Bellman-Ford 算法是一种用于计算带权有向图中单源最短路径(SSSP:Single-Source Shortest Path)的算法。该算法由 Richard Bellman 和 Lester Ford 分别发表于 1958 年和 1956 年,而实际上 Edward F. Moore 也在 1957 年发布了相同的算法,因此,此算法也常被称为 Bellman-Ford-Moore 算法。
Bellman-Ford 算法和 Dijkstra 算法同为解决单源最短路径的算法。对于带权有向图 G = (V, E),Dijkstra 算法要求图 G 中边的权值均为非负,而 Bellman-Ford 算法能适应一般的情况(即存在负权边的情况)。一个实现的很好的 Dijkstra 算法比 Bellman-Ford 算法的运行时间要低。
Bellman-Ford 算法采用动态规划(Dynamic Programming)进行设计,实现的时间复杂度为 O(V*E),其中 V 为顶点数量,E 为边的数量。Dijkstra 算法采用贪心算法(Greedy Algorithm)范式进行设计,普通实现的时间复杂度为 O(V2),若基于 Fibonacci heap 的最小优先队列实现版本则时间复杂度为 O(E + VlogV)。
Bellman-Ford 算法描述:
创建源顶点 v 到图中所有顶点的距离的集合 distSet,为图中的所有顶点指定一个距离值,初始均为 Infinite,源顶点距离为 0;
计算最短路径,执行 V - 1 次遍历;
对于图中的每条边:如果起点 u 的距离 d 加上边的权值 w 小于终点 v 的距离 d,则更新终点 v 的距离值 d;
检测图中是否有负权边形成了环,遍历图中的所有边,计算 u 至 v 的距离,如果对于 v 存在更小的距离,则说明存在环;
伪码实现如下:
1 BELLMAN-FORD(G, w, s) 2 INITIALIZE-SINGLE-SOURCE(G, s) 3 for i 1 to |V[G]| - 1 4 do for each edge (u, v) E[G] 5 do RELAX(u, v, w) 6 for each edge (u, v) E[G] 7 do if d[v] > d[u] + w(u, v) 8 then return FALSE 9 return TRUE
Bellman-Ford 算法的运行时间为 O(V*E),因为第 2 行的初始化占用了 Θ(V),第 3-4 行对边进行了 V - 1 趟操作,每趟操作的运行时间为 Θ(E)。第 6-7 行的 for 循环运行时间为 O(E)。
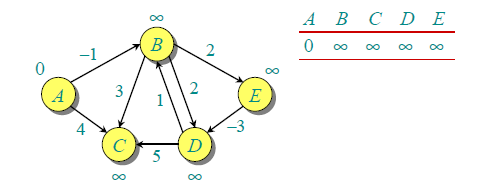
例如,下面的有向图 G 中包含 5 个顶点和 8 条边。假设源点 为 A。初始化 distSet 所有距离为 INFI,源点 A 为 0。
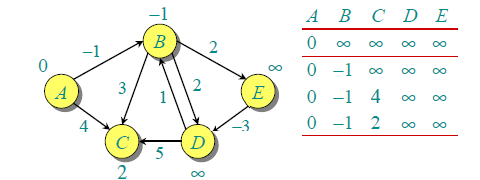
由于图中有 5 个顶点,按照步骤 1 需要遍历 4 次,第一次遍历的结果如下。
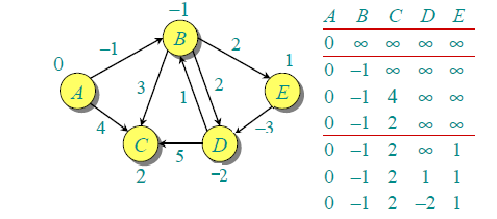
第二次遍历的结果如下。
以此类推可以得出完全遍历的结果。
C# 代码实现:
1 using System;
2 using System.Collections.Generic;
3 using System.Linq;
4
5 namespace GraphAlgorithmTesting
6 {
7 class Program
8 {
9 static void Main(string[] args)
10 {
11 int[,] graph = new int[9, 9]
12 {
13 {0, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0},
14 {4, 0, 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 11, 0},
15 {0, 8, 0, 7, 0, 4, 0, 0, 2},
16 {0, 0, 7, 0, 9, 14, 0, 0, 0},
17 {0, 0, 0, 9, 0, 10, 0, 0, 0},
18 {0, 0, 4, 0, 10, 0, 2, 0, 0},
19 {0, 0, 0, 14, 0, 2, 0, 1, 6},
20 {8, 11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 7},
21 {0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 6, 7, 0}
22 };
23
24 Graph g = new Graph(graph.GetLength(0));
25 for (int i = 0; i < graph.GetLength(0); i++)
26 {
27 for (int j = 0; j < graph.GetLength(1); j++)
28 {
29 if (graph[i, j] > 0)
30 g.AddEdge(i, j, graph[i, j]);
31 }
32 }
33
34 Console.WriteLine("Graph Vertex Count : {0}", g.VertexCount);
35 Console.WriteLine("Graph Edge Count : {0}", g.EdgeCount);
36 Console.WriteLine();
37
38 int[] distSet = g.BellmanFord(0);
39 Console.WriteLine("Vertex\t\tDistance from Source");
40 for (int i = 0; i < distSet.Length; i++)
41 {
42 Console.WriteLine("{0}\t\t{1}", i, distSet[i]);
43 }
44
45 // build a directed and negative weighted graph
46 Graph directedGraph = new Graph(5);
47 directedGraph.AddEdge(0, 1, -1);
48 directedGraph.AddEdge(0, 2, 4);
49 directedGraph.AddEdge(1, 2, 3);
50 directedGraph.AddEdge(1, 3, 2);
51 directedGraph.AddEdge(1, 4, 2);
52 directedGraph.AddEdge(3, 2, 5);
53 directedGraph.AddEdge(3, 1, 1);
54 directedGraph.AddEdge(4, 3, -3);
55
56 Console.WriteLine();
57 Console.WriteLine("Graph Vertex Count : {0}", directedGraph.VertexCount);
58 Console.WriteLine("Graph Edge Count : {0}", directedGraph.EdgeCount);
59 Console.WriteLine();
60
61 int[] distSet1 = directedGraph.BellmanFord(0);
62 Console.WriteLine("Vertex\t\tDistance from Source");
63 for (int i = 0; i < distSet1.Length; i++)
64 {
65 Console.WriteLine("{0}\t\t{1}", i, distSet1[i]);
66 }
67
68 Console.ReadKey();
69 }
70
71 class Edge
72 {
73 public Edge(int begin, int end, int weight)
74 {
75 this.Begin = begin;
76 this.End = end;
77 this.Weight = weight;
78 }
79
80 public int Begin { get; private set; }
81 public int End { get; private set; }
82 public int Weight { get; private set; }
83
84 public override string ToString()
85 {
86 return string.Format(
87 "Begin[{0}], End[{1}], Weight[{2}]",
88 Begin, End, Weight);
89 }
90 }
91
92 class Graph
93 {
94 private Dictionary<int, List<Edge>> _adjacentEdges
95 = new Dictionary<int, List<Edge>>();
96
97 public Graph(int vertexCount)
98 {
99 this.VertexCount = vertexCount;
100 }
101
102 public int VertexCount { get; private set; }
103
104 public int EdgeCount
105 {
106 get
107 {
108 return _adjacentEdges.Values.SelectMany(e => e).Count();
109 }
110 }
111
112 public void AddEdge(int begin, int end, int weight)
113 {
114 if (!_adjacentEdges.ContainsKey(begin))
115 {
116 var edges = new List<Edge>();
117 _adjacentEdges.Add(begin, edges);
118 }
119
120 _adjacentEdges[begin].Add(new Edge(begin, end, weight));
121 }
122
123 public int[] BellmanFord(int source)
124 {
125 // distSet[i] will hold the shortest distance from source to i
126 int[] distSet = new int[VertexCount];
127
128 // Step 1: Initialize distances from source to all other vertices as INFINITE
129 for (int i = 0; i < VertexCount; i++)
130 {
131 distSet[i] = int.MaxValue;
132 }
133 distSet[source] = 0;
134
135 // Step 2: Relax all edges |V| - 1 times. A simple shortest path from source
136 // to any other vertex can have at-most |V| - 1 edges
137 for (int i = 1; i <= VertexCount - 1; i++)
138 {
139 foreach (var edge in _adjacentEdges.Values.SelectMany(e => e))
140 {
141 int u = edge.Begin;
142 int v = edge.End;
143 int weight = edge.Weight;
144
145 if (distSet[u] != int.MaxValue
146 && distSet[u] + weight < distSet[v])
147 {
148 distSet[v] = distSet[u] + weight;
149 }
150 }
151 }
152
153 // Step 3: check for negative-weight cycles. The above step guarantees
154 // shortest distances if graph doesn't contain negative weight cycle.
155 // If we get a shorter path, then there is a cycle.
156 foreach (var edge in _adjacentEdges.Values.SelectMany(e => e))
157 {
158 int u = edge.Begin;
159 int v = edge.End;
160 int weight = edge.Weight;
161
162 if (distSet[u] != int.MaxValue
163 && distSet[u] + weight < distSet[v])
164 {
165 Console.WriteLine("Graph contains negative weight cycle.");
166 }
167 }
168
169 return distSet;
170 }
171 }
172 }
173 }运行结果如下:
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章