[TOC]
简介
-
上一章节我们简单了解了二级缓存的配置。今天我们详细分析下二级缓存以及为什么不建议使用二级缓存。
-
一级缓存针对的是sqlsession。二级缓存针对的是namespace层面的。
配置
- 之前我们已经提到了配置二级缓存以及配置自定义的二级缓存。下面我们从头开始实现二级缓存。
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
```
- 通过上面的代码我们可以看出来,`cacheEnabled`这个属性是控制二级缓存的配置的。而这个属性在Configuration中默认是true。这里说明了mybatis默认是开启缓存功能的。二级缓存和一级缓存的区别其实除了范围以外,他们的不同点就是顺序不同。真正开启二级缓存的是在mapper的xml中配置cache标签就行了。
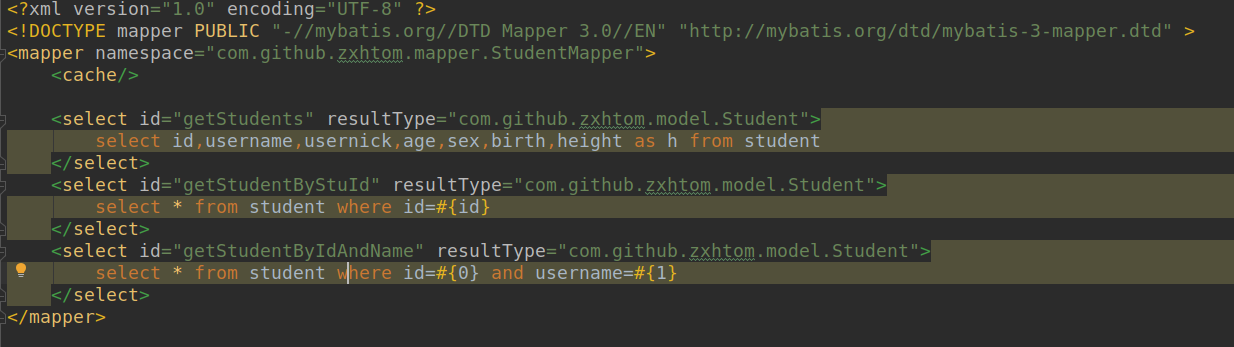
- 我们这里在StudentMapper.xml中配置.然后我们在test类中进行获取两次sqlsession调用同一个sql.
```java
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.openSqlsession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student = mapper.getStudentByIdAndName("1", "1");
System.out.println(student);
SqlSession sqlSession1 = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student studentByIdAndName = mapper1.getStudentByIdAndName("1", "1");
System.out.println(studentByIdAndName);
- 但是结果确实很意外。事实上并没有只调用一次sql。而是调用了两次。这仅仅是结果上的异常。我们用的是Student这个结果接受的。我们再从代码层面上看看
@Data
@Builder
@Accessors(chain = true)
public class Student {
/**
* 学生索引id
* */
* private String id;
* /**
* * 姓名
* */
* private String userName;
/**
* 用户昵称
* */
* private String userNick;
/**
* 年龄
* */
* private Integer age;
* /**
* * 性别 true : 男 ; false : 女
* */
* private SexEnum sex;
* /**
* * 生日
* */
* private Date birth;
* /**
* * 身高
* */
* private Double height;
* }
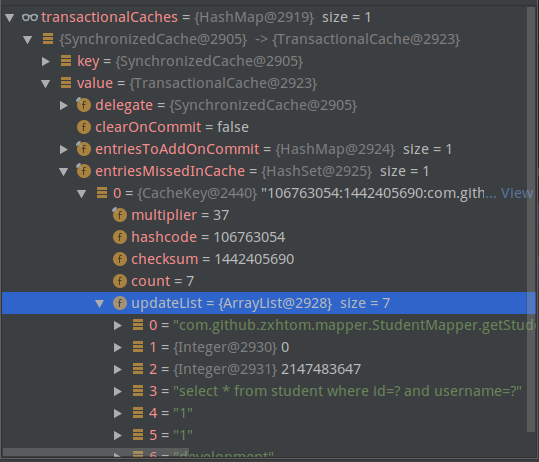
- 细心的伙伴也许能够发现。我们这个实体并没有实现序列化。但是之前我们已经说过了二级缓存的实体需要序列化。按道理来说应该报错的。这就说明我们二级缓存开启,或者确切的说应该说是二级缓存没有起到作用。
-
- 那么我们先将实体进行序列化。然后启动发现并没有任何效果。我们来看看
CacheingExecutor.commit()这个方法里面有事物的提交tcm.commit()。
- 那么我们先将实体进行序列化。然后启动发现并没有任何效果。我们来看看
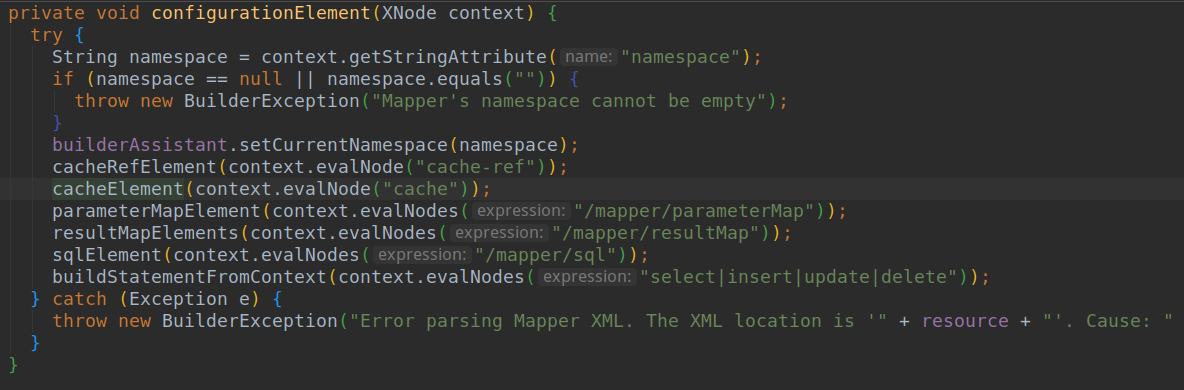
- 这个地方就是进行缓存存储的。我们再来看看mybatis是如何解析mapper.xml中配置的cache标签的。
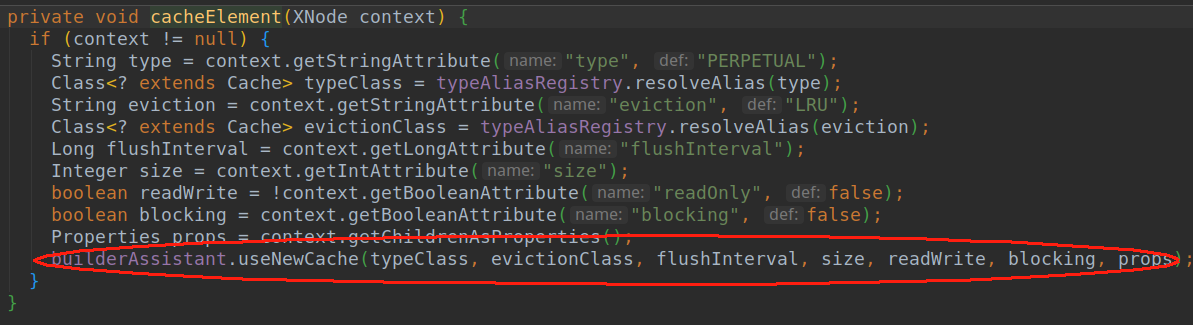
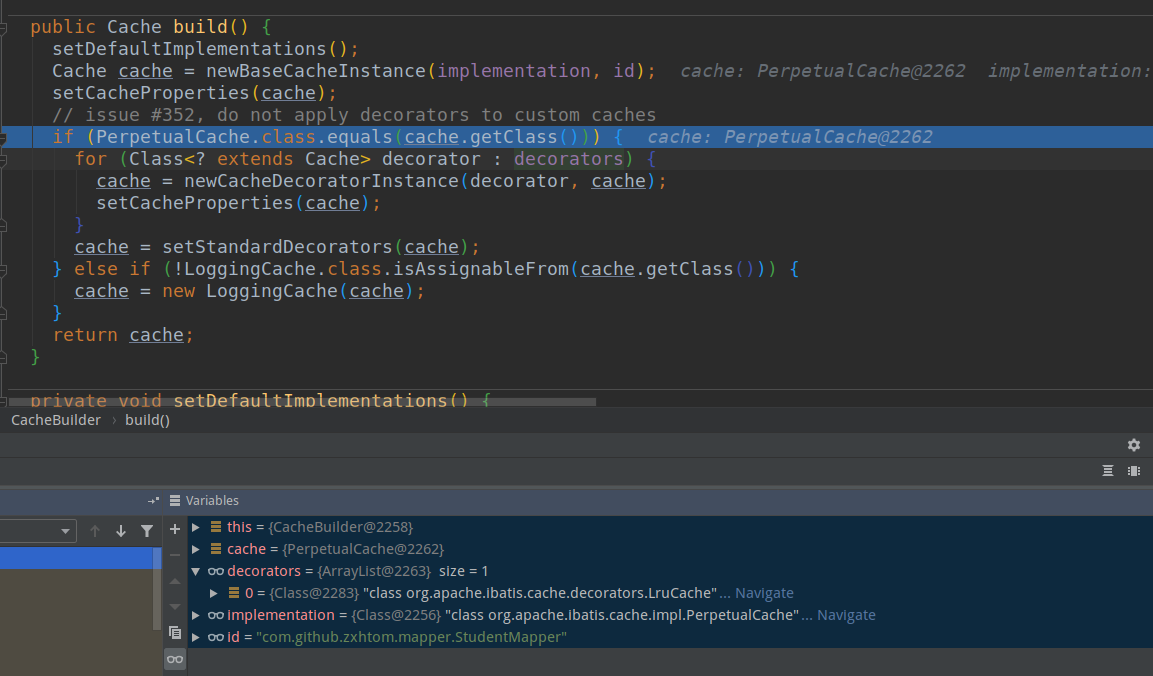
- 由上面代码我们得知mybatis会创建一个缓存对象。里面具体是通过一个build方法来创建的。我们在来看看build方法里是啥东西。
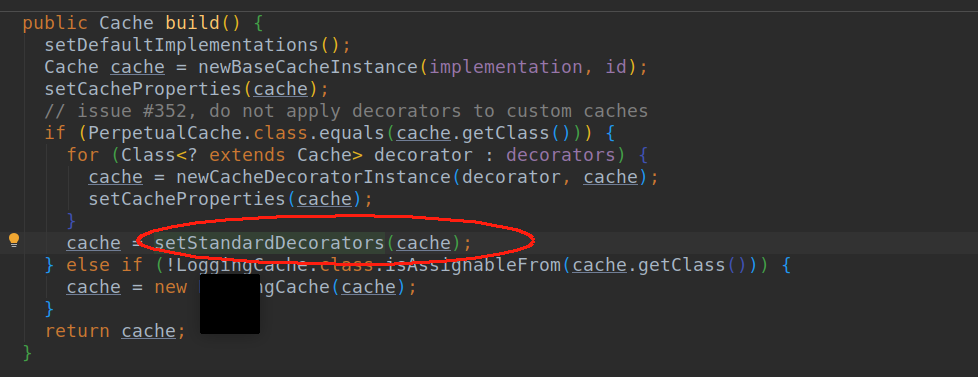
- setStandardDecorators这个方法我们不知道做啥的。但是熟悉设计模式的都知道Decorator这个词是装饰者模式。这里这个方法也是用来装饰用的。看看mybatis为我们装饰了那些东西。
- 首先在newBaseCacheInstance方法中创建原始对象PreprtualCache.然后是加载默认提供的回收机制用的Cache。这个实在build前设置的。
-
- 然后就是通过setStandardDecorators进行装饰了。
-
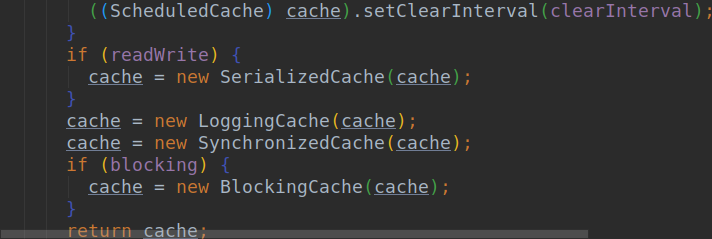
所以他的装饰链为:SynchronizedCache->LogginCache->SerializedCache->LruCache->PerPetualCache
-
而在上面的tcm.commit就是在SerializedCache进行缓存对象的。所以我们之前的代码是sqlsession没有提交。所以代码只要稍微改动下。
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.openSqlsession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student = mapper.getStudentByIdAndName("1", "1");
System.out.println(student);
sqlSession.commit();
SqlSession sqlSession1 = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student studentByIdAndName = mapper1.getStudentByIdAndName("1", "1");
System.out.println(studentByIdAndName);
-
SynchronizedCache : 同步Cache.这个类就是保证线程安全。所以他的方法基本上是加上
synchronized来保证线程安全的。 -
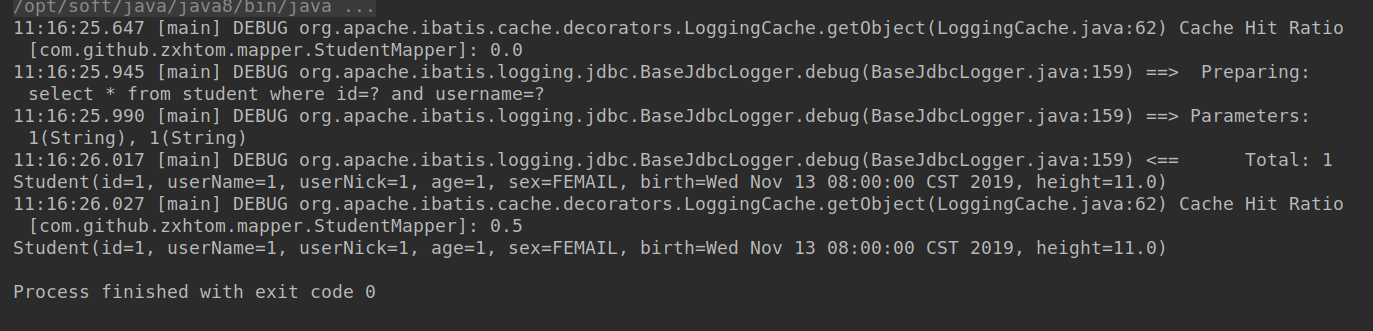
LoggingCache : 日志。在上面我们有个日志是Cache Hit Ratio 0.5 表示二级缓存的命中率。
-
SerializedCache : 就是用来序列化数据的。
-
LruCache : 回收cache的算法
-
PerPetualCache :基本Cache .
源码
CachingExecutor
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
//获取Cache对象
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
//根据statment配置刷新缓存,默认是insert、update、delete会刷新缓存
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
//二级缓存开启入口。
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
//这个方法主要用来处理存储过程。后续章节说明
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//通过缓存事物查询数据
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
//调用委托类查询数据
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
//加入缓存,供下次获取
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list);
}
return list;
}
}
//没有开启二级缓存则继续往下走
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
```
# 缺点
- 二级缓存因为更加广泛,所以容易造成脏数据。尤其是在关联查询的时候有序无法控制刷新力度。很容易出现脏读。

# 自定义二级缓存
- 在之前我们了解到的`PerpetualCache`是缓存链上最基本的缓存类。我们自定义的缓存就是替代这个类的。在mybatis中会现根据我们注册进来的类进行实例化。如果没有则用默认的`PerpetualCache`这个类作为基础缓存类。
-
> 本文由博客一文多发平台 [OpenWrite](https://openwrite.cn?from=article_bottom) 发布!
点击查看更多内容
为 TA 点赞
评论
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章
正在加载中
感谢您的支持,我会继续努力的~
扫码打赏,你说多少就多少
赞赏金额会直接到老师账户
支付方式
打开微信扫一扫,即可进行扫码打赏哦