本文,我们将基于 Spring Boot 技术来实现一个微服务天气预报服务接口——micro-weather-basic。micro-weather-basic 的作用是实现简单的天气预报功能,可以根据不同的城市,查询该城市的实时天气情况。
- Gradle 4.0
- Spring Boot 1.5.6
- Apache HttpClient 1.5.3
理论上,天气的数据是天气预报的实现基础。本应用与实际的天气数据无关,理论上,可以兼容多种数据来源。但为求简单,我们在网上找了一个免费、可用的天气数据接口。
- 天气数据来源为中华万年历。例如:
- 通过城市名字获得天气数据 :http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city=深圳
- 通过城市id获得天气数据:http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?citykey=101280601
- 城市ID列表。每个城市都有一个唯一的ID作为标识。见 http://cj.weather.com.cn/support/Detail.aspx?id=51837fba1b35fe0f8411b6df 或者 http://mobile.weather.com.cn/js/citylist.xml。
调用天气服务接口示例,我们以“深圳”城市为例,可用看到如下天气数据返回。
{
"data": {
"yesterday": {
"date": "1日星期五",
"high": "高温 33℃",
"fx": "无持续风向",
"low": "低温 26℃",
"fl": "<![CDATA[<3级]]>",
"type": "多云"
},
"city": "深圳",
"aqi": "72",
"forecast": [
{
"date": "2日星期六",
"high": "高温 32℃",
"fengli": "<![CDATA[<3级]]>",
"low": "低温 26℃",
"fengxiang": "无持续风向",
"type": "阵雨"
},
{
"date": "3日星期天",
"high": "高温 29℃",
"fengli": "<![CDATA[5-6级]]>",
"low": "低温 26℃",
"fengxiang": "无持续风向",
"type": "大雨"
},
{
"date": "4日星期一",
"high": "高温 29℃",
"fengli": "<![CDATA[3-4级]]>",
"low": "低温 26℃",
"fengxiang": "西南风",
"type": "暴雨"
},
{
"date": "5日星期二",
"high": "高温 31℃",
"fengli": "<![CDATA[<3级]]>",
"low": "低温 27℃",
"fengxiang": "无持续风向",
"type": "阵雨"
},
{
"date": "6日星期三",
"high": "高温 32℃",
"fengli": "<![CDATA[<3级]]>",
"low": "低温 27℃",
"fengxiang": "无持续风向",
"type": "阵雨"
}
],
"ganmao": "风较大,阴冷潮湿,较易发生感冒,体质较弱的朋友请注意适当防护。",
"wendu": "29"
},
"status": 1000,
"desc": "OK"
}
我们通过观察数据,来了解每个返回字段的含义。
- “city”: 城市名称
- “aqi”: 空气指数,
- “wendu”: 实时温度
- “date”: 日期,包含未来5天
- “high”:最高温度
- “low”: 最低温度
- “fengli”: 风力
- “fengxiang”: 风向
- “type”: 天气类型
以上数据,是我们需要的天气数据的核心数据,但是,同时也要关注下面两个字段:
- “status”: 接口调用的返回状态,返回值“1000”,意味着数据是接口正常
- “desc”: 接口状态的描述,“OK”代表接口正常
重点关注返回值不是“1000”的情况,说明,这个接口调用异常了。
初始化一个 Spring Boot 项目
初始化一个 Spring Boot 项目 micro-weather-basic,该项目可以直接在我们之前章节课程中的 basic-gradle 项目基础进行修改。同时,为了优化项目的构建速度,我们对Maven中央仓库地址和 Gradle Wrapper 地址做了调整。其中细节暂且不表,读者可以自行参阅源码,或者学习笔者所著的《Spring Boot 教程》(https://github.com/waylau/spring-boot-tutorial)。其原理,我也整理到我的博客中了:
添加 Apache HttpClient 的依赖,来作为我们Web请求的客户端。
// 依赖关系
dependencies {
//...
// 添加 Apache HttpClient 依赖
compile('org.apache.httpcomponents:httpclient:4.5.3')
//...
}
创建com.waylau.spring.cloud.vo包,用于相关值对象。创建天气信息类 Weather
public class Weather implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String city;
private String aqi;
private String wendu;
private String ganmao;
private Yesterday yesterday;
private List<Forecast> forecast;
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getAqi() {
return aqi;
}
public void setAqi(String aqi) {
this.aqi = aqi;
}
public String getWendu() {
return wendu;
}
public void setWendu(String wendu) {
this.wendu = wendu;
}
public String getGanmao() {
return ganmao;
}
public void setGanmao(String ganmao) {
this.ganmao = ganmao;
}
public Yesterday getYesterday() {
return yesterday;
}
public void setYesterday(Yesterday yesterday) {
this.yesterday = yesterday;
}
public List<Forecast> getForecast() {
return forecast;
}
public void setForecast(List<Forecast> forecast) {
this.forecast = forecast;
}
}
昨日天气信息:
public class Yesterday implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String date;
private String high;
private String fx;
private String low;
private String fl;
private String type;
public Yesterday() {
}
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public String getHigh() {
return high;
}
public void setHigh(String high) {
this.high = high;
}
public String getFx() {
return fx;
}
public void setFx(String fx) {
this.fx = fx;
}
public String getLow() {
return low;
}
public void setLow(String low) {
this.low = low;
}
public String getFl() {
return fl;
}
public void setFl(String fl) {
this.fl = fl;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
}
未来天气信息:
public class Forecast implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String date;
private String high;
private String fengxiang;
private String low;
private String fengli;
private String type;
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public String getHigh() {
return high;
}
public void setHigh(String high) {
this.high = high;
}
public String getFengxiang() {
return fengxiang;
}
public void setFengxiang(String fengxiang) {
this.fengxiang = fengxiang;
}
public String getLow() {
return low;
}
public void setLow(String low) {
this.low = low;
}
public String getFengli() {
return fengli;
}
public void setFengli(String fengli) {
this.fengli = fengli;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public Forecast() {
}
}
WeatherResponse 作为整个消息的返回对象
public class WeatherResponse implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Weather data; // 消息数据
private String status; // 消息状态
private String desc; // 消息描述
public Weather getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(Weather data) {
this.data = data;
}
public String getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(String status) {
this.status = status;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
public void setDesc(String desc) {
this.desc = desc;
}
}
定义了获取服务的两个接口方法
public interface WeatherDataService {
/**
* 根据城市ID查询天气数据
* @param cityId
* @return
*/
WeatherResponse getDataByCityId(String cityId);
/**
* 根据城市名称查询天气数据
* @param cityId
* @return
*/
WeatherResponse getDataByCityName(String cityName);
}
其实现为:
@Service
public class WeatherDataServiceImpl implements WeatherDataService {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
private final String WEATHER_API = "http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini";
@Override
public WeatherResponse getDataByCityId(String cityId) {
String uri = WEATHER_API + "?citykey=" + cityId;
return this.doGetWeatherData(uri);
}
@Override
public WeatherResponse getDataByCityName(String cityName) {
String uri = WEATHER_API + "?city=" + cityName;
return this.doGetWeatherData(uri);
}
private WeatherResponse doGetWeatherData(String uri) {
ResponseEntity<String> response = restTemplate.getForEntity(uri, String.class);
String strBody = null;
if (response.getStatusCodeValue() == 200) {
strBody = response.getBody();
}
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
WeatherResponse weather = null;
try {
weather = mapper.readValue(strBody, WeatherResponse.class);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return weather;
}
}
返回的天气信息采用了 Jackson 来进行反序列化成为 WeatherResponse 对象。
控制器层暴露了RESTful API 地址。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/weather")
public class WeatherController {
@Autowired
private WeatherDataService weatherDataService;
@GetMapping("/cityId/{cityId}")
public WeatherResponse getReportByCityId(@PathVariable("cityId") String cityId) {
return weatherDataService.getDataByCityId(cityId);
}
@GetMapping("/cityName/{cityName}")
public WeatherResponse getReportByCityName(@PathVariable("cityName") String cityName) {
return weatherDataService.getDataByCityName(cityName);
}
}
@RestController自动会将返回的数据,序列化成 JSON数据格式。
RestConfiguration 是 RestTemplate 的配置类。
@Configuration
public class RestConfiguration {
@Autowired
private RestTemplateBuilder builder;
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return builder.build();
}
}
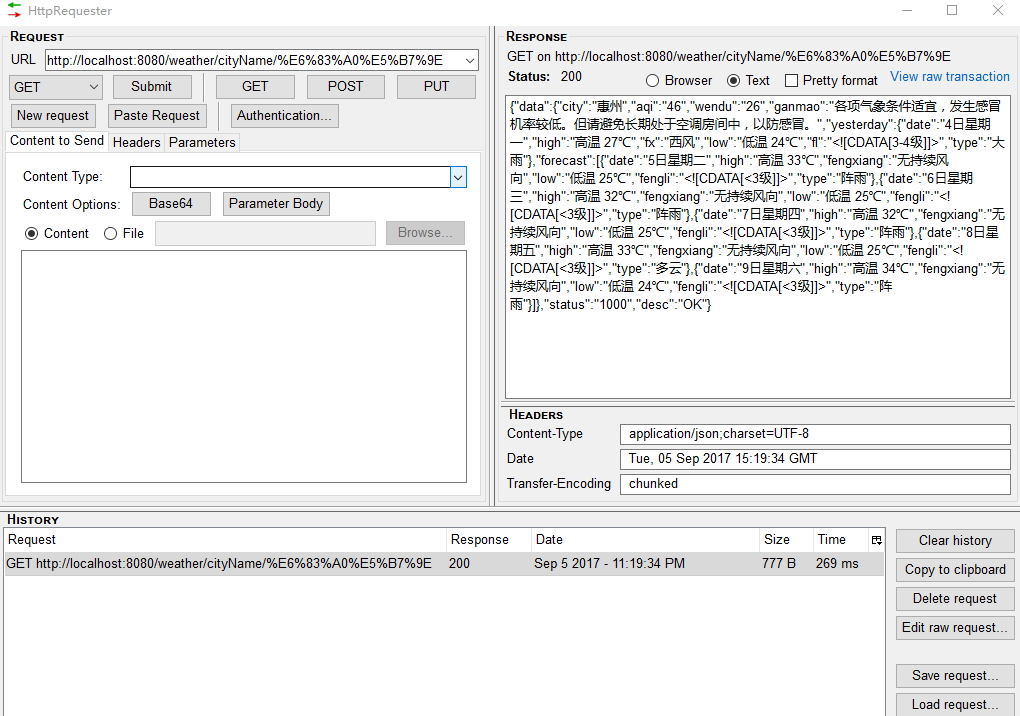
运行项目之后,访问项目的 API :
能看到如下的数据返回
本章节的源码,见 https://github.com/waylau/spring-cloud-tutorial/ samples目录下的micro-weather-basic。
- Spring Boot 教程:https://github.com/waylau/spring-boot-tutorial
- Spring Cloud 教程:https://github.com/waylau/spring-cloud-tutorial
- Spring Boot 开发企业级博客系统:https://coding.imooc.com/class/125.html
- 从天气项目看Spring Cloud微服务治理:
- 原文同步至:https://waylau.com/spring-boot-weather-report/
共同学习,写下你的评论
暂无评论
作者其他优质文章