JavaScript数据结构 实现链表
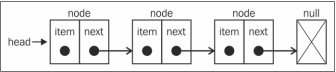
链表存储有序的元素集合,但不同于数组,链表中的元素在内存中并不是连续放置的。每个元素有一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的引用(指针)组成。
链表的好处在于,添加或删除元素的时候不需要移动其他元素。链表的另一个细节是可以直接访问任何位置的任何元素,而想要访问链表中间的一个元素,需要从起点(表头)开始迭代链表,直到找到所需的元素。
LinkedList类有以下方法:
append(element):向链表尾部添加一个新的项;
removeAt(position):从链表的特定位置移除一项;
insert(position, element):向链表的特定位置插入一个新的项;
indexOf(element):返回元素在链表中的索引,如果链表中没有该元素则返回-1;
remove(element):从链表中移除一项;
isEmpty():如果链表中不包含任何元素,返回true,如果链表长度大于0,则返回false;
size():返回链表包含的元素个数,与数组的length属性类似;
toString():由于列表中的使用了Node类,就需要重写继承自JavaScript对象默认的toStringfang方法,只让其输出元素值
function LinkedList () {
//Node类表示要加入列表的项
var Node = function (element) {
this.element = element;;//要添加到链表的值
this.next = null;//指向链表中下一个节点项的指针
};
var length = 0;//链表项的数量
var head = null;//存储第一个节点的引用
//向链表尾部追加元素
this.append = function (element) {
var node = new Node(element), //创建Node项
current;
if (head === null) {//若head元素为null,意味着向链表添加第一个元素
head = node;
} else {
current = head; //查询链表中的元素,需要从起点开始迭代
while (current.next) {
//当current.next元素为null时,就知道已经到达链表的尾部了
current = current.next;
}
current.next = node;
}
length++;
};
//从链表中移除元素
this.removeAt = function (position) {
if (position > -1 && position < length) { //验证位置有效
var current = head, //用current变量创建链表中第一个元素引用
previous, index = 0;
if (position === 0) {
head = cuttent.next; //如果想要移除第一个,就让head指向第二个元素
} else {
while (index++ < position) {//迭代直到到达目标位置
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
//将previous与current的下一项链接起来:跳过current,从而移除它
previous.next = current.next;
}
length--;
return current.element;
} else {
return null;
}
};
//在任意位置插入一个元素
this.insert = function (positon, element) {
if (position >= 0 && position <= length) {//检查是否越界
var node = new Node(element);
var index = 0, previous, current = head;
if (position === 0) {//在第一个位置添加
node.next = current;
head = node;
} else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
}
length++;//更新链表长度
return true;
} else {
return false;//如果越界返回false
}
};
//把LinkedList对象转换成一个字符串
this.toString = function () {
var current = head, //起点
string = '';
while (current) {//检查元素是否存在
string += ', ' + current.element;//拼接到字符串
current = current.next;
}
return string.slice(1);
};
//indexOf方法
this.indexOf = function (element) {
var current = head,
index = 0;//计算位置数
while (current) {//循环访问元素
if (element === current.element) {//检查当前元素是否是我们要找的
return index;
}
index++;
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
};
//实现了indexOf方法后可以根据元素的值来移除元素
this.remove = function (element) {
var index = this.indexOf(element);
return this.removeAt(element);
};
//isEmpty方法和size方法与栈和队列中实现一样
this.isEmpty = function () {
return length === 0;//如果列表中没有元素,isEmpty方法就返回true,否则返回false
};
this.size = function () {
return length;
};
/**
*head变量是LinkedList类的私有变量
*意味着它不能在LinkedList实例外部访问和更改,只有通过LinkedList实例才可以
*/
this.getHead = function () {
return head;
};
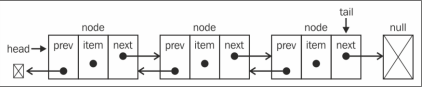
}链表有多种不同的类型,双向链表和普通链表的区别在于:普通链表中一个节点只有链向下一个节点的链接;而在双向链表中,链接是双向的:一个链向下一个元素,另一个链向前一个元素。
双向链表提供了两种迭代链表的方法:从头到尾,或者反过来。可以访问特定节点的下一个或前一个元素。在单向链表时错过了要找的元素,就需要返回到链表起点,重新开始迭代。这是双向链表的一个优点。
function doubleLinkedList () {
var Node = function (element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;//新增的,保存链表最后一项
};
var length = 0;
var head = null;
var tail = null;
//在任意一个位置插入一个新元素
this.insert = function (position, element) {
//检查是否越界
if (position >= 0 && position <= length) {
var node = new Node(element),
current = head,
previous,
index = 0;
if (position === 0) {
if (!head) {//如果链表为空,把head和tail都指向这个新节点
head = node;
tail = node;
} else {
node.next = current;
current.prev = node;
head = node;
}
} else if (position === length) {
current = tail;
current.next = node;
node.prev = current;
tail = node;
} else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
current.prev = node;
node.prev = previous;
}
length++;
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
};
//从任意位置移除元素
this.removeAt = function (position) {
if (position > -1 && position < length) {
var current = head;
previous, index = 0;
if (position === 0) {//移除第一项
head = current.next;
if(length === 1) {//如果只有一项
tail = null;
} else {
head.prev = null;//更新指向上一个元素的指针
}
} else if (position === length - 1) {//移除最后一项
current = tail;
tail = current.prev;
tail.next = null;
} else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
//将previous与current的下一项链接起来,跳过currrent
previous.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = previous;
}
length--;
return current.element;
} else {
return null;
}
};
}共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章