SpringBoot项目实战(10):自定义freemarker标签
前言
项目中使用到了springboot + freemarker的技术,同时项目里多个controller中都需要查询一个公有的数据集合,一般做法是直接在每个controller的方法中通过 model.addAttribute(“xx”,xx);的方式手动设置,但这样就有个明显的问题:重复代码。同一个实现需要在不同的controller方法中设置,这种重复代码会给后期维护造成不必要的麻烦。在以往的jsp项目中,可以通过taglib实现自定义标签,那么,在freemarker中是否也可以实现这种功能呢?今天就尝试一下在freemarker中如何使用自定义标签。
初识TemplateDirectiveModel
在freemarker中实现自定义的标签,主要就是靠TemplateDirectiveModel类。如字面意思:模板指令模型,主要就是用来扩展自定义的指令(和freemarker的宏类似,自定义标签也属于这个范畴)
public interface TemplateDirectiveModel extends TemplateModel {
void execute(Environment env, Map params, TemplateModel[] loopVars, TemplateDirectiveBody body) throws TemplateException, IOException;
}
TemplateDirectiveModel是一个接口,类中只有一个execute方法供使用者实现,而我们要做的就是通过实现execute方法,实现自定义标签的功能。当页面模板中使用自定义标签时,会自动调用该方法。
先来看一下execute方法的参数含义
- env : 表示模板处理期间的运行时环境。该对象会存储模板创建的临时变量集、模板设置的值、对数据模型根的引用等等,通常用它来输出相关内容,如
Writer out = env.getOut()。 - params : 传递给自定义标签的参数(如果有的话)。其中map的key是自定义标签的参数名,value值是
TemplateModel实例【1】。 - loopVars : 循环替代变量 (未发现有什么用,希望知道的朋友能指教一二)
- body : 表示自定义标签中嵌套的内容。说简单点就是自定义标签内的内容体。如果指令调用没有嵌套内容(例如,就像<@myDirective/>或者
<@myDirective></ mydirective >),那么这个参数就会为空。
【1】:TemplateModel是一个接口类型,代表FreeMarker模板语言(FTL)数据类型的接口的公共超接口,即所有的数据类型都会被freemarker转成对应的TemplateModel。通常我们都使用TemplateScalarModel接口来替代它获取一个String 值,如TemplateScalarModel.getAsString();当然还有其它常用的替代接口,如TemplateNumberModel获取number等
| 类型 | FreeMarker接口 | FreeMarker实现 |
|---|---|---|
| 字符串 | TemplateScalarModel | SimpleScalar |
| 数值 | TemplateNumberModel | SimpleNumber |
| 日期 | TemplateDateModel | SimpleDate |
| 布尔 | TemplateBooleanModel | TemplateBooleanModel.TRUE |
| 哈希 | TemplateHashModel | SimpleHash |
| 序列 | TemplateSequenceModel | SimpleSequence |
| 集合 | TemplateCollectionModel | SimpleCollection |
| 节点 | TemplateNodeModel | NodeModel |
实现自定义标签
前面了解了TemplateDirectiveModel的基本含义和用法,那么,接下来我们就以OneBlog中的例子来简单解释下如何实现自定义标签。
ps:为了方便阅读,本例只摘出了一部分关键代码,关于详细代码,请参考我的开源博客。
一、实现TemplateDirectiveModel接口
@Component
public class CustomTagDirective implements TemplateDirectiveModel {
private static final String METHOD_KEY = "method";
@Autowired
private BizTagsService bizTagsService;
@Override
public void execute(Environment environment, Map map, TemplateModel[] templateModels, TemplateDirectiveBody templateDirectiveBody) throws TemplateException, IOException {
if (map.containsKey(METHOD_KEY)) {
DefaultObjectWrapperBuilder builder = new DefaultObjectWrapperBuilder(Configuration.VERSION_2_3_25);
String method = map.get(METHOD_KEY).toString();
switch (method) {
case "tagsList":
// 将数据对象转换成对应的TemplateModel
TemplateModel tm = builder.build().wrap(bizTagsService.listAll())
environment.setVariable("tagsList", tm);
break;
case other...
default:
break;
}
}
templateDirectiveBody.render(environment.getOut());
}
}
二、创建freemarker的配置类
@Configuration
public class FreeMarkerConfig {
@Autowired
protected freemarker.template.Configuration configuration;
@Autowired
protected CustomTags customTags;
/**
* 添加自定义标签
*/
@PostConstruct
public void setSharedVariable() {
/*
* 向freemarker配置中添加共享变量;
* 它使用Configurable.getObjectWrapper()来包装值,因此在此之前设置对象包装器是很重要的。(即上一步的builder.build().wrap操作)
* 这种方法不是线程安全的;使用它的限制与那些修改设置值的限制相同。
* 如果使用这种配置从多个线程运行模板,那么附加的值应该是线程安全的。
*/
configuration.setSharedVariable("zhydTag", customTags);
}
}
三、ftl模板中使用自定义标签
<div class="sidebar-module">
<h5 class="sidebar-title"><i class="fa fa-tags icon"></i><strong>文章标签</strong></h5>
<ul class="list-unstyled list-inline">
<@zhydTag method="tagsList" pageSize="10">
<#if tagsList?exists && (tagsList?size > 0)>
<#list tagsList as item>
<li class="tag-li">
<a class="btn btn-default btn-xs" href="${config.siteUrl}/tag/${item.id?c}" title="${item.name?if_exists}">
${item.name?if_exists}
</a>
</li>
</#list>
</#if>
</@zhydTag>
</ul>
</div>
自定义标签的使用方法跟自定义宏(macro)用法一样,直接使用<@标签名>${值}</@标签名>即可。
注:ftl中通过@调用自定义标签时,后面可以跟任意参数,所有的参数都可以在execute方法的第二个参数(map)中获取,由此可以根据一个特定的属性开发一套特定的自定义标签,比如上面代码中通过method参数判断调用不同的处理方式。
四、扩展FreeMarkerConfig
上面提到的自定义标签,都是通过<@tagName>xxx</@tagName>方式调用的,那么针对我们系统中一些类环境变量的数据(全局的配置类属性等)如何像使用普通的el表达式一般直接通过${xx}获取呢?
看代码:
@Configuration
public class FreeMarkerConfig {
@Autowired
protected freemarker.template.Configuration configuration;
@Autowired
private SysConfigService configService;
/**
* 添加自定义标签
*/
@PostConstruct
public void setSharedVariable() {
try {
configuration.setSharedVariable("config", configService.get());
} catch (TemplateModelException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
如此而已,在使用的时候我们可以直接在页面上通过${config.siteName}调用config的参数即可。
五、可能遇到的问题
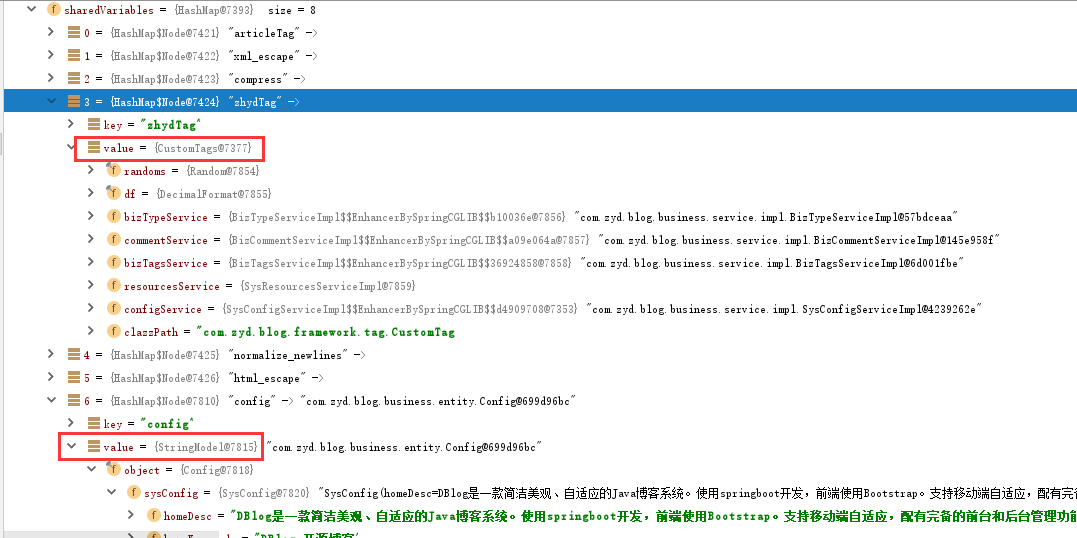
针对上面两种标签(类宏模式和类el表达式模式),会有一个问题存在,如下图
在程序启动时会初始化FreemarkerConfig类(@PostConstruct),并且当且仅当程序启动时才会初始化一次。像zhydTag这种自定义标签,因为是将整个标签类(CustomTag)保存到了共享变量中,那么在使用标签时,实际还是调用的相关接口获取数据库,当数据库发生变化时,也会同步更新到标签中;而像config这种类el表达式的环境变量(如图,value的类型是一个StringModel),只会在程序初始化时加载一次,在后续调用标签时也只是调用的SharedVariable中的config副本内容,并不会再次访问接口去数据库中获取数据。这样就造成了一个问题:当config表中的数据发生变化时,在前台通过${config.siteName}获取到的仍然是旧的数据。
六、解决问题
针对这一问题,我是通过实现一个简单的AOP,去监控、对比config表的内容,当config表发生变化时,将新的config副本保存到freeamrker的SharedVariable中。如下实现
/**
* 用于监控freemarker自定义标签中共享变量是否发生变化,发生变化时实时更新到内存中
*
* @author yadong.zhang (yadong.zhang0415(a)gmail.com)
* @version 2.0
* @date 2018/5/17 17:06
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(1)
public class FreemarkerSharedVariableMonitorAspects {
private static volatile long configLastUpdateTime = 0L;
@Autowired
protected freemarker.template.Configuration configuration;
@Autowired
private SysConfigService configService;
@Pointcut(value = "@annotation(org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping)" +
"|| @annotation(org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping)")
public void pointcut() {
// 切面切入点
}
@After("pointcut()")
public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Config config = configService.get();
if (null == config) {
log.error("config为空");
return;
}
Long updateTime = config.getUpdateTime().getTime();
if (updateTime == configLastUpdateTime) {
log.debug("config表未更新");
return;
}
log.debug("config表已更新,重新加载config到freemarker tag");
configLastUpdateTime = updateTime;
try {
configuration.setSharedVariable("config", config);
} catch (TemplateModelException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
当然, 解决问题的办法不仅仅只有一种。使用过滤器、拦截器也是一样的道理。
代码调优
上面介绍的编码实现方式,我们必须通过switch ... case去挨个判断实际的处理逻辑,在同一个标签类中有多个case时,就显得比较笨重。因此,我们简单的优化一下代码,使它看起来不是那么糟糕并且易于扩展。
一、首先,分析代码,然后将公共模块提取出来。
TemplateDirectiveModel类的execute方法是每个自定义标签类都必须实现的,并且每个自定义标签都是根据method参数去使用具体的实现,这一块我们可以提成公共模块:
/**
* 所有自定义标签的父类,负责调用具体的子类方法
*
* @author yadong.zhang (yadong.zhang0415(a)gmail.com)
* @version 1.0
* @website https://www.zhyd.me
* @date 2018/9/18 16:19
* @since 1.8
*/
public abstract class BaseTag implements TemplateDirectiveModel {
private String clazzPath = null;
public BaseTag(String targetClassPath) {
clazzPath = targetClassPath;
}
private String getMethod(Map params) {
return this.getParam(params, "method");
}
protected int getPageSize(Map params) {
int pageSize = 10;
String pageSizeStr = this.getParam(params, "pageSize");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(pageSizeStr)) {
pageSize = Integer.parseInt(pageSizeStr);
}
return pageSize;
}
private void verifyParameters(Map params) throws TemplateModelException {
String permission = this.getMethod(params);
if (permission == null || permission.length() == 0) {
throw new TemplateModelException("The 'name' tag attribute must be set.");
}
}
String getParam(Map params, String paramName) {
Object value = params.get(paramName);
return value instanceof SimpleScalar ? ((SimpleScalar) value).getAsString() : null;
}
private DefaultObjectWrapper getBuilder() {
return new DefaultObjectWrapperBuilder(Configuration.VERSION_2_3_25).build();
}
private TemplateModel getModel(Object o) throws TemplateModelException {
return this.getBuilder().wrap(o);
}
@Override
public void execute(Environment environment, Map map, TemplateModel[] templateModels, TemplateDirectiveBody templateDirectiveBody) throws TemplateException, IOException {
this.verifyParameters(map);
String funName = getMethod(map);
Method method = null;
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName(clazzPath);
method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod(funName, Map.class);
if (method != null) {
Object res = method.invoke(this, map);
environment.setVariable(funName, getModel(res));
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException | IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
templateDirectiveBody.render(environment.getOut());
}
}
BaseTag作为所有自定义标签的父类,只需要接受一个参数:targetClassPath,即子类的类路径(全类名),在实际的execute方法中,只需要根据指定的method,使用反射调用子类的相关方法即可。
优化后的标签类
/**
* 自定义的freemarker标签
*
* @author yadong.zhang (yadong.zhang0415(a)gmail.com)
* @version 1.0
* @website https://www.zhyd.me
* @date 2018/4/16 16:26
* @since 1.0
* @modify by zhyd 2018-09-20
* 调整实现,所有自定义标签只需继承BaseTag后通过构造函数将自定义标签类的className传递给父类即可。
* 增加标签时,只需要添加相关的方法即可,默认自定义标签的method就是自定义方法的函数名。
* 例如:<@zhydTag method="types" ...></@zhydTag>就对应 {{@link #types(Map)}}方法
*/
@Component
public class CustomTags extends BaseTag {
@Autowired
private BizTypeService bizTypeService;
public CustomTags() {
super(CustomTags.class.getName());
}
public Object types(Map params) {
return bizTypeService.listTypeForMenu();
}
// 其他自定义标签的方法...
}
如上,所有自定义标签只需继承BaseTag后通过构造函数将自定义标签类的className传递给父类即可。增加标签时,只需要添加相关的方法即可,默认自定义标签的method就是自定义方法的函数名。
例如:<@zhydTag method="types" ...></@zhydTag>就对应 CustomTags#types(Map)方法
如此一来,我们想扩展标签时,只需要添加相关的自定义方法,在后在ftl中通过method指定调用哪个方法即可。
最后的最后
我可以对一个人无限的好,前提是值得。 ——慕冬雪
相关文章导读
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章