProcessor implements EntryProcessor<String,String,String> {
private final String PREFIX = "prefix_";
@Override
public String process(MutableEntry<String,String> entry, Object... arguments) throws EntryProcessorException {
//判断entry是否存在
if (entry.exists()) {
System.out.println("value存在,实现writeThrough");
entry.setValue(PREFIX+entry.getValue());
}else {
System.out.println("value不存在,实现readThrough");
}
return entry.getValue();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CachingProvider cachingProvider = Caching.getCachingProvider();
CacheManager cacheManager = cachingProvider.getCacheManager();
//创建缓存配置类
MutableConfiguration mutableConfiguration = new MutableConfiguration();
mutableConfiguration.setTypes(String.class, String.class);
//配置readThrough
mutableConfiguration.setReadThrough(true);
mutableConfiguration.setCacheLoaderFactory(FactoryBuilder.factoryOf(ReadThroughLoader.class));
//配置writeThrough
mutableConfiguration.setWriteThrough(true);
mutableConfiguration.setCacheWriterFactory(FactoryBuilder.factoryOf(WriteThroughWriter.class));
//创建缓存
Cache<String, String> cache = cacheManager.createCache("simpleCache", mutableConfiguration);
cache.put("key1","value1");
System.out.println("-----------");
String value = cache.invoke("key", new ReadThroughEntryProcessor());
System.out.println("-----------");
String value1 = cache.invoke("key1", new ReadThroughEntryProcessor());
System.out.println("获取的值:"+value);
System.out.println("获取的值:"+value1);
}
运行效果:
[CacheWrite] write方法 key:key1 value:value1
-----------
value不存在,实现readThrough
[loader加载] 传入key:key
-----------
value存在,实现writeThrough
[CacheWrite] write方法 key:key1 value:prefix_value1
获取的值:datasource4
获取的值:prefix_value1
上文例子展现了当key存在时,会将value添加一个前缀prefix。
剖析源码
可以看一下invoke()方法源码
public <T> T invoke(K key, javax.cache.processor.EntryProcessor<K, V,
T> entryProcessor, Object... arguments) {
// 已省略部分代码
T result = null;
try {
//1 创建一个缓存对象事件记录实例
RICacheEventDispatcher<K, V> dispatcher = new RICacheEventDispatcher<K, V>();
//2 转换成内部类型
Object internalKey = keyConverter.toInternal(key);
RICachedValue cachedValue = entries.get(internalKey);
//3 构建一个EntryProcessorEntry对象 这个对象用于处理EntryProcessor的实现类处理
EntryProcessorEntry<K, V> entry = new EntryProcessorEntry<>(valueConverter, key,
cachedValue, now, dispatcher, configuration.isReadThrough() ? cacheLoader : null);
//4 调用process 实现对缓存的处理
result = entryProcessor.process(entry, arguments);
//5 这里对不同的操作事件进行处理
Duration duration;
long expiryTime;
switch (entry.getOperation()) {
case NONE:
break;
case ACCESS:
//...省略
break;
case CREATE:
case LOAD:
//...省略
break;
case UPDATE:
//...省略
break;
case REMOVE:
//...省略
break;
default:
break;
}
dispatcher.dispatch(listenerRegistrations);
} finally {
lockManager.unLock(key);
}
return result;
}
以下序号是上文invoke()方法源码的代码序号
3 EntryProcessorEntry是cache-ri-impl包的类,实现MutableEntry接口。
那么我们看看MutableEntry用途是什么。MutableEntry继承了Cache.Entry,用于处理变化的Cache.Entry对象。
public interface MutableEntry<K, V> extends Cache.Entry<K, V> {
boolean exists();
void remove();
V getValue();
void setValue(V value);
}
4 调用demo的实现类ReadThroughEntryProcessor#process()方法,ReadThroughEntryProcessor类实现了EntryProcessor。EntryProcessor主要定义了可以通过函数处理Cache.Entry,并且是原子性的。
5 对于4的对缓存处理事件(NONE,ACCESS,CREATE…)实现不同的逻辑。
总结
本篇介绍了JCache缓存的代码结构。其中着重介绍了四个核心模块:processor,integration,expiry,event和构建模块configuration。
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章