一 集合概述
一方面, 面向对象语言对事物的体现都是以对象的形式,为了方便对多个对象的操作,就要对对象进行存储。另一方面,使用Array存储对象方面具有一些弊端,而Java 集合就像一种容器,可以动态地把多个对象的引用放入容器中。Java 集合类可以用于存储数量不等的多个对象,还可用于保存具有映射关系的关联数组。
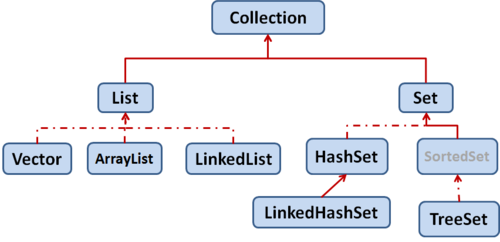
JAVA集合可分为Collection和Map两中体系:
Collection接口:
Set: 元素无序,不可重复的集合.
List:元素有序,可重复的集合.
Map接口:
具有映射关系“key-value对”的集合.
如下图:
具体信息请查看API.
二 常用集合类型
下面介绍下JAVA中常用的集合类型
List实现类:
1) ArrayList
ArrayList 是 List 接口的典型实现类,本质上,ArrayList是对象引用的一个变长数组,ArrayList 是线程不安全的,而 Vector 是线程安全的,即使为保证 List 集合线程安全,也不推荐使用Vector,Arrays.asList(…) 方法返回的 List 集合既不是 ArrayList 实例,也不是 Vector 实例。 Arrays.asList(…) 返回值是一个固定长度的 List 集合.
@Test
public void testArrayList() {
List<Student> lists = new ArrayList<Student>();
lists.add(new Student(1,"张三"));
lists.add(new Student(2,"李四"));
lists.add(new Student(3,"王五"));
for (Student student : lists) {
System.out.println(student);
}
lists = Arrays.asList(new Student(4,"赵六"),new Student(5,"田七"));
for (Student student : lists) {
System.out.println(student);
}
} 运行结果:
Student [id=1, name=张三]
Student [id=2, name=李四]
Student [id=3, name=王五]
Student [id=4, name=赵六]
Student [id=5, name=田七]
2) LinkedList
对于频繁的插入或删除元素的操作,建议使用LinkedList类,效率较高,操作与ArrayList差不多。
3) Vector
Vector 是一个古老的集合,JDK1.0就有了。大多数操作与ArrayList相同,区别之处在于Vector是线程安全的。
在各种list中,最好把ArrayList作为缺省选择。当插入、删除频繁时,使用LinkedList;Vector总是比ArrayList慢,所以尽量避免使用。
/**
* Sets the size of this vector. If the new size is greater than the
* current size, new {@code null} items are added to the end of
* the vector. If the new size is less than the current size, all
* components at index {@code newSize} and greater are discarded.
*
* @param newSize the new size of this vector
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the new size is negative
*/
public synchronized void setSize(int newSize) {
modCount++;
if (newSize > elementCount) {
ensureCapacityHelper(newSize);
} else {
for (int i = newSize ; i < elementCount ; i++) {
elementData[i] = null;
}
}
elementCount = newSize;
}Set实现类:
Set接口是Collection的子接口,set接口没有提供额外的方法
Set 集合不允许包含相同的元素,如果试把两个相同的元素加入同一个 Set 集合中,则添加操作失败。
Set 判断两个对象是否相同不是使用 == 运算符,而是根据 equals 方法
1) HashSet
HashSet 是 Set 接口的典型实现,大多数时候使用 Set 集合时都使用这个实现类。
HashSet 按 Hash 算法来存储集合中的元素,因此具有很好的存取和查找性能。
HashSet 具有以下特点:
Ø不能保证元素的排列顺序
ØHashSet 不是线程安全的
Ø集合元素可以是 null
当向 HashSet 集合中存入一个元素时,HashSet 会调用该对象的 hashCode() 方法来得到该对象的 hashCode 值,然后根据 hashCode 值决定该对象在 HashSet 中的存储位置。
HashSet 集合判断两个元素相等的标准:两个对象通过 hashCode() 方法比较相等,并且两个对象的 equals() 方法返回值也相等。
@Test
public void testHashSet() {
Set<Student> set = new HashSet<Student>();
//Student需要重写hashCode()和equals()方法
set.add(new Student(1,"张三"));
set.add(new Student(2,"李四"));
set.add(new Student(3,"王五"));
set.add(new Student(3,"王五"));
for (Student student : set) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}运行结果:
Student [id=2, name=李四]
Student [id=1, name=张三]
Student [id=3, name=王五]
2) LinkedHashSet
LinkedHashSet 是 HashSet 的子类
LinkedHashSet 根据元素的 hashCode 值来决定元素的存储位置,但它同时使用链表维护元素的次序,这使得元素看起来是以插入顺序保存的。
LinkedHashSet插入性能略低于 HashSet,但在迭代访问 Set 里的全部元素时有很好的性能。
LinkedHashSet 不允许集合元素重复。
3) TreeSet
TreeSet 是 SortedSet 接口的实现类,TreeSet 可以确保集合元素处于排序状态。
TreeSet 两种排序方法:自然排序和定制排序。默认情况下,TreeSet 采用自然排序。
①自然排序 TreeSet 会调用集合元素的 compareTo(Object obj) 方法来比较元素之间的大小关系,然后将集合元素按升序排列
向 TreeSet 中添加元素时,只有第一个元素无须比较compareTo()方法,后面添加的所有元素都会调用compareTo()方法进行比较。
因为只有相同类的两个实例才会比较大小,所以向 TreeSet 中添加的应该是同一个类的对象
对于 TreeSet 集合而言,它判断两个对象是否相等的唯一标准是:两个对象通过 compareTo(Object obj) 方法比较返回值
当需要把一个对象放入 TreeSet 中,重写该对象对应的 equals() 方法时,应保证该方法与 compareTo(Object obj) 方法有一致的结果:如果两个对象通过 equals() 方法比较返回 true,则通过 compareTo(Object obj) 方法比较应返回 0
@Test
public void testTreeSet() {
Set<Student> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add(new Student(1,"张三"));
set.add(new Student(2,"李四"));
set.add(new Student(3,"王五"));
set.add(new Student(1,"王五"));
for (Student student : set) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}package com.lxj.collection;
public class Student implements Comparable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Student(Integer id,String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public Student() {
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((id == null) ? 0 : id.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Student other = (Student) obj;
if (id == null) {
if (other.id != null)
return false;
} else if (!id.equals(other.id))
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
//如果id相同就按照name排序
if(o instanceof Student) {
Student s = (Student)o;
int i = this.id.compareTo(s.getId());
if(i == 0) {
return this.name.compareTo(s.getName());
}else {
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
}结果:
Student [id=1, name=张三]
Student [id=1, name=王五]
Student [id=2, name=李四]
Student [id=3, name=王五]
②定制排序
TreeSet的自然排序是根据集合元素的大小,进行元素升序排列。如果需要定制排序,比如降序排列,可通过Comparator接口的帮助。需要重写compare(T o1,T o2)方法。利用int compare(T o1,T o2)方法,比较o1和o2的大小:如果方法返回正整数,则表示o1大于o2;如果返回0,表示相等;返回负整数,表示o1小于o2。要实现定制排序,需要将实现Comparator接口的实例作为形参传递给TreeSet的构造器。
此时,仍然只能向TreeSet中添加类型相同的对象。否则发生ClassCastException异常。
使用定制排序判断两个元素相等的标准是:通过Comparator比较两个元素返回了0。
@Test
public void testTreeSet2() {
//定制排序
Set<Student2> treeSet = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Object>() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
if(o1 instanceof Student2 && o2 instanceof Student2) {
Student2 s1 = (Student2)o1;
Student2 s2 = (Student2)o2;
int i = s1.getId().compareTo(s2.getId());
if(i == 0) {
return s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName());
}
return i;
}
return 0;
}
});
treeSet.add(new Student2(1,"张三"));
treeSet.add(new Student2(2,"李四"));
treeSet.add(new Student2(3,"王五"));
treeSet.add(new Student2(1,"王五"));
for (Student2 student : treeSet) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}运行结果:
Student [id=1, name=张三]
Student [id=1, name=王五]
Student [id=2, name=李四]
Student [id=3, name=王五]
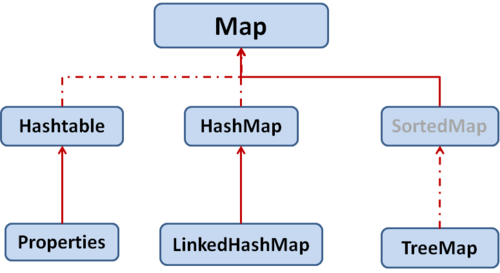
Map实现类:
Map与Collection并列存在。用于保存具有映射关系的数据:Key-Value
Map 中的 key 和 value 都可以是任何引用类型的数据
Map 中的 key 用Set来存放,不允许重复,即同一个 Map 对象所对应的类,须重写hashCode()和equals()方法。
常用String类作为Map的“键”。
key 和 value 之间存在单向一对一关系,即通过指定的 key 总能找到唯一的、确定的 value。
1) hashMap
@Test
public void testHashMap() {
Map<Object,Student> stus = new HashMap<>();
stus.put("aa", new Student(1,"aa"));
stus.put("c", new Student(1,"aa"));
stus.put("bb", new Student(2,"bb"));
stus.put("cc", new Student(3,"cc"));
stus.put(null, new Student(3,"cc"));
for (Entry<Object, Student> student : stus.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(student.getKey()+" : " + student.getValue());
}
}运行结果:
aa : Student [id=1, name=aa]
bb : Student [id=2, name=bb]
cc : Student [id=3, name=cc]
null : Student [id=3, name=cc]
c : Student [id=1, name=aa]
2) LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap 是 HashMap 的子类
与LinkedHashSet类似,LinkedHashMap 可以维护 Map 的迭代顺序:迭代顺序与 Key-Value 对的插入顺序一致
3)TreeMap
TreeMap存储 Key-Value 对时,需要根据 key-value 对进行排序。TreeMap 可以保证所有的 Key-Value 对处于有序状态。
TreeMap 的 Key 的排序:
Ø自然排序:TreeMap 的所有的 Key 必须实现 Comparable 接口,而且所有的 Key 应该是同一个类的对象,否则将会抛出 ClasssCastException
Ø定制排序:创建 TreeMap 时,传入一个 Comparator 对象,该对象负责对 TreeMap 中的所有 key 进行排序。此时不需要 Map 的 Key 实现 Comparable 接口
@Test
public void testTreeMap() {
Map<Object,Object> stus = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Object>() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
if(o1 instanceof Student2 && o2 instanceof Student2) {
Student2 s1 = (Student2)o1;
Student2 s2 = (Student2)o2;
int i = s1.getId().compareTo(s2.getId());
if(i == 0) {
return s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName());
}
return i;
}
return 0;
}
});
stus.put( new Student2(1,"aa"),"aa");
stus.put( new Student2(1,"aa"),"bb");
stus.put( new Student2(2,"bb"),"cc");
stus.put( new Student2(3,"cc"),"dd");
stus.put( new Student2(3,"dd"),"ee");
for (Entry<Object, Object> student : stus.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(student.getKey()+" : " + student.getValue());
}
}运行结果:
Student [id=1, name=aa] : bb
Student [id=2, name=bb] : cc
Student [id=3, name=cc] : dd
Student [id=3, name=dd] : ee
4) Hashtable
Hashtable是个古老的 Map 实现类,线程安全。
与HashMap不同,Hashtable 不允许使用 null 作为 key 和 value
与HashMap一样,Hashtable 也不能保证其中 Key-Value 对的顺序
Hashtable判断两个key相等、两个value相等的标准,与hashMap一致。
5) Properties
Properties 类是 Hashtable 的子类,该对象用于处理属性文件
由于属性文件里的 key、value 都是字符串类型,所以 Properties 里的 key 和 value 都是字符串类型
存取数据时,建议使用setProperty(String key,String value)方法和getProperty(String key)方法
@Test
public void testProperty() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties"));
String name = properties.getProperty("name");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(password);
}运行结果:
root
123456
Collections 操作集合的工具类
Collections 是一个操作 Set、List 和 Map 等集合的工具类
Collections 中提供了一系列静态的方法对集合元素进行排序、查询和修改等操作,还提供了对集合对象设置不可变、对集合对象实现同步控制等方法
Collections 类中提供了多个 synchronizedXxx() 方法,该方法可使将指定集合包装成线程同步的集合,从而可以解决多线程并发访问集合时的线程安全问题
相关的信息请查阅API。
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章