1.bitmap位图
1.1 bitmap位图的概念
首先来看一个例子,字符串big,
字母b的ASCII码为98,转换成二进制为 01100010 字母i的ASCII码为105,转换成二进制为 01101001 字母g的ASCII码为103,转换成二进制为 01100111
如果在Redis中,设置一个key,其值为big,此时可以get到big这个值,也可以获取到 big的ASCII码每一个位对应的值,也就是0或1
例如:
127.0.0.1:6379> set hello bigOK127.0.0.1:6379> getbit hello 0 # b的二进制形式的第1位,即为0 (integer) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> getbit hello 1 # b的二进制形式的第2位,即为1 (integer) 1
big长度为3个字节,对应的长度为24位,使用getbit命令可以获取到big对应的位的对应的值
所以Redis是可以直接对位进行操作的
1.2 bitmap的常用命令
1.2.1 setbit命令
setbit key offset vlaue 给位图指定索引设置值
例子:
127.0.0.1:6379> set hello big # 设置键值对,key为'hello',value为'big'OK127.0.0.1:6379> setbit hello 7 1 # 把hello二进制形式的第8位设置为1,之前的ASCII码为98,现在改为99,即把b改为c(integer) 0 # 返回的是之前这个位上的值127.0.0.1:6379> get hello # 修改之后,获取'hello'的值,为'cig'"cig"
上面big的长度只有24位,如果使用setbit命令时,指定的位大于目标的长度时
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit hello 50 1 (integer) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> get hello"cig\x00\x00\x00 "
从第25开始到第49位,中间用0来填充,第50位才会被设置为1
1.2.2 getbit命令
getbit key offset 获取位图指定索引的值
例子:
127.0.0.1:6379> getbit hello 25 (integer) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> getbit hello 49 (integer) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> getbit hello 50 (integer) 1
1.2.3 bitcount命令
bitcount key [start end] 获取位图指定范围(start到end,单位为字节,如果不指定就是获取全部)位值为1的个数
例子:
127.0.0.1:6379> bitcount hello(integer) 14 127.0.0.1:6379> bitcount hello 0 23 (integer) 14
1.2.4 bitop命令
bitop op dtstkey key [key...] 做多个bitmap的and(交集),or(并集),not(非),xor(异或)操作并将结果保存在destkey中 bitpos key targetBit [start] [end] 计算位图指定范围(start到end,单位为字节,如果不指定就是获取全部)第一个偏移量对应的值等于targetBit的位置
1.3 bitmap位图应用
如果一个网站有1亿用户,假如user_id用的是整型,长度为32位,每天有5千万独立用户访问,如何判断是哪5千万用户访问了网站
1.3.1 方式一:用set来保存
使用set来保存数据运行一天需要占用的内存为
32bit * 50000000 = (4 * 50000000) / 1024 /1024 MB,约为200MB
运行一个月需要占用的内存为6G,运行一年占用的内存为72G
30 * 200 = 6G
1.3.2 方式二:使用bitmap的方式
如果user_id访问网站,则在user_id的索引上设置为1,没有访问网站的user_id,其索引设置为0,此种方式运行一天占用的内存为
1 * 100000000 = 100000000 / 1014 /1024/ 8MB,约为12.5MB
运行一个月占用的内存为375MB,一年占用的内存容量为4.5G
由此可见,使用bitmap可以节省大量的内存资源
1.4 bitmap使用经验
bitmap是string类型,单个值最大可以使用的内存容量为512MB setbit时是设置每个value的偏移量,可以有较大耗时 bitmap不是绝对好,用在合适的场景最好
2.HyperLoglog
2.1 HyperLoglog简介
基于HyperLogLog算法,极小空间完成独立数量统计
2.2 常用命令
pfadd key element [element...] 向hyperloglog添加元素pfcount key [key...] 计算hyperloglog的独立总数prmerge destkey sourcekey [sourcekey...] 合并多个hyperloglog
例子:
127.0.0.1:6379> pfadd unique_ids1 'uuid_1' 'uuid_2' 'uuid_3' 'uuid_4' # 向unique_ids1中添加4个元素(integer) 1127.0.0.1:6379> pfcount unique_ids1 # 查看unique_ids1中元素的个数(integer) 4127.0.0.1:6379> pfadd unique_ids1 'uuid_1' 'uuid_2' 'uuid_3' 'uuid_10' # 再次向unique_ids1中添加4个元素(integer) 1127.0.0.1:6379> pfcount unique_ids1 # 由于两次添加的value有重复,所以unique_ids1中只有5个元素(integer) 5127.0.0.1:6379> pfadd unique_ids2 'uuid_1' 'uuid_2' 'uuid_3' 'uuid_4' # 向unique_ids2中添加4个元素(integer) 1127.0.0.1:6379> pfcount unique_ids2 # 查看unique_ids2中元素的个数(integer) 4127.0.0.1:6379> pfadd unique_ids2 'uuid_4' 'uuid_5' 'uuid_6' 'uuid_7' # 再次向unique_ids2中添加4个元素(integer) 1127.0.0.1:6379> pfcount unique_ids2 # 再次查看unique_ids2中元素的个数,由于两次添加的元素中有一个重复,所以有7个元素(integer) 7127.0.0.1:6379> pfmerge unique_ids1 unique_ids2 # 合并unique_ids1和unique_ids2OK127.0.0.1:6379> pfcount unique_ids1 # unique_ids1和unique_ids2中有重复元素,所以合并后的hyperloglog中只有8个元素(integer) 8
2.3 HyperLoglog内存消耗(百万独立用户)
例子:
127.0.0.1:6379> flushall # 清空Redis中所有的key和valueOK127.0.0.1:6379> info # 查看Redis占用的内存量 ...省略 # Memoryused_memory:833528used_memory_human:813.99K # 此时Redis中没有任何键值对,占用814k内存used_memory_rss:5926912used_memory_rss_human:5.65Mused_memory_peak:924056used_memory_peak_human:902.40Ktotal_system_memory:1023938560total_system_memory_human:976.50Mused_memory_lua:37888used_memory_lua_human:37.00Kmaxmemory:0maxmemory_human:0Bmaxmemory_policy:noevictionmem_fragmentation_ratio:7.11mem_allocator:jemalloc-3.6.0...省略
运行如下python代码:
import redis import timeclient = redis.StrictRedis(host='192.168.81.101',port=6379) key = 'unique' start_time = time.time()for i in range(1000000): client.pfadd(key,i)
等待python代码运行完成,再次查看Redis占用的内存数
127.0.0.1:6379> info...省略 # Memoryused_memory:849992used_memory_human:830.07Kused_memory_rss:5939200used_memory_rss_human:5.66Mused_memory_peak:924056used_memory_peak_human:902.40Ktotal_system_memory:1023938560total_system_memory_human:976.50Mused_memory_lua:37888used_memory_lua_human:37.00Kmaxmemory:0maxmemory_human:0Bmaxmemory_policy:noevictionmem_fragmentation_ratio:6.99mem_allocator:jemalloc-3.6.0...省略
可以看到,使用hyperloglog向redis中存入100万条数据,需占用的内存为
830.07K - 813.99K约为16k
占用的内存很少。
当然天下没有免费的午餐,hyperloglog也有非常明显的局限性
首先,hyperloglog有一定的错误率,在使用hyperloglog进行数据统计的过程中,hyperloglog给出的数据不一定是对的 按照维基百科的说法,使用hyperloglog处理10亿条数据,占用1.5Kb内存时,错误率为2%其次,没法从hyperloglog中取出单条数据,这很容易理解,使用16KB的内存保存100万条数据,此时还想把100万条数据取出来,显然是不可能的
2.4 HyperLoglog注意事项
使用hyperloglog进行数据统计时,需要考虑三个因素:
1.是否需要很少的内存去解决问题, 2.是否能容忍错误 3.是否需要单条数据
3.GEO
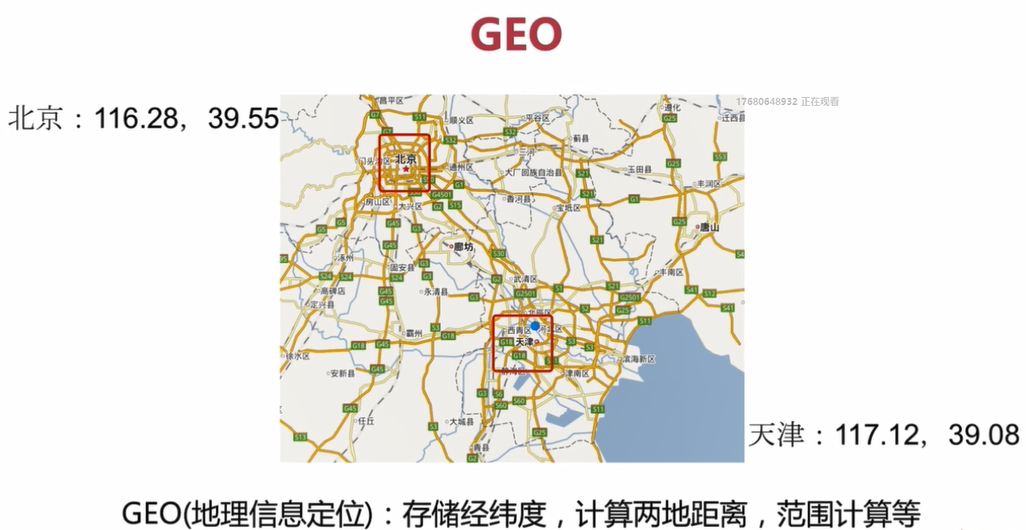
3.1 GEO简介
GEO即地址信息定位
可以用来存储经纬度,计算两地距离,范围计算等
如上图中,计算北京到天津两地之间的距离
3.2 GEO常用命令
3.2.1 geoadd命令
geoadd key longitude latitude member [longitude latitude member...] 增加地理位置信息
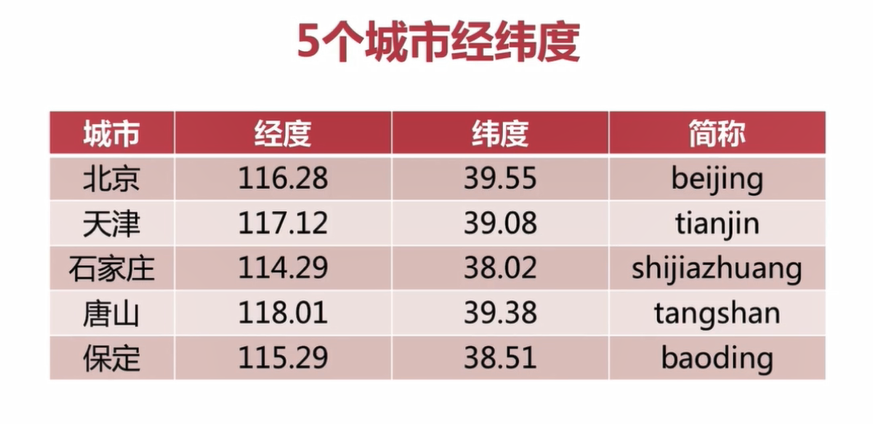
如上图是5个城市经纬度相关数据
127.0.0.1:6379> geoadd cities:locations 116.28 39.55 beijing # 添加北京的经纬度 (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> geoadd cities:locations 117.12 39.08 tianjin 114.29 38.02 shijiazhuang # 添加天津和石家庄的经纬度 (integer) 2 127.0.0.1:6379> geoadd cities:locations 118.01 39.38 tangshan 115.29 38.51 baoding # 添加唐山和保定的经纬度 (integer) 2
3.2.2 geppos命令
geopos key member [member...] 获取地理位置信息
例子:
127.0.0.1:6379> geopos cities:locations tianjin # 获取天津的地址位置信息 1) 1) "117.12000042200088501" 2) "39.0800000535766543"
3.2.3 geodist命令
geodist key member1 member2 [unit] 获取两个地理位置的距离,unit:m(米),km(千米),mi(英里),ft(尺)
例子:
127.0.0.1:6379> geodist cities:locations tianjin beijing km"89.2061" 127.0.0.1:6379> geodist cities:locations tianjin baoding km"170.8360"
3.2.4 georadius命令和georadiusbymember命令
georedius key longitude latitude radiusm|km|ft|mi [withcoord] [withdist] [withhash] [COUNT count] [asc|desc] [store key][storedist key] georadiusbymember key member radiusm|km|ft|mi [withcoord] [withdist] [withhash] [COUNT count] [asc|desc] [store key][storedist key] 获取指定位置范围内的地理位置信息集合 withcoord:返回结果中包含经纬度 withdist:返回结果中包含距离中心节点位置 withhash:返回结果中包含geohash COUNT count:指定返回结果的数量 asc|desc:返回结果按照距离中心节点的距离做升序或者降序 store key:将返回结果的地理位置信息保存到指定键 storedist key:将返回结果距离中心节点的距离保存到指定键
例子:
127.0.0.1:6379> georadiusbymember cities:locations beijing 150 km # 获取距离北京150km范围内的城市1) "beijing"2) "tianjin"3) "tangshan"4) "baoding"
3.3 GEO相关说明
Redis的GEO功能是从3.2版本添加geo功能基于zset实现geo没有删除命令
3.3.1 使用zrem命令来进行geo的删除操作
命令:
zrem key member
例子:
127.0.0.1:6379> georadiusbymember cities:locations beijing 150 km1) "beijing" 2) "tianjin" 3) "tangshan" 4) "baoding" 127.0.0.1:6379> zrem cities:locations baoding(integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> georadiusbymember cities:locations beijing 150 km1) "beijing" 2) "tianjin" 3) "tangshan"
3.4 GEO的应用场景
微信摇一摇
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章