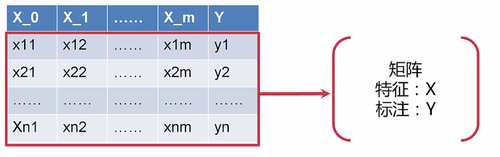
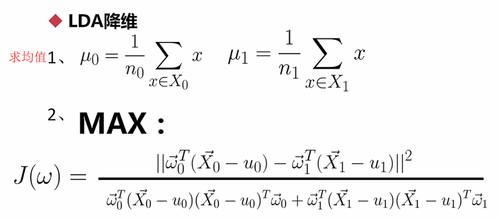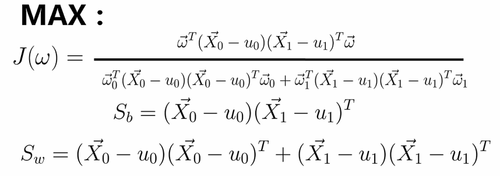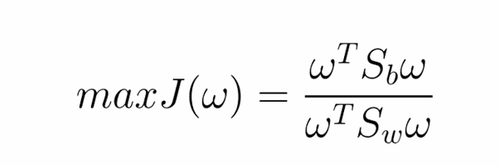一,实现步骤:
1.首先假设标签Y是个二分类,只有0和1
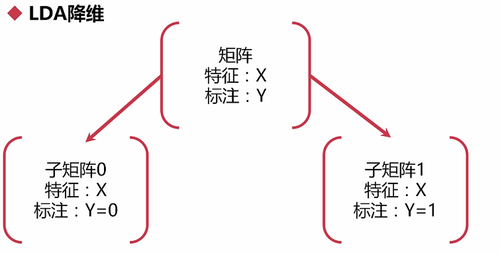
2.对矩阵进行分块儿,分成两个子矩阵(Y=0的N1行子矩阵和Y=1的N2行子矩阵):
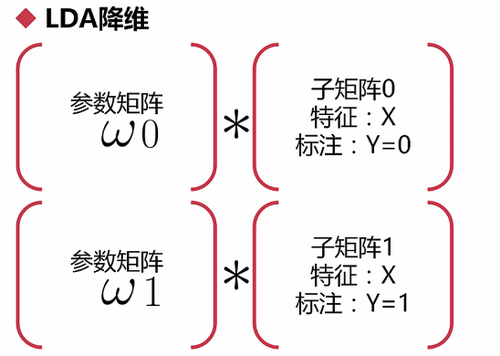
3.对子矩阵进行线性变换:每个子矩阵分别乘一个参数w(欧米伽)
注意:只有X(特征)参与计算,Y不参与计算
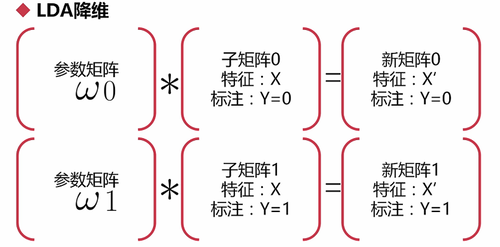
得到新的矩阵:
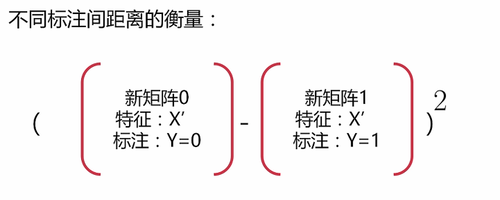
4.计算子矩阵间的距离
a.衡量不同标注间的距离:将两个矩阵相减后取平方
注意:是直观意义上的”相减”,运算时可能不是真的相减
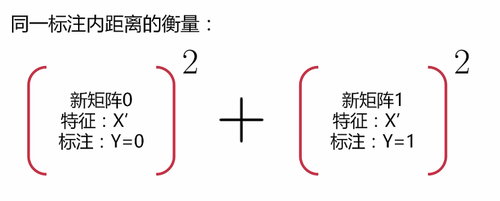
b.衡量相同标注间的距离:先平方,后相加,”相加”的原因同上。
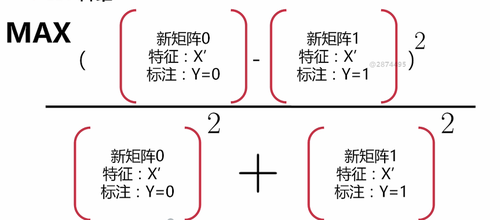
5.相减的作为分子,相加的作为分母,求:使这个分式最大时的W值
目的是为了让标注间的距离尽可能大,标注内的距离尽可能小:
计算方式:
和PCA很像,都要减去均值
提取出Sw和Sb,由这两个式子得出最优化函数(表示方式有点像向量化):
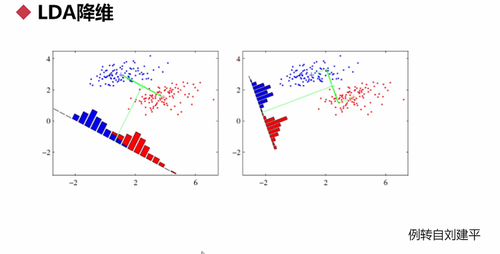
求出W(压缩系数)后,就得出LDA的方向,如图:
Sklearn实现LDA实例:
实例1:
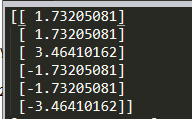
import numpy as np import pandas as pd from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis #建一个二维数组X X = np.array([[-1,-1],[-2,-1],[-3,-2],[1,1],[2,1],[3,2]]) Y = np.array([1,1,1,0,0,0]) #n_components = 1 :降到1维 print(LinearDiscriminantAnalysis(n_components = 1).fit_transform(X,Y))
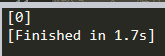
运行结果
实例2:
import numpy as np import pandas as pd from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis #建一个二维数组X X = np.array([[-1,-1],[-2,-1],[-3,-2],[1,1],[2,1],[3,2]]) Y = np.array([1,1,1,0,0,0]) #n_components = 1 :降到1维 #clf:把LDA模型当分类器用 clf=LinearDiscriminantAnalysis(n_components = 1).fit(X,Y) #输入一个二维的数据,得到分类结果 print(clf.predict([[6,0.1]]))
运行结果:Y=0
大体流程:
实战1——LDA辅助Logistic回归用于啤酒的多分类问题:
# Importing the libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
# Importing the dataset
dataset = pd.read_csv('Wine.csv')
X = dataset.iloc[:, 0:13].values
y = dataset.iloc[:, 13].values
# Splitting the dataset into the Training set and Test set
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 0)
# Feature Scaling
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
sc = StandardScaler()
X_train = sc.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = sc.transform(X_test)
# Applying LDA
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis as LDA
lda = LDA(n_components = 2)
X_train = lda.fit_transform(X_train, y_train)
X_test = lda.transform(X_test)
# Fitting Logistic Regression to the Training set
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
classifier = LogisticRegression(random_state = 0)
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Predicting the Test set results
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
# Making the Confusion Matrix
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
# Visualising the Training set results
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
X_set, y_set = X_train, y_train
X1, X2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(start = X_set[:, 0].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 1, step = 0.01),
np.arange(start = X_set[:, 1].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1, step = 0.01))
plt.contourf(X1, X2, classifier.predict(np.array([X1.ravel(), X2.ravel()]).T).reshape(X1.shape),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green', 'blue')))
plt.xlim(X1.min(), X1.max())
plt.ylim(X2.min(), X2.max())
for i, j in enumerate(np.unique(y_set)):
plt.scatter(X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1],
c = ListedColormap(('red', 'green', 'blue'))(i), label = j)
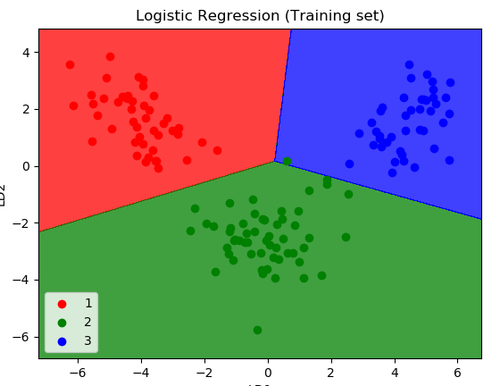
plt.title('Logistic Regression (Training set)')
plt.xlabel('LD1')
plt.ylabel('LD2')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# Visualising the Test set results
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
X_set, y_set = X_test, y_test
X1, X2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(start = X_set[:, 0].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 1, step = 0.01),
np.arange(start = X_set[:, 1].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1, step = 0.01))
plt.contourf(X1, X2, classifier.predict(np.array([X1.ravel(), X2.ravel()]).T).reshape(X1.shape),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green', 'blue')))
plt.xlim(X1.min(), X1.max())
plt.ylim(X2.min(), X2.max())
for i, j in enumerate(np.unique(y_set)):
plt.scatter(X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1],
c = ListedColormap(('red', 'green', 'blue'))(i), label = j)
plt.title('Logistic Regression (Test set)')
plt.xlabel('LD1')
plt.ylabel('LD2')
plt.legend()
plt.show()运行结果:
实战2——将鸢尾花数据集降成二维:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
target_names = iris.target_names
lda = LinearDiscriminantAnalysis(n_components=2)
X_r2 = lda.fit(X, y).transform(X)
plt.figure()
for c, i, target_name in zip("rgb", [0, 1, 2], target_names):
plt.scatter(X_r2[y == i, 0], X_r2[y == i, 1], c=c, label=target_name)
plt.legend()
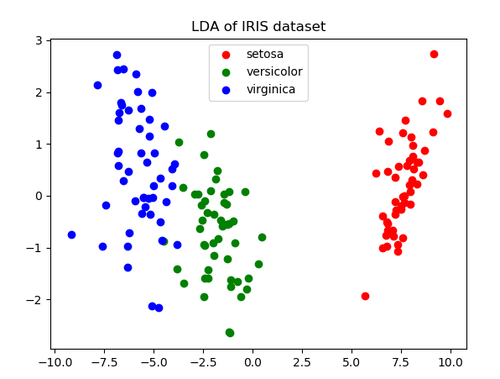
plt.title('LDA of IRIS dataset')
plt.show()运行结果:
点击查看更多内容
2人点赞
评论
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章
正在加载中
感谢您的支持,我会继续努力的~
扫码打赏,你说多少就多少
赞赏金额会直接到老师账户
支付方式
打开微信扫一扫,即可进行扫码打赏哦